Virginia/Projects/1
From 2007.igem.org
(→Biobrick and pathway design) |
|||
| (37 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| - | + | [[Image:UVA Logo.gif|center]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | {| cellspacing="6px" cellpadding="16" border="0" width="100%" | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Virginia|HOME]] | ||
| + | |[[Virginia/Projects|PROJECT INTRO]] | ||
| + | |[[Virginia/Projects/1|APPROACH]] | ||
| + | |[[Virginia/Projects/2|PROCEDURES]] | ||
| + | |[[Virginia/Projects/3|RESULTS]] | ||
| + | |[http://partsregistry.org/cgi/partsdb/pgroup.cgi?pgroup=iGEM2007&group=Virginia BIOBRICKS] | ||
| + | |[http://openwetware.org/wiki/IGEM:VGEM/2007/Notebook eNOTEBOOK] | ||
| + | |[http://www.seas.virginia.edu/VGEM/ WEBSITE] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | ==Harvesting Cellulose and Light to Power Butanol Biosynthesis== | ||
| - | + | Send comments to [mailto:mcarthur@virginia.edu?subject=VGEM_Query George McArthur] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ===Approach=== | |
| + | ---- | ||
| + | New approaches to metabolic engineering made possible by the development of genomics, systems biology, and synthetic biology have enabled metabolic pathway design in microorganisms for the production of transportation fuels such as ethanol, butanol and hydrogen (Stephanopoulos 2007). The novel microbial metabolism developed by the 2007 Virginia Genetically Engineered Machine (VGEM) Team for the production of butanol from cellulose and light is illustrated below in Figure 1. The four main systems that comprise the pathway- cellulose metabolism, light metabolism, butanol biosynthesis, and butanol tolerance- have extended E. coli K-12’s natural central metabolic pathway. In this way, a valuable chemical product such as butanol biofuel can be biologically manufactured using inexpensive feedstock material. The cellulose and light metabolizing systems may one day serve as engines in future system designs to drive forward the biosynthesis of chemical products in microorganisms. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:VGEM 2007 metabolic pathway.jpg|800px]]</center> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <center>'''Figure 1'''</center> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | The cellulase system was designed using three cellulases discovered in Saccharophagus degradans. Cel5F, Cel6A, and Bgl3C have been predicted to code for an endo-1,4,-β-glucanase, cellobiohydrolase, and cellobiase respectively (Taylor et al. 2006). These enzymes are capable of converting crystalline cellulose to long cellulose chains, then to cellobiose units containing two or four β-glucose monomers, and finally to β-glucose units that can be taken up by E. coli. Cellulose is a complex polysaccharide that is too large to be transported to the inside of the cell. Therefore, the three enzymes must be secreted to act on the cellulose substrate. According to Taylor et al., these three genes include a type II secretion signal sequence, which should take advantage of the type II secretion system that is native to E. coli. | ||
