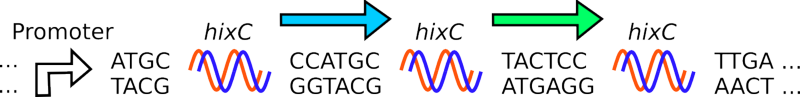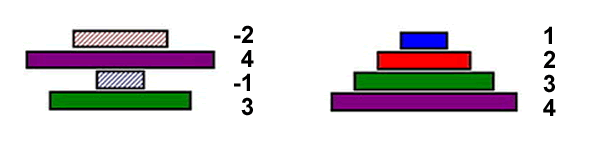Davidson Missouri W/Background Information
From 2007.igem.org
Wideloache (Talk | contribs) |
Wideloache (Talk | contribs) (→Why Use Bacteria?) |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <center>[[Davidson Missouri W| <span style="color:red">Home</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Background Information| <span style="color:black">Background Information</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Solving the HPP in vivo| <span style="color:red">Current Project: Solving the Hamiltonian Path Problem ''in vivo''</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Mathematical Modeling| <span style="color:red">Mathematical Modeling</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Gene splitting| <span style="color:red"> Gene Splitting </span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/ | + | <center>[[Davidson Missouri W| <span style="color:red">Home</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Background Information| <span style="color:black">Background Information</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Solving the HPP in vivo| <span style="color:red">Current Project: Solving the Hamiltonian Path Problem ''in vivo''</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Mathematical Modeling| <span style="color:red">Mathematical Modeling</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Gene splitting| <span style="color:red"> Gene Splitting </span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Results| <span style="color:red">Results</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Traveling Salesperson Problem| <span style="color:red">Traveling Salesperson Problem</span> ]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Software|<span style="color:red">Software</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Resources and Citations|<span style="color:red">Resources and Citations</span>]]</center> |
<hr> | <hr> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | In 1994 Adleman developed a system to solve the Hamiltonian Path problem using DNA ''in vitro''. We have implemented a bacterial system to solve Hamiltonian Path problems ''in vivo''. Our bacterial computer works by taking advantage of the Hin Recombinase protein and '' | + | In 1994 Adleman developed a system to solve the Hamiltonian Path problem using DNA ''in vitro''. We have implemented a bacterial system to solve Hamiltonian Path problems ''in vivo''. Our bacterial computer works by taking advantage of the Hin Recombinase protein and ''hixC'' sites to perform a "flipping" operation. By strategically placing ''hixC'' sites on a plasmid, along with reporter genes, we can simulate paths on a graph through flipping. |
| - | =The Hin Recombinase/'' | + | =The Hin Recombinase/''hixC'' System Revisited= |
| - | ''Salmonella typhimurium'' is a bacterium | + | ''Salmonella typhimurium'' is a bacterium that moves using flagella. Depending on its environment, it expresses different sets of surface proteins on its flagella. It is able to change this expression through the use of Hin Recombinase and ''hixC'' sites. The Hin Recombinase enzyme catalyzes the inversion of DNA that lies between a pair of ''hixC'' sites. By flipping DNA segments between ''hixC'' sites ''S. typhimurium'' can express alternate flagellar surface proteins. |
| - | # Given a segment of DNA, flanked by '' | + | # Given a segment of DNA, flanked by ''hixC'' sites (blue arrow):<br>[[Image:hinhix1.png|thumb|none|800px|Figure 1.]] |
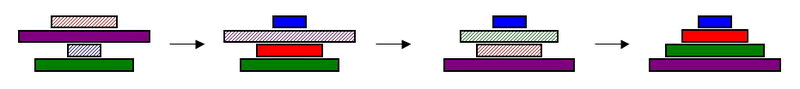
| - | # Two dimers of Hin Recombinase protein attach to a pair of '' | + | # Two dimers of Hin Recombinase protein attach to a pair of ''hixC'' sites around the DNA segment.<br>[[Image:hinhix2.png|thumb|none|800px|Figure 2.]] |
| - | # The DNA segment between the pair of '' | + | # The DNA segment between the pair of ''hixC'' sites is inverted. Note that the green arrow is unaffected.<br>[[Image:hinhix3.png|thumb|none|800px|Figure 3.]] |
=Flipping Pancakes= | =Flipping Pancakes= | ||
| - | In the 2006 iGEM competition, [https://2006.igem.org/wiki/index.php/Davidson_2006 Davidson] and [https://2006.igem.org/wiki/index.php/Missouri_Western_State_University_2006 Missouri Western] used | + | In the 2006 iGEM competition, [https://2006.igem.org/wiki/index.php/Davidson_2006 Davidson] and [https://2006.igem.org/wiki/index.php/Missouri_Western_State_University_2006 Missouri Western] used Hin Recombinase and ''hixC'' to model a mathematical problem, called the Pancake Flipping problem. The problem is the following: given a stack of pancakes which are burnt on one side and golden on the other, and two spatulas, what is the minimum number of flips required to sort the stack by pancake size and with all burnt sides facing downwards? |
[[Image:pancake_sorting.gif|frame|none|How many flips does this take?]] | [[Image:pancake_sorting.gif|frame|none|How many flips does this take?]] | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
=Why Use Bacteria?= | =Why Use Bacteria?= | ||
| - | + | We have demonstrated that it is possible to solve mathematical problems using bacteria, though it may not be obvious why bacterial computers are helpful. Although the initial programming of bacterial software is expensive and slow when compared with standard computer software, the hardware costs of each bacterial computer are negligible. | |
| + | |||
