Davidson Missouri W/Traveling Salesperson Problem
From 2007.igem.org
Wideloache (Talk | contribs) |
Wideloache (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <center>[[Davidson Missouri W| <span style="color:red">Home</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Background Information| <span style="color:red">Background Information</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Solving the HPP in vivo| <span style="color:red">Current Project: Solving the Hamiltonian Path Problem ''in vivo''</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Mathematical Modeling| <span style="color:red">Mathematical Modeling</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Gene splitting| <span style="color:red"> Gene Splitting </span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/ | + | <center>[[Davidson Missouri W| <span style="color:red">Home</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Background Information| <span style="color:red">Background Information</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Solving the HPP in vivo| <span style="color:red">Current Project: Solving the Hamiltonian Path Problem ''in vivo''</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Mathematical Modeling| <span style="color:red">Mathematical Modeling</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Gene splitting| <span style="color:red"> Gene Splitting </span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Results| <span style="color:red">Results</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Traveling Salesperson Problem| <span style="color:black">Traveling Salesperson Problem</span> ]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Software|<span style="color:red">Software</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Resources and Citations|<span style="color:red">Resources and Citations</span>]]</center> |
<hr> | <hr> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | Although our current project is to develop a bacterial computer that solves Hamiltonian path problems, in the future we would like to tackle the Traveling Salesman problem using similar methods. Given a directed graph where each edge has a cost associated with it, what is the cheapest, or shortest, path to take such that you end at your starting point and visit every node exactly once? | + | Although our current project is to develop a bacterial computer that solves Hamiltonian path problems, in the future we would also like to tackle the Traveling Salesman problem using similar methods. The TSP asks: Given a directed graph where each edge has a cost associated with it, what is the cheapest, or shortest, path to take such that you end at your starting point and visit every node exactly once? |
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | [[Image:TSP 4N shortest.jpg|900px]] | + | [[Image:TSP 4N shortest.jpg|thumb|900px|The solution to the Traveling Salesman Problem.]] |
Instead of putting each half-gene back to back along an edge, we could add in spacers of specified lengths that would allow us to model the various weights in the graph above. These weights would give edges different lengths (in base pairs). After performing PCR on all of the solved plasmids (with primers binding to the promoter and terminator), we would be able to find the shortest path through all of the nodes by running the PCR products on a gel. Because the total length of the genes in any Hamiltonian Path through the graph is a constant, the smallest solved fragment will have the lowest total spacer length and will, therefore, be the solution to the Traveling Salesperson Problem (shown above). | Instead of putting each half-gene back to back along an edge, we could add in spacers of specified lengths that would allow us to model the various weights in the graph above. These weights would give edges different lengths (in base pairs). After performing PCR on all of the solved plasmids (with primers binding to the promoter and terminator), we would be able to find the shortest path through all of the nodes by running the PCR products on a gel. Because the total length of the genes in any Hamiltonian Path through the graph is a constant, the smallest solved fragment will have the lowest total spacer length and will, therefore, be the solution to the Traveling Salesperson Problem (shown above). | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | [[Image:TSP 4N longer.jpg|900px | + | [[Image:TSP 4N longer.jpg|thumb|900px|This image shows an alternate route through the graph. The length of this fragment is longer than the length of the solution to the TSP.]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | This image shows an alternate route through the graph. The length of this fragment is longer than the length of the solution to the TSP. | + | |
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | [[Image:TSP 4N falsepos.jpg|900px]] | + | [[Image:TSP 4N falsepos.jpg|thumb|900px|A possible false positive solution.]] |
| - | False positives can also come into play with this construct. However, certain rules can be put into place when choosing spacer lengths to avoid having false positive PCR products that are | + | False positives can also come into play with this construct. However, certain rules can be put into place when choosing spacer lengths to avoid having false positive PCR products that are shorter than the true solution. |
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <[[Davidson Missouri W/Results | Previous Section]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Software | Next Section>]] | ||
| + | </center> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:28, 26 October 2007
Although our current project is to develop a bacterial computer that solves Hamiltonian path problems, in the future we would also like to tackle the Traveling Salesman problem using similar methods. The TSP asks: Given a directed graph where each edge has a cost associated with it, what is the cheapest, or shortest, path to take such that you end at your starting point and visit every node exactly once?
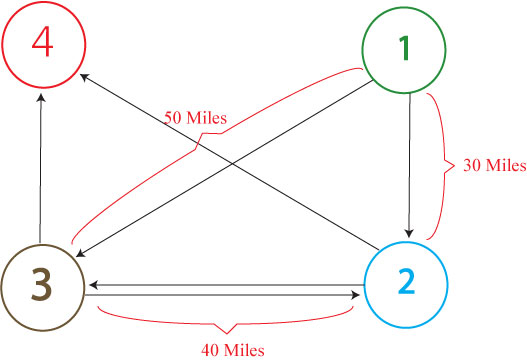
The graph above shows a modified complete graph with edges leaving the ending node (#4), returning to the start node (#1), and moving from the start to the stop node removed. If we wanted to solve this weighted and directed graph for the shortest path through all nodes, starting at node #1, ending at node #4, and passing through each node only once, we could use our current HPP E. coli computer construct with one slight modification.
Instead of putting each half-gene back to back along an edge, we could add in spacers of specified lengths that would allow us to model the various weights in the graph above. These weights would give edges different lengths (in base pairs). After performing PCR on all of the solved plasmids (with primers binding to the promoter and terminator), we would be able to find the shortest path through all of the nodes by running the PCR products on a gel. Because the total length of the genes in any Hamiltonian Path through the graph is a constant, the smallest solved fragment will have the lowest total spacer length and will, therefore, be the solution to the Traveling Salesperson Problem (shown above).
False positives can also come into play with this construct. However, certain rules can be put into place when choosing spacer lengths to avoid having false positive PCR products that are shorter than the true solution.