| - | ''' | + | To aid in powering E. coli growth and butanol production, proteorhodopsin was incorporated into the pathway design. Proteorhodopsin re-establishes the proton motive force that is decreased under non-ideal conditions such as low glucose concentrations or respiratory stress (Walter et al., 2006)). Butanol biosynthesis occurs under anaerobic conditions naturally in Clostridia. |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:VGEM 2007 BioBrick table.jpg|800px]]</center> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <center>'''Table 1'''</center> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | The ten genes that were used to design the system, listed above in Table 1 in BioBrick nomenclature, were standardized to facilitate system construction via BioBrick assembly methods. Each BioBrick was designed by combining the gene of interest (i.e., the protein coding region) with other basic parts including a promoter (BBa_J23119), a ribosomal binding site (BBa_B0030), and two terminators (BBa_0012 and BBa_0011). The construct is defined as a BioBrick once it includes a standard prefix (before the promoter) and a standard suffix (after the terminator) that code for restriction enzyme sites. EcoRI, NotI, and XbaI are sites contained in the prefix while SpeI, NotI, and PstI are included in the suffix sequence. | ||
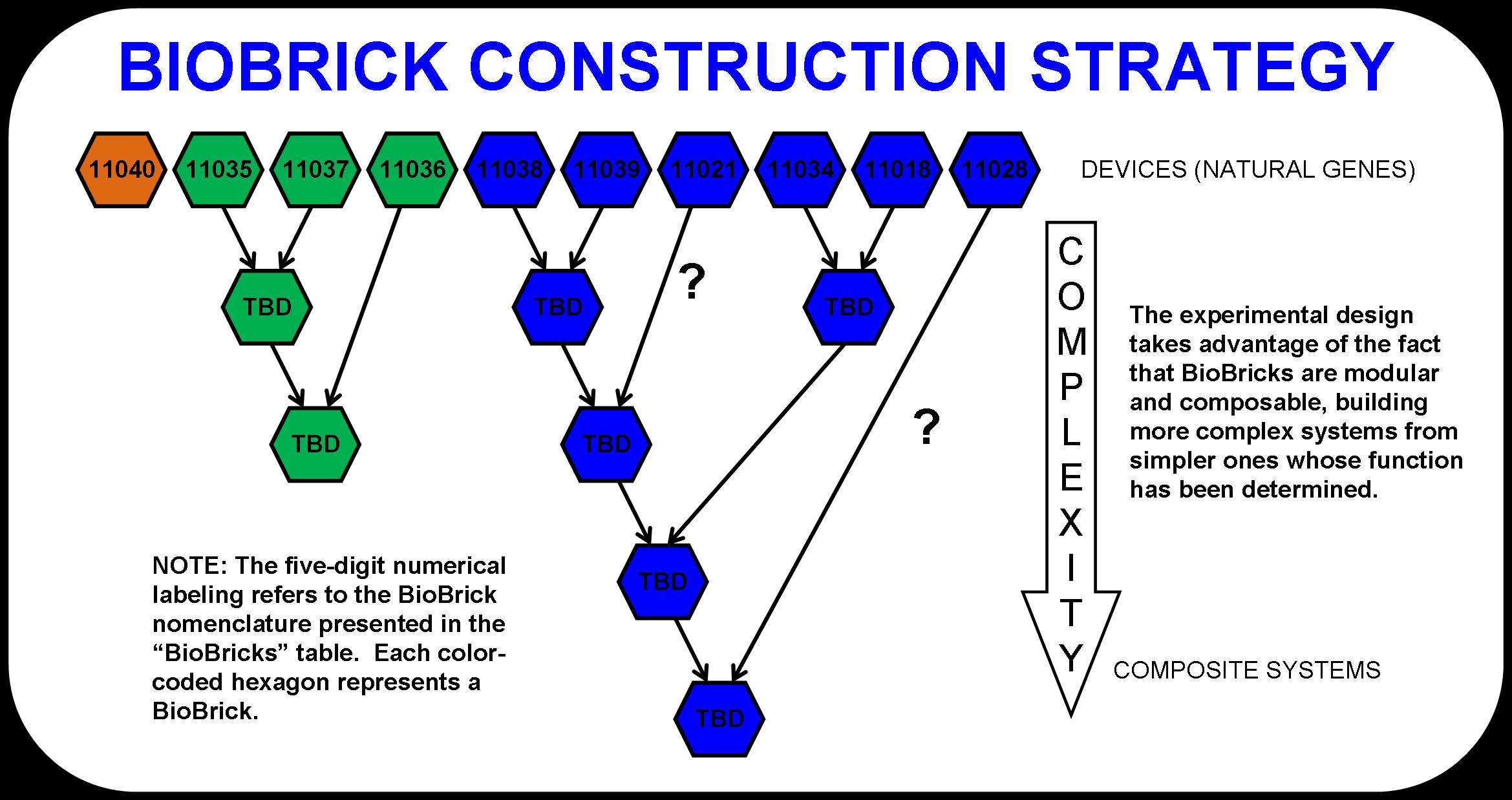
| - | + | The experimental design was determined by the metabolic pathway and the fact that more complex BioBrick systems can be assembled from simpler ones. The modularity of BioBricks can be taken full advantage of in this project by taking a bottom-up approach to pathway design. For example, butanol dehydrogenase (BBa_I711021) may or may not be a necessary enzyme for the production of butanol (6). That is, the butyraldehyde dehydrogenases in the prior enzymatic step may actually be responsible for both steps. To test this, we designed an experiment that compares the fermentation product distribution of E. coli that would be transformed with both butyraldehyde dehydrogenases and butanol dehydrogenase to E. coli that would be transformed with only the butyraldehyde dehydrogenases. | |
| - | + | The detailed schematic shown below (Figure 2) demonstrates this powerful approach to biological system design and construction. As simpler systems are tested and characterized, they are consolidated into more complex systems. Eventually, the four main systems that make up this pathway would become abstracted. This is the goal. At that point, one could look at the entire metabolic pathway as a black box with cellulose and light going in and butanol and waste products coming out. | |
| - | + | <br /> | |
| - | + | <br /> | |
| - | + | <center>[[Image:VGEM 2007 biobrick construction strategy.jpg|800px]]</center> | |
| - | + | <br /> | |
| - | + | <center>'''Figure 2'''</center> | |
| - | + | <br /> | |
| - | + | ===References=== | |
