Boston University/Plasmid Customization
From 2007.igem.org
Contents |
Overview
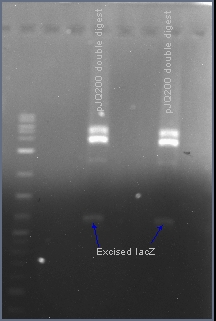
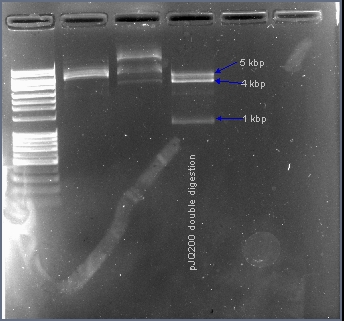
Excising the sacB gene from plasmid pJQ200
The native sacB gene was excised from the plasmid pJQ200 with the restriction enzymes EcoRI and HindIII. In the presence of 10% sucrose, the sacB gene acts as a suicide gene. After ligating a gene into this multiple cloning site, the plasmid pJQ200 should no longer be sucrose sensitive and should retain the gentamicin antibiotic resistance gene. Positive transformants will survive in the presence of gentamicin and sucrose.
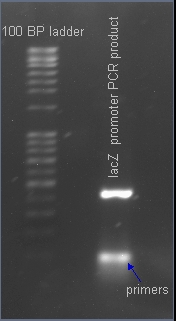
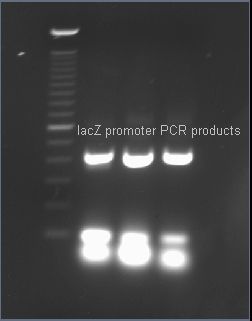
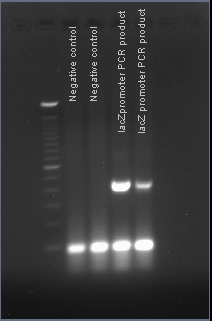
Verifying the presence of the lacZ promoter in the plasmid pJQ200
After PCR amplification, the PCR products are run through a gel to verify the proper amplificationn of lacZ. Positive verification means that the primers were correctly designed, the PCR was run correctly, and that lacZ exists in a plasmid in our cell cultures.
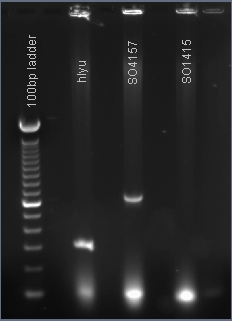
PCR amplification of the global transcription factors SO1415, SO4157, hlyU
The PCR products hlyU and SO4157 were made. These genes will be inserted into the plasmid pJQ200 immediately downstream of the lacZ promoter that was previously inserted by our team.