Waterloo
From 2007.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
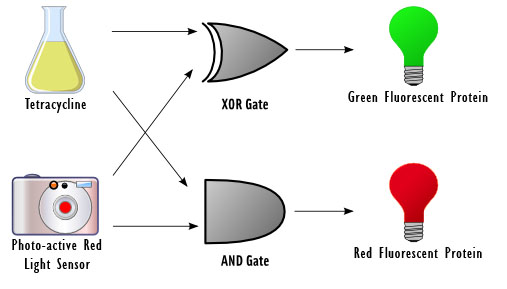
| colspan="2" style="vertical-align:top; border-bottom-width:thin; border-bottom-color:black; border-bottom-style:solid; padding:5px" | The goal of this project is to design a basic device for computing. Our idea was to reproduce a circuit element called a half adder with DNA, which takes in two 1-bit inputs, adds them, and outputs a sum and a carry. Our device responds to two inputs: red light and the chemical tetracycline. The input sensors control a set of genetic switches in order to carry out the computation and fluoresces green and/or red depending on the outcome. | | colspan="2" style="vertical-align:top; border-bottom-width:thin; border-bottom-color:black; border-bottom-style:solid; padding:5px" | The goal of this project is to design a basic device for computing. Our idea was to reproduce a circuit element called a half adder with DNA, which takes in two 1-bit inputs, adds them, and outputs a sum and a carry. Our device responds to two inputs: red light and the chemical tetracycline. The input sensors control a set of genetic switches in order to carry out the computation and fluoresces green and/or red depending on the outcome. | ||
| - | + | Half adders are an essential component in a device called the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), which is the fundamental building block of the central processing unit (CPU) in modern computers. ALUs perform simple and complex operations such as bitwise logical operations (i.e. AND, OR, NOT) and mathematical operations including integer arithmetic. Half adders are also used as building blocks for full adders | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| colspan="2" style="border-bottom-width:thin; border-bottom-color:black; border-bottom-style:solid; padding:5px; vertical-align:middle" | [[Image:Design schematic.jpg|center|400px|Schematic Design of Biological Half-Adder]] | | colspan="2" style="border-bottom-width:thin; border-bottom-color:black; border-bottom-style:solid; padding:5px; vertical-align:middle" | [[Image:Design schematic.jpg|center|400px|Schematic Design of Biological Half-Adder]] | ||
| Line 43: | Line 35: | ||
* Biological half-adder implementation | * Biological half-adder implementation | ||
| style="vertical-align:top; border-right-width:thin; border-right-color:black; border-right-style:solid; padding:5px" | | | style="vertical-align:top; border-right-width:thin; border-right-color:black; border-right-style:solid; padding:5px" | | ||
| - | + | * Predictive models for each scenario in the biological half adder system | |
| style="vertical-align:top; border-right-width:thin; border-right-color:black; border-right-style:solid; padding:5px" | | | style="vertical-align:top; border-right-width:thin; border-right-color:black; border-right-style:solid; padding:5px" | | ||
* Strategy for half-adder construction | * Strategy for half-adder construction | ||
| - | * Testing | + | * Testing constructs for device |
| + | * Test execution plan | ||
| style="vertical-align:top; padding:5px" | | | style="vertical-align:top; padding:5px" | | ||
| - | * | + | * What is a full adder? |
* Gene design for full adder | * Gene design for full adder | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 20:21, 26 October 2007

| Our Project | |||
| Abstract | |||
| The goal of this project is to design a basic device for computing. Our idea was to reproduce a circuit element called a half adder with DNA, which takes in two 1-bit inputs, adds them, and outputs a sum and a carry. Our device responds to two inputs: red light and the chemical tetracycline. The input sensors control a set of genetic switches in order to carry out the computation and fluoresces green and/or red depending on the outcome.
Half adders are an essential component in a device called the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), which is the fundamental building block of the central processing unit (CPU) in modern computers. ALUs perform simple and complex operations such as bitwise logical operations (i.e. AND, OR, NOT) and mathematical operations including integer arithmetic. Half adders are also used as building blocks for full adders | |||
| Project Design | Mathematical Modelling | Construction and Testing | Future Work |
|
|
|
|