| - | + | ---- | |
| - | + | #Andrykovitch, G., & Marx, I. (1988). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54(4), 1061-1062. | |
| - | + | #Beja, O., Aravind, L., Koonin, E., Suzuki, M., Hadd, A., Nguyen, L., et al. (2000). Science, 289(5486), 1902-#906. | |
| - | + | #Borden, J., & Papoutsakis, E. (2007). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(9), 3061-3068. | |
| - | + | #Kennedy, J., Murli, S., & Kealey, J. T. (2003). Biochemistry, 42(48), 14342-14348. | |
| - | ''' | + | #Martinez, A., Bradley, A. S., Waldbauer, J. R., Summons, R. E., & DeLong, E. F. (2007). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(13), 5590-5595. |
| - | + | #Nolling, J., Breton, G., Omelchenko, M., Makarova, K., Zeng, Q., Gibson, R., et al. (2001). The Journal of Bacteriology, 183(16), 4823-4838. | |
| - | + | #Taylor, L.,II, Henrissat, B., Coutinho, P., Ekborg, N., Hutcheson, S., & Weiner, R. (2006). The Journal of Bacteriology, 188(11), 3849-3861. | |
| - | + | #Schwarz, W.H. (2001). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56, 634–649 | |
| - | + | #Demain, A., Newcomb, M., & Wu, J. H. D. (2005) Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 69(1), 124-154. | |
| - | + | #Ekborg, N., Gonzalez, J., Howard, M., Taylor, L., Hutcheson, S., & Weiner, R. (2005). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 55(4), 1545-1549. | |
| - | + | #Stephanopoulos, G. (2007). Science, 315(5813), 801-804. | |
| - | + | #Walter, J., Greenfield, D., Bustamante, C., & Liphardt, J. (2007). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(7), 2408-2412. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Latest revision as of 05:23, 27 October 2007
| HOME | PROJECT INTRO | APPROACH | PROCEDURES | RESULTS | [http://partsregistry.org/cgi/partsdb/pgroup.cgi?pgroup=iGEM2007&group=Virginia BIOBRICKS] | [http://openwetware.org/wiki/IGEM:VGEM/2007/Notebook eNOTEBOOK] | [http://www.seas.virginia.edu/VGEM/ WEBSITE] |
Harvesting Cellulose and Light to Power Butanol Biosynthesis
Send comments to George McArthur
Approach
New approaches to metabolic engineering made possible by the development of genomics, systems biology, and synthetic biology have enabled metabolic pathway design in microorganisms for the production of transportation fuels such as ethanol, butanol and hydrogen (Stephanopoulos 2007). The novel microbial metabolism developed by the 2007 Virginia Genetically Engineered Machine (VGEM) Team for the production of butanol from cellulose and light is illustrated below in Figure 1. The four main systems that comprise the pathway- cellulose metabolism, light metabolism, butanol biosynthesis, and butanol tolerance- have extended E. coli K-12’s natural central metabolic pathway. In this way, a valuable chemical product such as butanol biofuel can be biologically manufactured using inexpensive feedstock material. The cellulose and light metabolizing systems may one day serve as engines in future system designs to drive forward the biosynthesis of chemical products in microorganisms.
