ETHZ/Model
From 2007.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Detailed Model) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | == Test Protocol == | |
For our project we decided on designing a systems that is able to learn or adapt to its environment. Please note that this is only a minimal system that should be able to act as a proof of concept. A protocol how the system should react according to an input is shown in Figure 1. | For our project we decided on designing a systems that is able to learn or adapt to its environment. Please note that this is only a minimal system that should be able to act as a proof of concept. A protocol how the system should react according to an input is shown in Figure 1. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* During a recognition phase the inputs aTc or IPTG are (re-) presented again. The system reports by changing its color depending on the input and its current memory state. That is why the system can have different florescence properties even in the presence of the same input. The recognition phase takes place in the presence of AHL to keep the memory enabled and avoid another learning phase. | * During a recognition phase the inputs aTc or IPTG are (re-) presented again. The system reports by changing its color depending on the input and its current memory state. That is why the system can have different florescence properties even in the presence of the same input. The recognition phase takes place in the presence of AHL to keep the memory enabled and avoid another learning phase. | ||
| - | + | == Model Overview == | |
To define our system we start with the classical back box approach as shown in Figure 2. | To define our system we start with the classical back box approach as shown in Figure 2. | ||
Revision as of 10:32, 15 October 2007
Contents |
Test Protocol
For our project we decided on designing a systems that is able to learn or adapt to its environment. Please note that this is only a minimal system that should be able to act as a proof of concept. A protocol how the system should react according to an input is shown in Figure 1.
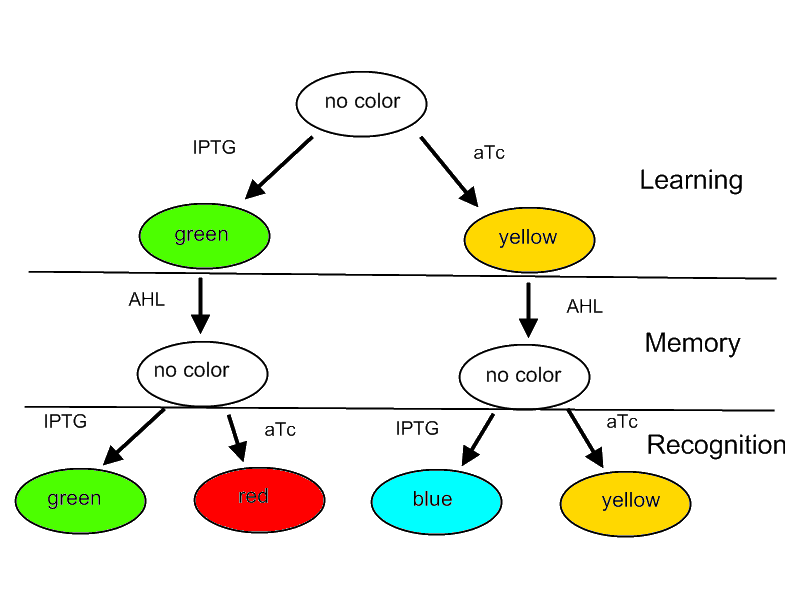
Fig. 1: Flow diagram. This figure shows the protocol with which the final system should be tested as well as the test results in form of the reported colors. There are tree phases the systems has to perform: (1) a training or learning phase in which the system learns an input and stores it in its memory, (2) a memory phase in which the system has to keep the content of its memory and finally (3) a recognition phase where the output of the system depends on the content of its memory as well as on the current input.
The idea behind this protocol is that
- The system will be able to learn one of two input signals - aTc or IPTG - furing a learning phase if no input signal AHL is present. Depending on the input it will report by either green or yellow florescence.
- Once the system learned, the inputs - aTc or IPTG - can be released and the system goes into a memory state in the presence of AHL. In this state no output color is reported.
- During a recognition phase the inputs aTc or IPTG are (re-) presented again. The system reports by changing its color depending on the input and its current memory state. That is why the system can have different florescence properties even in the presence of the same input. The recognition phase takes place in the presence of AHL to keep the memory enabled and avoid another learning phase.
Model Overview
To define our system we start with the classical back box approach as shown in Figure 2.
