Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Applications
From 2007.igem.org
(→Division Frequency Analysis) |
(→Coupling to a PoPS counting device) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
===Coupling to a PoPS counting device=== | ===Coupling to a PoPS counting device=== | ||
| - | Couple the output of the Division PoPper to another counting device (such as the [https://2006.igem.org/wiki/index.php/ETH_Zurich_2005#Abstract ETH Zurich counter] or other variants) to count the number of cell divisions. This | + | Couple the output of the Division PoPper to another counting device (such as the [https://2006.igem.org/wiki/index.php/ETH_Zurich_2005#Abstract ETH Zurich counter] or other variants) to count the number of cell divisions. This is difficult to test due to the nature of colonies and cells dividing out of phase. We get around this problem by using high-power microscopy to study the activity of single cells. |
===Counting using more recombination sections=== | ===Counting using more recombination sections=== | ||
Revision as of 19:42, 8 August 2007
Edinburgh > DivisionPopper
Introduction | Applications | Design | Status | References
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2007/f/f5/800px-Edinburgh_City_15_mod.JPG
Applications and further research
Contents |
This page details some of the potential uses of the Division PoPper and other ways of using the recombination systems
Division Frequency Analysis
The output of the Division PoPper could be linked to the production of a slowly degrading protein. The more frequent the divisions, the greater the concentration of the protein.
Division Counting
Coupling to a PoPS counting device
Couple the output of the Division PoPper to another counting device (such as the ETH Zurich counter or other variants) to count the number of cell divisions. This is difficult to test due to the nature of colonies and cells dividing out of phase. We get around this problem by using high-power microscopy to study the activity of single cells.
Counting using more recombination sections
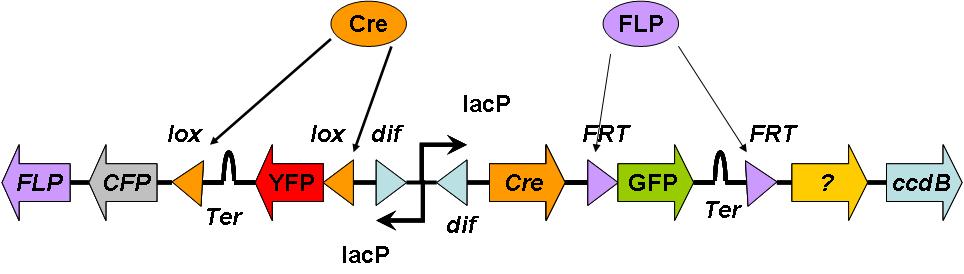
Rather than using the DivisionPoPper directly, this uses the flipping dif sites to activate the different recombination sites and cut out the sections of DNA
Introduction | Applications | Design | Status | References