Mechanism I
From 2007.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:TJU_TEAM2_MIFiguer1.jpg|thumb| | + | [[Image:TJU_TEAM2_MIFiguer1.jpg|thumb|300px|right|'''Figure1 plasmid puc18-ADH1 p+t''']] |
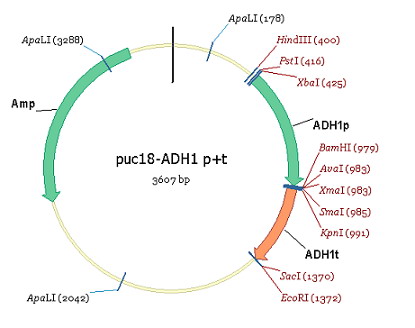
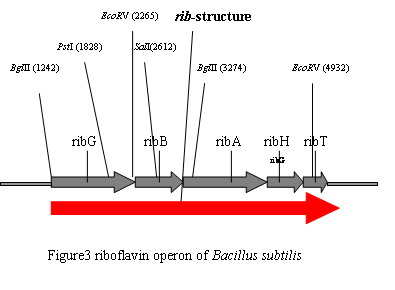
We propose to link the riboflavin operon of Bacillus subtilis to plasmid puc18-ADH1 p+t(figure1). ADH1p(560bp) is a strong promoter of Yeast and ADH1t is the terminater corresponding to this promoter. The initial carrier of puc18-ADH1 p+t is PUC18. The construction of this plamid is: | We propose to link the riboflavin operon of Bacillus subtilis to plasmid puc18-ADH1 p+t(figure1). ADH1p(560bp) is a strong promoter of Yeast and ADH1t is the terminater corresponding to this promoter. The initial carrier of puc18-ADH1 p+t is PUC18. The construction of this plamid is: | ||
#Digest ADH1p with XbaI and BAMHI and link it to the relevant site of PUB18; | #Digest ADH1p with XbaI and BAMHI and link it to the relevant site of PUB18; | ||
Latest revision as of 09:59, 5 August 2007
We propose to link the riboflavin operon of Bacillus subtilis to plasmid puc18-ADH1 p+t(figure1). ADH1p(560bp) is a strong promoter of Yeast and ADH1t is the terminater corresponding to this promoter. The initial carrier of puc18-ADH1 p+t is PUC18. The construction of this plamid is:
- Digest ADH1p with XbaI and BAMHI and link it to the relevant site of PUB18;
- Digest ADH1t with KpnI and SacI and link it to the relevant site of PUC18.
Our main work is :
- Design the primer and amplify the riboflavin operon of bacillus subtilis. The restriction site of up- and down-primer are SmaI(Cfr9I) and KpnI, respectively.
- Digest the PCR product with SmaI(Cfr9I) and KpnI, and then link it to plasmid puc18-ADH1 p+t.
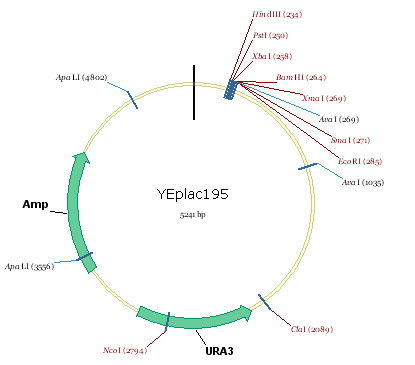
- Digest the linked ADH1p+rib operon+ADH1t(5kb) fragment with XbaI and EcoRI, and link it to plasmid Yeplac195(figure2)
- Trandfer the constructed Yeplac195 into Yeast
- Test the expression of riboflavin operon of Bacillus subtilis in Yeast and the yield of accumulated riboflavin.