Glasgow/Plan
From 2007.igem.org
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <center>[[Image:ElectrEcoBlu.jpg]]</center> | + | <center>[[Image:ElectrEcoBlu.jpg|frame]]</center> |
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | [[Image:Phz genes.JPG|500px]]<br> | + | [[Image:Phz genes.JPG|500px|frame|Model of pyocyanin genes.]]<br> |
<br> | <br> | ||
'''Microbial Fuel Cells''' | '''Microbial Fuel Cells''' | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | [[Image:Fuelcell.JPG]] | + | [[Image:Fuelcell.JPG|frame|Structure of a basic fuel cell.]] |
Revision as of 16:23, 8 October 2007
| https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2007/thumb/c/cc/Uog.jpg/50px-Uog.jpg | Back To Glasgow's Main Page |
|---|
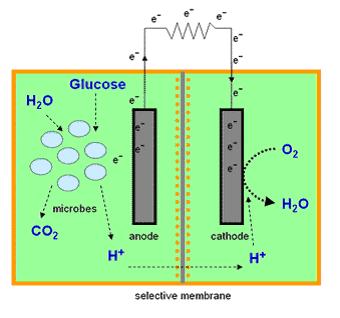
ElectrEcoBlu is microbial fuel cell which produces electricity in the presence of selected pollutants providing a suitable system for in situ and on-line monitoring of contamination remediation.
Environmental Biosensor
On-line and in situ monitoring methods which use electrochemical means to measure gene expression in biosensors are of increasing value in the detection of environmentally relevant pollutants. Whole-cell biosensors are ideal for detection of pollutants groundwater and soil as they can be contained in simple, compact mobile equipment (Paitan et al, 2003) and offer a more time-effective and cost-effective monitoring system then their chemical alternatives (Ron, 2007).
Novel Reporter System
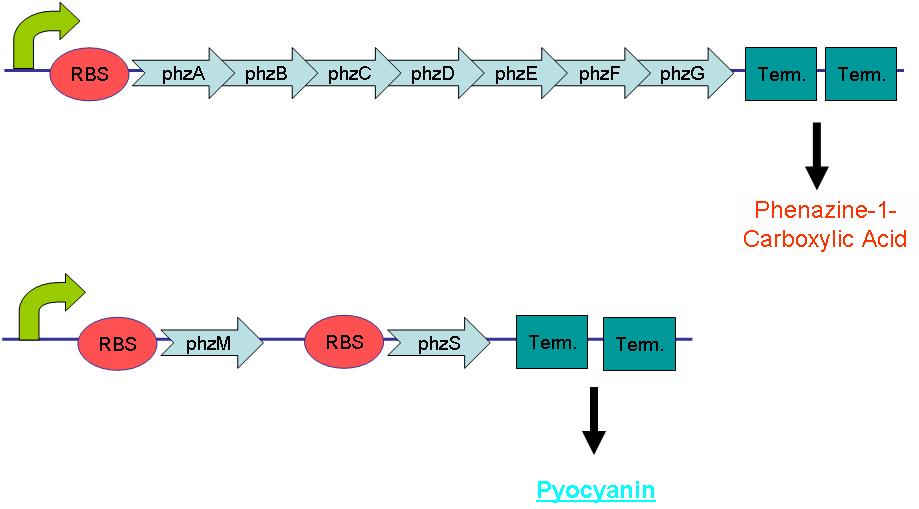
Pyocyanin is the main phenazine compound produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a result of quorum sensing. Pyocyanin engages in oxidation-reduction reactions which deplete cells of NADH, glutathione, and other antioxidants and produces oxidants such as superoxide and peroxides (Parsons, 2006). By using the genes phzM, phzS and the seven gene operon phzABCDEFG which express pyocyanin in P. aeruginosa, we intend to harness the oxidation-reduction potential of pyocyanin to power a microbial fuel cell.
Microbial Fuel Cells