Peking Hop-Count
From 2007.igem.org
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | ==='''Abstract:''' === | |
To meet the need of spatial differentiation in an assembly line, the hop count provides the number of network devices between the starting node and the destination node. We have developed the system of hop-count conjugation for cell-cell communication within a network of Escherichia coli. Here, the signals transferred are represented by DNA sequence, and record the times of transfer by losing tandem region at every conjugation event. To construct this system, tandem oriT pairs (<bbpart>BBa_J01002</bbpart> and more) are inserted into signaling plasmid, and relaxase responsible for initiating conjugation events are removed from natural conjugation system and (attaching a terminator) inserted between these oriT pairs. At each single conjugation event, with the expression relaxase, the corresponding tandem oriT pair is lost with the rolling-cycle replication. Sequential conjugation and deletion of the different oriT pairs can be achieved by fine control of relaxase expression. The resulting tandem signaling conjugation process will allow us to develop networks of bacteria capable of sequentially assembling tasks. | To meet the need of spatial differentiation in an assembly line, the hop count provides the number of network devices between the starting node and the destination node. We have developed the system of hop-count conjugation for cell-cell communication within a network of Escherichia coli. Here, the signals transferred are represented by DNA sequence, and record the times of transfer by losing tandem region at every conjugation event. To construct this system, tandem oriT pairs (<bbpart>BBa_J01002</bbpart> and more) are inserted into signaling plasmid, and relaxase responsible for initiating conjugation events are removed from natural conjugation system and (attaching a terminator) inserted between these oriT pairs. At each single conjugation event, with the expression relaxase, the corresponding tandem oriT pair is lost with the rolling-cycle replication. Sequential conjugation and deletion of the different oriT pairs can be achieved by fine control of relaxase expression. The resulting tandem signaling conjugation process will allow us to develop networks of bacteria capable of sequentially assembling tasks. | ||
| - | + | ==='''Achievement:'''=== | |
[[Image:Peking Pass.JPG|60px]]'''Measure conjugation efficiency of multiple conjugative strains''' | [[Image:Peking Pass.JPG|60px]]'''Measure conjugation efficiency of multiple conjugative strains''' | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | + | ===Design principle=== | |
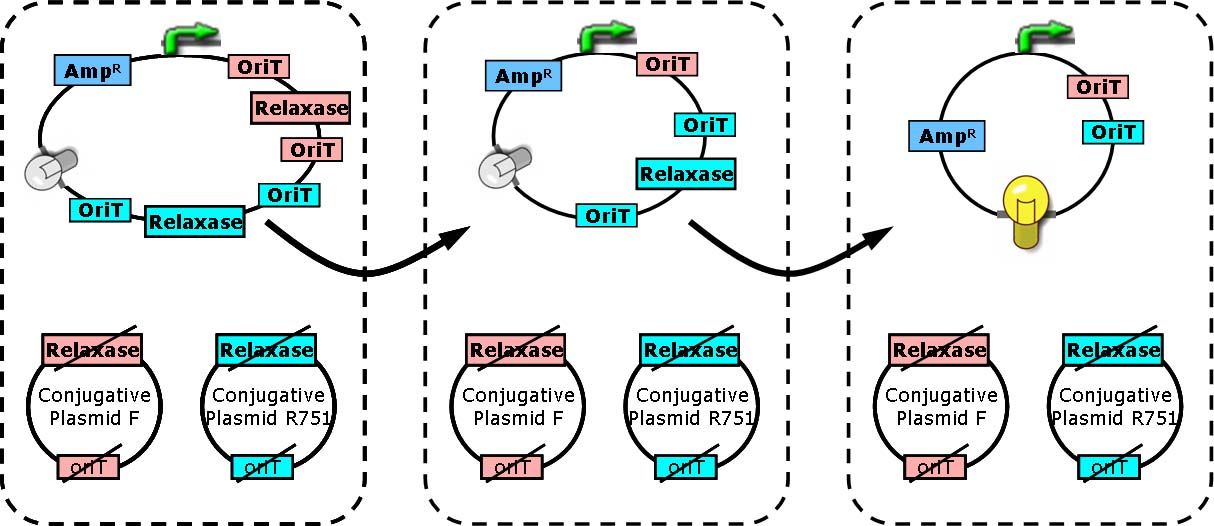
Two key players of bacterial conjugation from donor cells to recipients we concern here are relaxase and oriT (origin of transfer). oriT is responsible for the initiation and termination of roll-cycling DNA replication during conjugation. The transfer of conjugative plasmid from one cell to another, in the form of single strand, starts from one half of oriT and ends at another half, separated by a “nick”. The nick site is generated by relaxosome, and relaxase is a major composition of it. | Two key players of bacterial conjugation from donor cells to recipients we concern here are relaxase and oriT (origin of transfer). oriT is responsible for the initiation and termination of roll-cycling DNA replication during conjugation. The transfer of conjugative plasmid from one cell to another, in the form of single strand, starts from one half of oriT and ends at another half, separated by a “nick”. The nick site is generated by relaxosome, and relaxase is a major composition of it. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