To fill that back box we have to think a bit more about the properties of our system. From our protocol we know that we need:
- 2 inputs that should be learned/detected/adapted to,
- 1 input to switch on the memory.
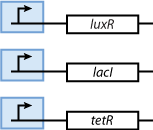
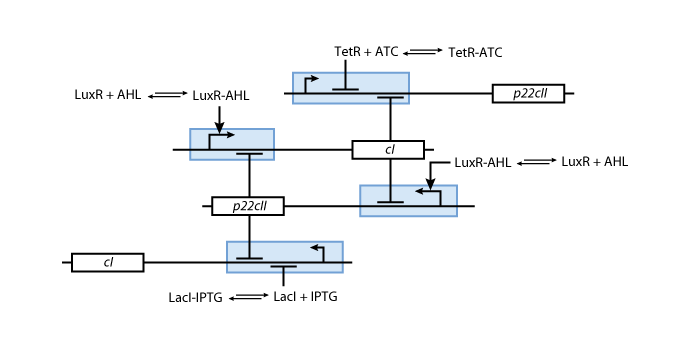
- We need to store at least 3 states. That is why we decided to use 2 state variables - cI and p22cII.
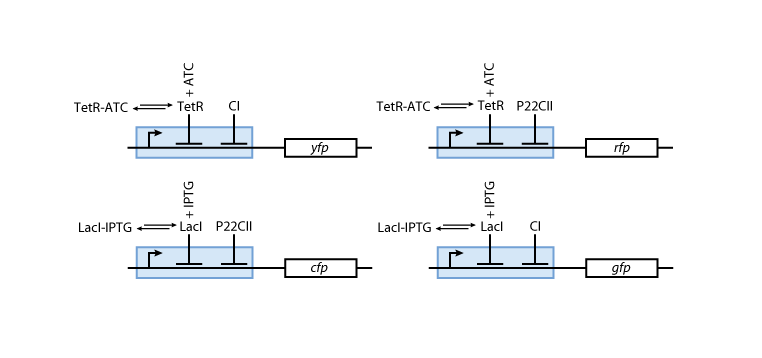
- We need 4 florescense signals for the outputs. Actually one could also decide to take 6 output signals into account to further distinguish the learning phase from the recognition phase but we restricted ourself to 4 outputs to reduce the number of genes that we will need to implement the signals.
An overview about the final system is shown in Figure 3.
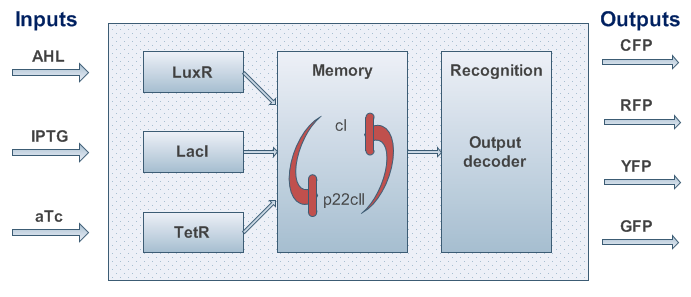
Fig.3: System overview. AHL, IPTG and aTc are passing the cell membrane where they build complexes with the sensor proteins LuxR, LacI and TetR. These sensor proteins and/or complexes are used to control memory formation and the production of the reporter proteins. The memory content is represented by the proteins cI and p22cII that repress the production of each other. YFP, RFP, CFP and GFP stand for yellow, red, cyan and green florescence protein, respectively.
- To be more robust against pertubations we couple the state variables cI and p22cII in the way that is well known from memory circuits that engineers build where one state variable is depressing the other one.
- We know that the system should finally be implemented in form of DNA and proteins in a bacteria. Since - due to their size - proteins can only hardly pass the cell membrane (if they are not actively transported through the cell membrane) we decided on the much smaller inducer molecules AHL, IPTG and aTc to act as the inputs. However, since those inducers cannot directly act on the transciption of DNA nor on the production of proteins we need to produce the sensor proteins LuxR, LacI and TetR that build complexes with AHL, IPTG and aTc, respectively.
- The sensor proteins and complexes are used to control the memory formation and the production of the florescence reporter proteins YFP, RFP, CFP and GFP.