From 2007.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| - | <center>[[Davidson Missouri W| <span style="color:red">Home</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Background Information| <span style="color:red">Background Information</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Solving the HPP in vivo| <span style="color:red">Current Project: Solving the Hamiltonian Path Problem ''in vivo''</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Mathematical Modeling| <span style="color:red">Mathematical Modeling</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Gene splitting| <span style="color:black"> Gene Splitting </span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Traveling Salesperson Problem| <span style="color:red">Traveling Salesperson Problem</span> ]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Backwards promotion and read-through transcription| <span style="color:red">Backwards Promotion and Read-Through Transcription</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Resources and Citations|<span style="color:red">Resources and Citations</span>]]</center> | + | <center>[[Davidson Missouri W| <span style="color:black">Home</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Background Information| <span style="color:red">Background Information</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Solving the HPP in vivo| <span style="color:red">Current Project: Solving the Hamiltonian Path Problem ''in vivo''</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Mathematical Modeling| <span style="color:red">Mathematical Modeling</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Gene splitting| <span style="color:red"> Gene Splitting </span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Traveling Salesperson Problem| <span style="color:red">Traveling Salesperson Problem</span> ]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Software|<span style="color:red">Software</span>]] | [[Davidson Missouri W/Resources and Citations|<span style="color:red">Resources and Citations</span>]]</center> |
| | <hr> | | <hr> |
| | | | |
Revision as of 19:34, 10 October 2007
Home | Background Information | Current Project: Solving the Hamiltonian Path Problem in vivo | Mathematical Modeling | Gene Splitting | Traveling Salesperson Problem | Software | Resources and Citations
What is Gene Splitting?
"Gene splitting" refers to the insertion of a hixC site within the coding region of a gene. Although this allows us to create edges for the simulation of a graph, it will change the protein sequence, potentially interfering with proper functionality. We successfully inserted hixC in two different reporter genes, GFP and RFP. Cells transformed with plasmids containing these "split" genes still fluoresce the appropriate color.
To facilitate the splitting process we developed software to help us. Our [http://gcat.davidson.edu/iGEM07/genesplitter.html online] gene splitting web tool helps us choose PCR primers that will amplify the appropriate segments of a gene of interest.
The Genes
| Gene
| Description
| Protein 3D Structure and hixC Insertion Point
|
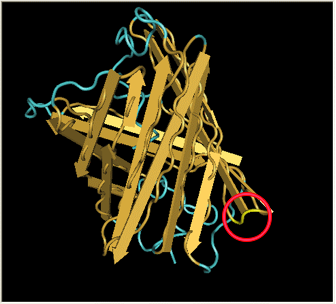
| GFP - Green Fluorescent Protein
| In the spring of 2007, Karen Acker pioneered the gene-splitting process by splitting GFP. According to previous research, it had been shown that it was possible to insert extra amino acids within a particular region of the protein without disrupting green fluorescence. Acker successfully inserted a hixC site at the same location, between amino acids 157 and 158.
| 
|
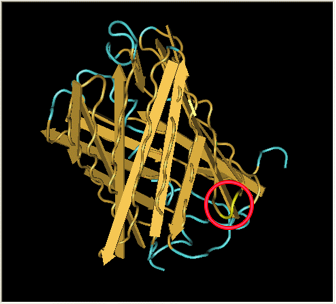
| DsRed - Red Fluorescent Protein
| After Acker demonstrated that GFP fluoresces despite a Hix insertion, we tested the same process on RFP, [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_E1010 RFP] (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=86600 Discosoma sp.]). Although its DNA sequence is markedly different from GFP's, it has some amino acid similarity and a remarkable structural similarity. Both proteins have a Beta-barrel structure which surrounds an internal chromophore.
Fortunately, the similarity between GFP and RFP allowed us to make an educated guess for where to insert. RFP's amino acid position 154 is homologous to GFP's amino acid position 157, which is where GFP was split. This was therefore our best guess for where to insert the hixC site.
RFP was also successfully split. However, the color is much weaker and takes a day at room temperature to become visible by eye.
| 
|