| - | ====Construct signaling plasmid with tandem-oriT pairs | + | ===Measure conjugation efficiency of strain with conjugative plasmid F=== |
| + | {|border=''1'' cellspacing=''1'' | ||
| + | | Donor strain || Signaling plasmid || Conjugation efficiency | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | F-wild-type || one F-oriT || 0.050 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | F-wild-type || a pair of F-oriT || 0.032 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | F-oriT-Knockout || one F-oriT || 0.061 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | F-oriT-Knockout || a pair of F-oriT || 0.037 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Conjugation efficiency: percentage of successful conjugation events to donor cells | ||
| + | |||
| + | Conclusion: | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. The deletion of oriT in wild type conjugative plasmid increases the conjugation efficiency of signaling plasmid by 20%. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. A pair of oriT decreases the conjugation efficiency by 40%. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Construct signaling plasmid with tandem-oriT pairs=== | ||
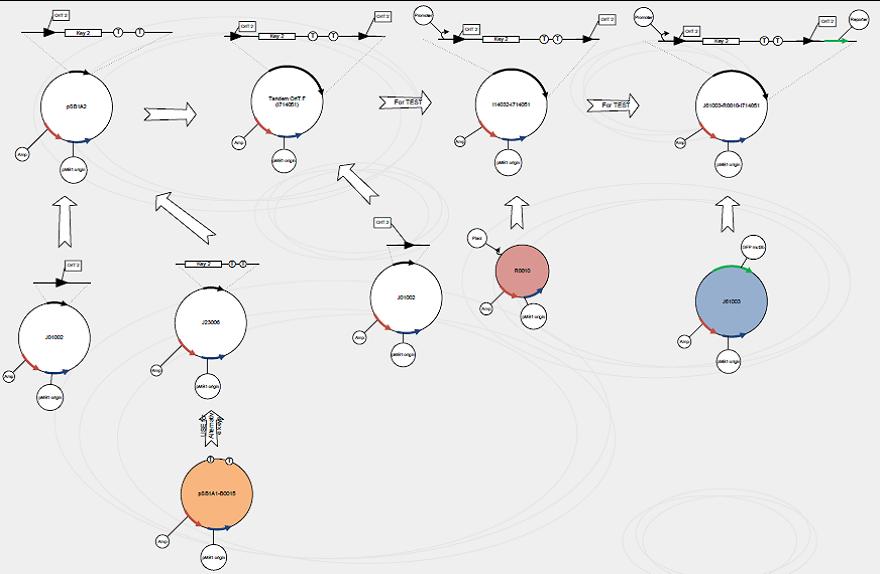
We use standard assembly protocols to construct signaling plasmid. To make sure every achievement is a solid progress to our goal, we designed a product map following industrial principle. | We use standard assembly protocols to construct signaling plasmid. To make sure every achievement is a solid progress to our goal, we designed a product map following industrial principle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Peking_Product_Map.jpg|500px]] | ||
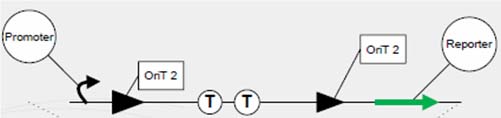
One outstanding achievement is that we have constructed 【brick name】 and tested it with conjugation experiment, getting a positive result with the reporter gene expressed. | One outstanding achievement is that we have constructed 【brick name】 and tested it with conjugation experiment, getting a positive result with the reporter gene expressed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Peking_oriT_pair.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Peking_GFP_both.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
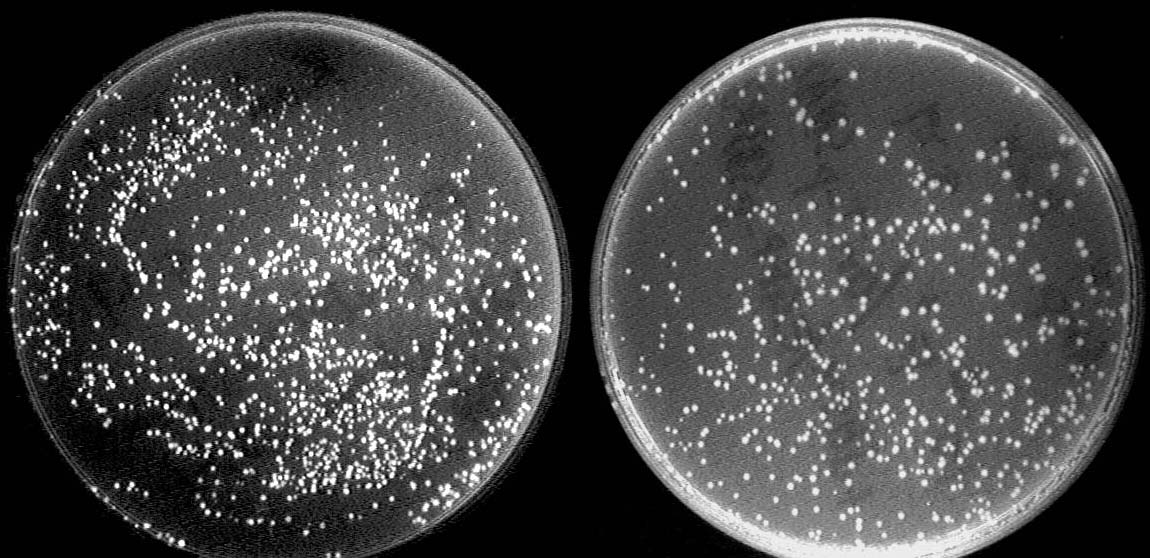
| + | Left: After conjugation with a pair of oriT. The reporter GFP expresses due to the deletion of terminator. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Right: Control strain with no GFP expressed. | ||
Conclusion: | Conclusion: | ||
| Line 36: | Line 67: | ||
2. We successfully implemented and verified conjugation-deletion events with F system (binary hop count). | 2. We successfully implemented and verified conjugation-deletion events with F system (binary hop count). | ||
| - | |||
| - | [ | + | ===Construct conjugative mutant strains with oriT and relaxase deleted=== |
