Anti-Myosin Heavy Chain Targeting and Signaling
From 2007.igem.org
Amendelsohn (Talk | contribs) (→How It works) |
Amendelsohn (Talk | contribs) (→How It works) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
1) Myosin Heavy Chain (MHC) is exposed on infarcted heart tissue. | 1) Myosin Heavy Chain (MHC) is exposed on infarcted heart tissue. | ||
| - | 2) scFv chimeric receptor | + | 2) scFv chimeric receptor targeting MHC, binds to a repeated domain of MHC. |
| + | |||
| + | The scFv chimeric receptor contains a fusion of the following protein domains: anti-MHC-Fc, EporD2, EporTM, and gp130i, dnaEC-VP16. EpoR= erythopoeitin receptor. dnaEC= carboxy domain of the Sp Synechosystis split intein. | ||
3) EporD2 facilitates the dimerization of the chimeric receptors | 3) EporD2 facilitates the dimerization of the chimeric receptors | ||
| - | 4) | + | 4) A mutant version of EporTM inhibits ligand independent dimerization of the chimeric receptors |
5) gp130i becomes activated and JAK's phosphorylate tyrosines on gp130i, including Y759. | 5) gp130i becomes activated and JAK's phosphorylate tyrosines on gp130i, including Y759. | ||
| - | 6) Shp2-mLexA-dnEN binds to phosphorylated Y759 of gp130i | + | 6) Shp2-mLexA-dnEN binds to phosphorylated Y759 of gp130i. (mLexA is a mutated form of E coli DNA binding protein LexA that does not contain a cryptic nuclear localization sequence found in the wild-type). |
| - | 7) Shp2-mLexA-dnEN comes in close proximity to the dnaEC-VP16 fused to the c- | + | 7) Shp2-mLexA-dnEN comes in close proximity to the dnaEC-VP16 fused to the c-terminus of the gp130i |
| - | 8) dnaEN and dnaEC, parts of the split intein system, undergo peptide processing resulting in the release of newly constituted fusion transcription factor mLexA-VP16 | + | 8) dnaEN and dnaEC, parts of the Sp Synechosystis split intein system, undergo peptide processing resulting in the release of newly constituted fusion transcription factor mLexA-VP16. |
9) mLexA-VP16 translocates to the nucleus where it binds to minimal promoters containing lexA operators to switch on expression of cell-cell interaction proteins such as N-Cadherin , anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-XL,p35 and IAP and blood vessel growth factors such as VEGF. | 9) mLexA-VP16 translocates to the nucleus where it binds to minimal promoters containing lexA operators to switch on expression of cell-cell interaction proteins such as N-Cadherin , anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-XL,p35 and IAP and blood vessel growth factors such as VEGF. | ||
[[Image:scfv-circuit.jpg]] | [[Image:scfv-circuit.jpg]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:14, 27 October 2007
How It works
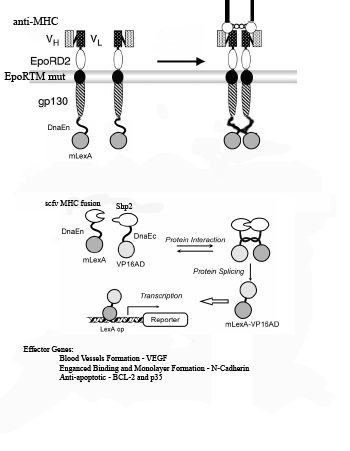
1) Myosin Heavy Chain (MHC) is exposed on infarcted heart tissue.
2) scFv chimeric receptor targeting MHC, binds to a repeated domain of MHC.
The scFv chimeric receptor contains a fusion of the following protein domains: anti-MHC-Fc, EporD2, EporTM, and gp130i, dnaEC-VP16. EpoR= erythopoeitin receptor. dnaEC= carboxy domain of the Sp Synechosystis split intein.
3) EporD2 facilitates the dimerization of the chimeric receptors
4) A mutant version of EporTM inhibits ligand independent dimerization of the chimeric receptors
5) gp130i becomes activated and JAK's phosphorylate tyrosines on gp130i, including Y759.
6) Shp2-mLexA-dnEN binds to phosphorylated Y759 of gp130i. (mLexA is a mutated form of E coli DNA binding protein LexA that does not contain a cryptic nuclear localization sequence found in the wild-type).
7) Shp2-mLexA-dnEN comes in close proximity to the dnaEC-VP16 fused to the c-terminus of the gp130i
8) dnaEN and dnaEC, parts of the Sp Synechosystis split intein system, undergo peptide processing resulting in the release of newly constituted fusion transcription factor mLexA-VP16.
9) mLexA-VP16 translocates to the nucleus where it binds to minimal promoters containing lexA operators to switch on expression of cell-cell interaction proteins such as N-Cadherin , anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-XL,p35 and IAP and blood vessel growth factors such as VEGF.