| + | Others have emulated computer logic ''in vivo'', yet the practical value is limited by the ease with which bacterial software can be programmed. Furthermore, traditional computers are already adept at logic and arithmetic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Instead of adapting an electronics mindset to a bacterial system, we envision another type of bacterial computer that benefits from the ease of hardware fabrication through bacterial growth and minimizes the dependency on algorithmic sophistication.''' It is desirable, but not always possible, to develop efficient algorithms that reduce computational time. In the absence of an efficient algorithm, the only way to decrease the time until a solution is found is to buy more hardware. For problems of this type, bacterial computers have an innate advantage over traditional computers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If each plasmid within a bacterium is a processor with software, each bacterial computer contains several plasmids, and a single flask of bacteria contains billions of bacteria, then it is trivial to produce billions of computers. Each computer will be acting in parallel with the others, drastically reducing the amount of time required to reach a solution. The use of bacterial computers is thus a way to allow us to solve computational problems which traditional computers cannot. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
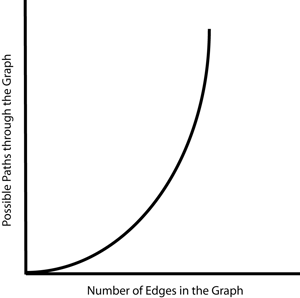
| + | [[Image:Complexity.png|thumb|300px|left|For the Hamiltonian Path Problem, as the number of edges on a graph increases linearly, the number of possible paths through the graph increases exponentially. There exists no efficient algorithm for solving this problem.]] | ||
| + | |||
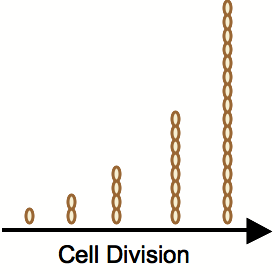
| + | [[Image:Expcellgrowth.png|thumb|300px|none|Exponential cell growth maintains parity with the exponential increase in graph complexity. Bacterial computers are so cheap to produce, that they could theoretically be more efficient than traditional computers at solving complex problems that have unsophisticated algorithmic solutions.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | [[Davidson Missouri W | <Previous Section]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Solving the HPP in vivo| Next Section>]] | ||
| + | </center> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:23, 25 October 2007
In 1994 Adleman developed a system to solve the Hamiltonian Path problem using DNA in vitro. We have implemented a bacterial system to solve Hamiltonian Path problems in vivo. Our bacterial computer works by taking advantage of the Hin Recombinase protein and hixC sites to perform a "flipping" operation. By strategically placing hixC sites on a plasmid, along with reporter genes, we can simulate paths on a graph through flipping.
The Hin Recombinase/hixC System Revisited
Salmonella typhimurium is a bacterium that moves using flagella. Depending on its environment, it expresses different sets of surface proteins on its flagella. It is able to change this expression through the use of Hin Recombinase and hixC sites. The Hin Recombinase enzyme catalyzes the inversion of DNA that lies between a pair of hixC sites. By flipping DNA segments between hixC sites S. typhimurium can express alternate flagellar surface proteins.
- Given a segment of DNA, flanked by hixC sites (blue arrow):
- Two dimers of Hin Recombinase protein attach to a pair of hixC sites around the DNA segment.
- The DNA segment between the pair of hixC sites is inverted. Note that the green arrow is unaffected.
Flipping Pancakes
In the 2006 iGEM competition, Davidson and Missouri Western used Hin Recombinase and hixC to model a mathematical problem, called the Pancake Flipping problem. The problem is the following: given a stack of pancakes which are burnt on one side and golden on the other, and two spatulas, what is the minimum number of flips required to sort the stack by pancake size and with all burnt sides facing downwards?
Using mathematical models it is possible to compute these estimates for small stacks. However, adding pancakes to a stack increases the number of possible permutations non-linearly. The number of possible stacks of n pancakes is equal to: 2^n (n!). Thus traditional computers are not well-suited for computations involving large pancake stacks.
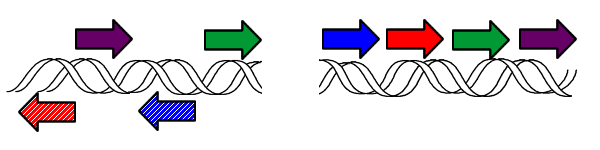
However, it is possible to model pancake flipping using bacteria. If each pancake is given an identification number, along with a sign designating its orientation, then this can be stated equivalently using genes. Thus the following images show equivalent notations for pancake stacks:
By taking advantage of this notation it is possible to use bacteria as computers to solve pancake-flipping problems.
Why Use Bacteria?
We have demonstrated that it is possible to solve mathematical problems using bacteria, though it may not be obvious why bacterial computers are helpful. Although the initial programming of bacterial software is expensive and slow when compared with standard computer software, the hardware costs of each bacterial computer are negligible.
Others have emulated computer logic in vivo, yet the practical value is limited by the ease with which bacterial software can be programmed. Furthermore, traditional computers are already adept at logic and arithmetic.
Instead of adapting an electronics mindset to a bacterial system, we envision another type of bacterial computer that benefits from the ease of hardware fabrication through bacterial growth and minimizes the dependency on algorithmic sophistication. It is desirable, but not always possible, to develop efficient algorithms that reduce computational time. In the absence of an efficient algorithm, the only way to decrease the time until a solution is found is to buy more hardware. For problems of this type, bacterial computers have an innate advantage over traditional computers.
If each plasmid within a bacterium is a processor with software, each bacterial computer contains several plasmids, and a single flask of bacteria contains billions of bacteria, then it is trivial to produce billions of computers. Each computer will be acting in parallel with the others, drastically reducing the amount of time required to reach a solution. The use of bacterial computers is thus a way to allow us to solve computational problems which traditional computers cannot.