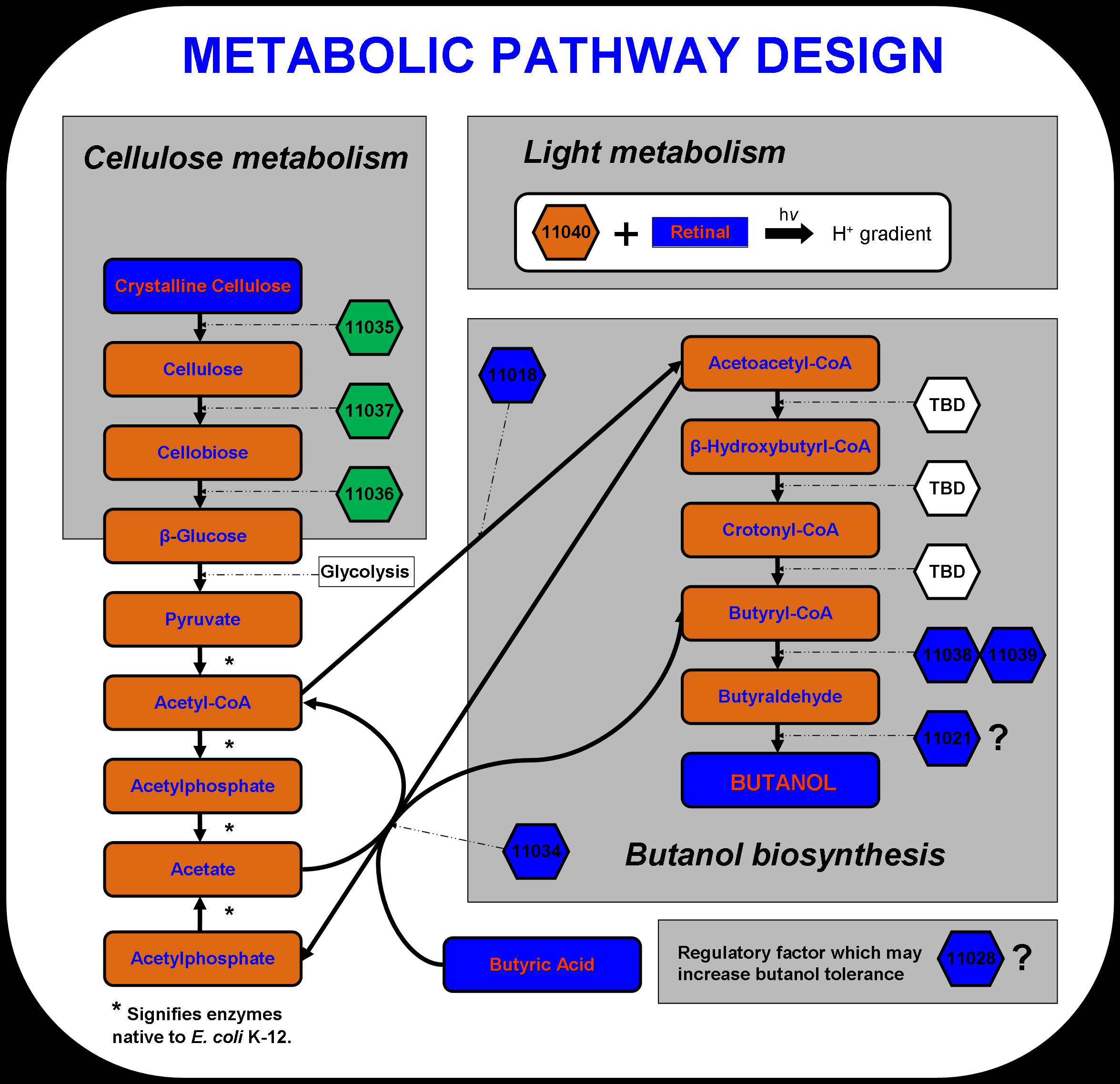
The cellulase system was designed using three cellulases discovered in Saccharophagus degradans. Cel5F, Cel6A, and Bgl3C have been predicted to code for an endo-1,4,-β-glucanase, cellobiohydrolase, and cellobiase respectively (Taylor et al. 2006). These enzymes are capable of converting crystalline cellulose to long cellulose chains, then to cellobiose units containing two or four β-glucose monomers, and finally to β-glucose units that can be taken up by E. coli. Cellulose is a complex polysaccharide that is too large to be transported to the inside of the cell. Therefore, the three enzymes must be secreted to act on the cellulose substrate. According to Taylor et al., these three genes include a type II secretion signal sequence, which should take advantage of the type II secretion system that is native to E. coli.
