MIT
From 2007.igem.org
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
<!-- END INFORMATION HEADER--> | <!-- END INFORMATION HEADER--> | ||
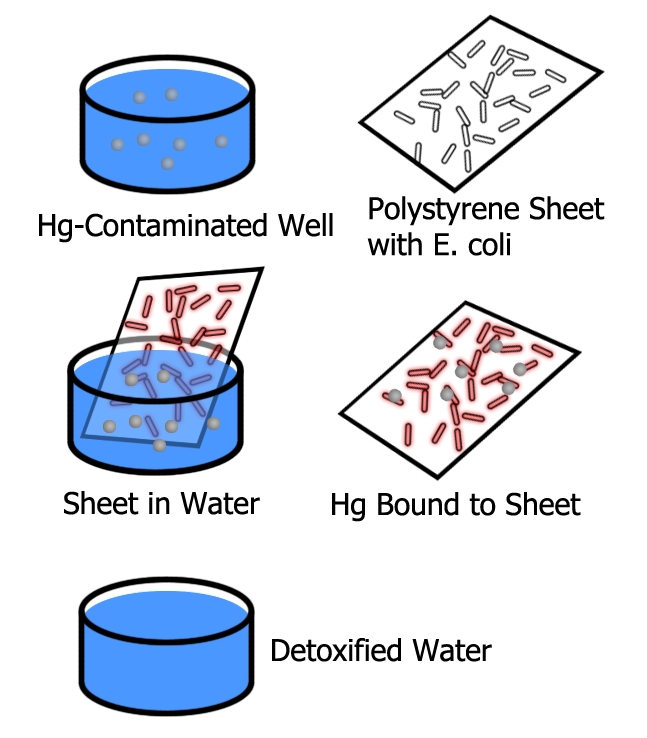
Mercury contamination of drinking water is a significant problem in both developed and developing countries. Techniques to filter it out are both costly and intensive. Thus, the MIT iGEM 2007 team is engineering a biological mechanism to cost-effectively sense and remove Mercury ions from contaminated water through a two cell system. One cell will use the Mer promoter to sense the presence of Mercury ions, then activate the GFP fused downstream. The other uses a cell surface display mechanism to exhibit a Mercury capturing peptide, extracting the Mercury from the water. Both cells also display polystyrene binding peptides, and will thus be attached to a polystyrene filter. This setup would be easy to use, cheap to manufacture, and economical to distribute. It could be used from very small scales to even an entire village's drinking water supply. | Mercury contamination of drinking water is a significant problem in both developed and developing countries. Techniques to filter it out are both costly and intensive. Thus, the MIT iGEM 2007 team is engineering a biological mechanism to cost-effectively sense and remove Mercury ions from contaminated water through a two cell system. One cell will use the Mer promoter to sense the presence of Mercury ions, then activate the GFP fused downstream. The other uses a cell surface display mechanism to exhibit a Mercury capturing peptide, extracting the Mercury from the water. Both cells also display polystyrene binding peptides, and will thus be attached to a polystyrene filter. This setup would be easy to use, cheap to manufacture, and economical to distribute. It could be used from very small scales to even an entire village's drinking water supply. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<!--Resources section--> | <!--Resources section--> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 26: | ||
<!--End Resources Header--> | <!--End Resources Header--> | ||
*[http://openwetware.org/wiki/IGEM:MIT/2007/Notebook Team Notebook] | *[http://openwetware.org/wiki/IGEM:MIT/2007/Notebook Team Notebook] | ||
| + | *[[/Background|Background]] | ||
| + | *[[/Approach|Approach]] | ||
| + | *[[/Results|Results]] | ||
| + | *[[/Future|Future Experiments]] | ||
| + | |||
<!--*[[Team Notebook]]--> | <!--*[[Team Notebook]]--> | ||
*'''Brainstorming''': | *'''Brainstorming''': | ||
| Line 58: | Line 48: | ||
<hr/> | <hr/> | ||
<!-- END PHOTOS HEADER--> | <!-- END PHOTOS HEADER--> | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Wholeoverview.jpg|thumb|center|300px|center|MIT's Project Goal: Sensing and Removing Hg ions from contaminated water.]] |
[[Image:IGEM_team.jpg|thumb|center|300px|Top Row: Forrest Liau, Aditya Kohli, Brian Cook, Alex Lue, Semmie Kim, Bernice Huang, Jess Ho. Bottom Row: Debbie Liu, Laure-Anne Ventouras, Toan Tran-Phu]] | [[Image:IGEM_team.jpg|thumb|center|300px|Top Row: Forrest Liau, Aditya Kohli, Brian Cook, Alex Lue, Semmie Kim, Bernice Huang, Jess Ho. Bottom Row: Debbie Liu, Laure-Anne Ventouras, Toan Tran-Phu]] | ||
|width="220px" class="green3" valign="top"| | |width="220px" class="green3" valign="top"| | ||
| + | <!--Parts section--> | ||
| + | <h3> | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <img src="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/images/d/db/Buttonaddpart.gif" width=20> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | BioBrick Parts | ||
| + | </h3> | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | <!--End Parts Header--> | ||
| + | *[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I728005 OmpC Surface Display] | ||
| + | *[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I728004 CPX Surface Display] | ||
| + | *[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I728500 CPX display of a polystyrene binding peptide] | ||
| + | *[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I728200 Simple System of Transcriptional Regulator, RBS, and CPX Surface Display Mechanism] | ||
| + | *[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I728201 Complex System of Promoter, RBS, CPX, and terminator] | ||
<!-- PEOPLE HEADER--> | <!-- PEOPLE HEADER--> | ||
<h3><html> | <h3><html> | ||
| Line 68: | Line 72: | ||
</html>People</h3> | </html>People</h3> | ||
<hr/> | <hr/> | ||
| + | |||
<!-- END PEOPLE HEADER--> | <!-- END PEOPLE HEADER--> | ||
====Students==== | ====Students==== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:46, 27 October 2007
|
|
|
 Graphics
Graphics