| + | Method 1: pKO3 system | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Use plasmid pKO3 to generate precise deletions of oriT region in conjugative plasmids through homologous recombination. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. For working principle of pKO3 please refer to: Link A. et al., (1997) J Bacteriol 179: 6228. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. For more experimental details please visit [http://www.openwetware.org/wiki/IGEM:Peking/2007/Count:Knockout| Knockout protocol in our OWW site]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Method 2: Lambda Red system | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Use plasmid pKD46 and homologous PCR products to inactivate genes of relaxase in conjugative plasmids. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. For working principle of Lambda Red system please refer to: Datsenko KA et al., (2000). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 6640 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. All experimental details are essentially the same as it is mentioned in the paper above. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Method 3: Reversed cyclic PCR | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Used for in vitro construction of plasmid pSC101, a conjugative plasmid in size of 9 kbp. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. For deletion a region in the plasmid, a pair of primers adjacent to the target region is first design (with the same restriction site), then mixed with plasmid pSC101 for PCR. The resulting product is self-ligated using single enzyme digestion condition and transferred into DH5a. | ||
| - | |||
| + | Achievement: | ||
| - | + | 1. Successfully deleted oriT region in plasmid F and plasmid pSC101 【brick name】. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | 2. Successfully inactivated genes of relaxase in plasmid F, R751 and pSC101 【brick name】. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ===Construct one unified strain containing multiple conjugation systems=== | |
| - | + | To construct one unified strain containing multiple conjugative plasmids (all with relaxase deleted), it is relatively difficult to extract the mutated plasmids from constructed mutants and transform them into one strain, because of the large size of conjugative plasmid (50 – 100 kbp). We propose to transfer all conjugative plasmids into one recipient cell before deleting the oriT region and relaxase. Proper selective markers will be added to conjugative plasmids before transferring. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
====Summary ==== | ====Summary ==== | ||
| - | |||
Revision as of 14:45, 26 October 2007
Abstract:
To meet the need of spatial differentiation in an assembly line, the hop count provides the number of network devices between the starting node and the destination node. We have developed the system of hop-count conjugation for cell-cell communication within a network of Escherichia coli. Here, the signals transferred are represented by DNA sequence, and record the times of transfer by losing tandem region at every conjugation event. To construct this system, tandem oriT pairs (BBa_J01002 and more) are inserted into signaling plasmid, and relaxase responsible for initiating conjugation events are removed from natural conjugation system and (attaching a terminator) inserted between these oriT pairs. At each single conjugation event, with the expression relaxase, the corresponding tandem oriT pair is lost with the rolling-cycle replication. Sequential conjugation and deletion of the different oriT pairs can be achieved by fine control of relaxase expression. The resulting tandem signaling conjugation process will allow us to develop networks of bacteria capable of sequentially assembling tasks.