To aid in powering E. coli growth and butanol production, proteorhodopsin was incorporated into the pathway design. Proteorhodopsin re-establishes the proton motive force that is decreased under non-ideal conditions such as low glucose concentrations or respiratory stress (Walter et al., 2006)). Butanol biosynthesis occurs under anaerobic conditions naturally in Clostridia.
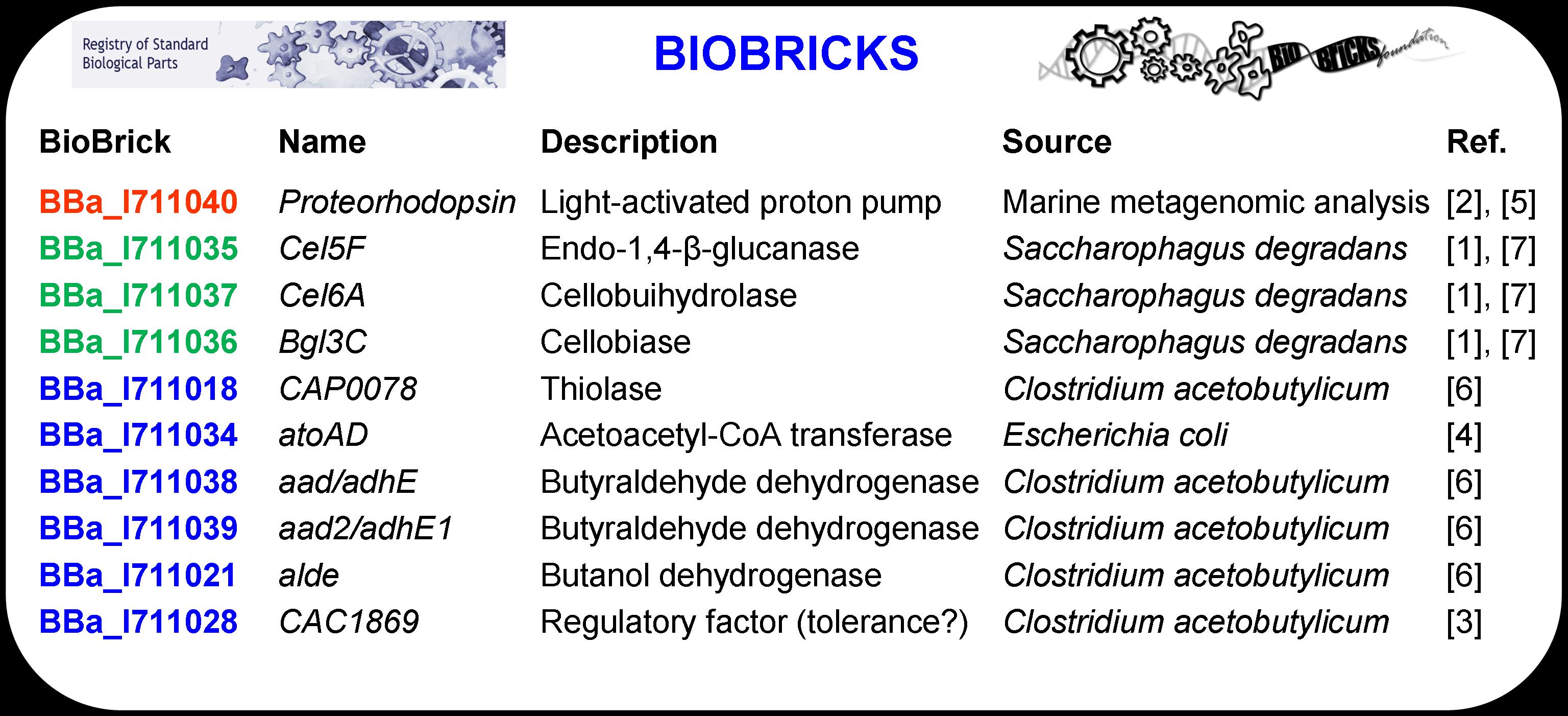
The ten genes that were used to design the system, listed above in Table 1 in BioBrick nomenclature, were standardized to facilitate system construction via BioBrick assembly methods. Each BioBrick was designed by combining the gene of interest (i.e., the protein coding region) with other basic parts including a promoter (BBa_J23119), a ribosomal binding site (BBa_B0030), and two terminators (BBa_0012 and BBa_0011). The construct is defined as a BioBrick once it includes a standard prefix (before the promoter) and a standard suffix (after the terminator) that code for restriction enzyme sites. EcoRI, NotI, and XbaI are sites contained in the prefix while SpeI, NotI, and PstI are included in the suffix sequence.
The experimental design was determined by the metabolic pathway and the fact that more complex BioBrick systems can be assembled from simpler ones. The modularity of BioBricks can be taken full advantage of in this project by taking a bottom-up approach to pathway design. For example, butanol dehydrogenase (BBa_I711021) may or may not be a necessary enzyme for the production of butanol (6). That is, the butyraldehyde dehydrogenases in the prior enzymatic step may actually be responsible for both steps. To test this, we designed an experiment that compares the fermentation product distribution of E. coli that would be transformed with both butyraldehyde dehydrogenases and butanol dehydrogenase to E. coli that would be transformed with only the butyraldehyde dehydrogenases.
The detailed schematic shown below (Figure 2) demonstrates this powerful approach to biological system design and construction. As simpler systems are tested and characterized, they are consolidated into more complex systems. Eventually, the four main systems that make up this pathway would become abstracted. This is the goal. At that point, one could look at the entire metabolic pathway as a black box with cellulose and light going in and butanol and waste products coming out.
References
- Andrykovitch, G., & Marx, I. (1988). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54(4), 1061-1062.
- Beja, O., Aravind, L., Koonin, E., Suzuki, M., Hadd, A., Nguyen, L., et al. (2000). Science, 289(5486), 1902-#906.
- Borden, J., & Papoutsakis, E. (2007). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(9), 3061-3068.
- Kennedy, J., Murli, S., & Kealey, J. T. (2003). Biochemistry, 42(48), 14342-14348.
- Martinez, A., Bradley, A. S., Waldbauer, J. R., Summons, R. E., & DeLong, E. F. (2007). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(13), 5590-5595.
- Nolling, J., Breton, G., Omelchenko, M., Makarova, K., Zeng, Q., Gibson, R., et al. (2001). The Journal of Bacteriology, 183(16), 4823-4838.
- Taylor, L.,II, Henrissat, B., Coutinho, P., Ekborg, N., Hutcheson, S., & Weiner, R. (2006). The Journal of Bacteriology, 188(11), 3849-3861.
- Schwarz, W.H. (2001). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56, 634–649
- Demain, A., Newcomb, M., & Wu, J. H. D. (2005) Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 69(1), 124-154.
- Ekborg, N., Gonzalez, J., Howard, M., Taylor, L., Hutcheson, S., & Weiner, R. (2005). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 55(4), 1545-1549.
- Stephanopoulos, G. (2007). Science, 315(5813), 801-804.
- Walter, J., Greenfield, D., Bustamante, C., & Liphardt, J. (2007). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(7), 2408-2412.