Achievement:
Measure conjugation efficiency of multiple conjugative strains
Construct conjugative mutant strains with oriT and relaxase deleted
Measure efficiency and specificity of multiple riboregulator pairs
![]() Construct signaling plasmid with tandem-oriT pairs
Construct signaling plasmid with tandem-oriT pairs
![]() Construct one unified strain containing multiple conjugation systems
Construct one unified strain containing multiple conjugation systems
Design principle
Two key players of bacterial conjugation from donor cells to recipients we concern here are relaxase and oriT (origin of transfer). oriT is responsible for the initiation and termination of roll-cycling DNA replication during conjugation. The transfer of conjugative plasmid from one cell to another, in the form of single strand, starts from one half of oriT and ends at another half, separated by a “nick”. The nick site is generated by relaxosome, and relaxase is a major composition of it.
In cells with relaxase deleted, the process of conjugation is not supposed to happen due to the failure of nick site formation. Furthermore, if two oriT instead of one are located on the conjugative plasmid, the process of transferring DNA will start from one oriT and ends at another. Consequently, regions between two oriT without vegetative replication origin will be lost in recipient cells [Draper O et al., (2000). J Bacteriol 182:3191].
Each group of conjugative plasmid has specific relaxase and oriT. Therefore, the sequential conjugation process can be achieved by using one signaling plasmid with multiple sets of oriT pairs and relaxase (and terminators), and multiple conjugative plasmids with their relaxases deleted. All relaxases are controlled by the same promoter. As a result, the next relaxase expresses following the success of the former conjugation. To report the ending of tandem conjugation process, a reporter gene is attached after the last oriT pair, and hence expresses after all conjugation events happened.
Measure conjugation efficiency of strain with conjugative plasmid F
| Donor strain | Signaling plasmid | Conjugation efficiency |
| F-wild-type | one F-oriT | 0.050 |
| F-wild-type | a pair of F-oriT | 0.032 |
| F-oriT-Knockout | one F-oriT | 0.061 |
| F-oriT-Knockout | a pair of F-oriT | 0.037 |
- Conjugation efficiency: percentage of successful conjugation events to donor cells
Conclusion:
1. The deletion of oriT in wild type conjugative plasmid increases the conjugation efficiency of signaling plasmid by 20%.
2. A pair of oriT decreases the conjugation efficiency by 40%.
Construct signaling plasmid with tandem-oriT pairs
We use standard assembly protocols to construct signaling plasmid. To make sure every achievement is a solid progress to our goal, we designed a product map following industrial principle.
One outstanding achievement is that we have constructed 【brick name】 and tested it with conjugation experiment, getting a positive result with the reporter gene expressed.
Left: After conjugation with a pair of oriT. The reporter GFP expresses due to the deletion of terminator.
Right: Control strain with no GFP expressed.
Conclusion:
1. Genes express properly in a signaling plasmid with the oriT pair deleted.
2. We successfully implemented and verified conjugation-deletion events with F system (binary hop count).
Construct conjugative mutant strains with oriT and relaxase deleted
Method 1: pKO3 system
1. Use plasmid pKO3 to generate precise deletions of oriT region in conjugative plasmids through homologous recombination.
2. For working principle of pKO3 please refer to: Link A. et al., (1997) J Bacteriol 179: 6228.
3. For more experimental details please visit [http://www.openwetware.org/wiki/IGEM:Peking/2007/Count:Knockout| Knockout protocol in our OWW site].
Method 2: Lambda Red system
1. Use plasmid pKD46 and homologous PCR products to inactivate genes of relaxase in conjugative plasmids.
2. For working principle of Lambda Red system please refer to: Datsenko KA et al., (2000). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 6640
3. All experimental details are essentially the same as it is mentioned in the paper above.
Method 3: Reversed cyclic PCR
1. Used for in vitro construction of plasmid pSC101, a conjugative plasmid in size of 9 kbp.
2. For deletion a region in the plasmid, a pair of primers adjacent to the target region is first design (with the same restriction site), then mixed with plasmid pSC101 for PCR. The resulting product is self-ligated using single enzyme digestion condition and transferred into DH5a.
Achievement:
1. Successfully deleted oriT region in plasmid F and plasmid pSC101 【brick name】.
2. Successfully inactivated genes of relaxase in plasmid F, R751 and pSC101 【brick name】.
Construct one unified strain containing multiple conjugation systems
To construct one unified strain containing multiple conjugative plasmids (all with relaxase deleted), it is relatively difficult to extract the mutated plasmids from constructed mutants and transform them into one strain, because of the large size of conjugative plasmid (50 – 100 kbp). We propose to transfer all conjugative plasmids into one recipient cell before deleting the oriT region and relaxase. Proper selective markers will be added to conjugative plasmids before transferring.