Chiba/Engeneering Flagella
From 2007.igem.org
(→References) |
(→Procedure) |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
**no plasmid | **no plasmid | ||
| - | ====Procedure==== | + | ====Testing Procedure==== |
#pUC19-FliC-His was transformed to JW1908(''fliC'') and GI826(''fliC'' ''motB''). | #pUC19-FliC-His was transformed to JW1908(''fliC'') and GI826(''fliC'' ''motB''). | ||
| - | # | + | #Grown to stationary phase |
| - | #Culture | + | #Culture suspended with Dynabeads (Metal-IDA), allowing to the affinity adsorption |
| - | # | + | #Beads washed with a phosphate buffer (x4) |
| - | #The | + | #E" coli" detached from beads by adding imidazole then spreaded on agar plates. |
| + | #The number of the colonies on resultant plates. | ||
====Results&Discussion==== | ====Results&Discussion==== | ||
Revision as of 01:47, 27 October 2007
|
Introduction | Project Design ( 1.Sticky Hands | 2.Communication | 3.Size Control ) | Making Marimos | Our Goal || Team Members | メンバ連絡簿 |
Stickey Tags
Our Aim
To make stickey hands on E.coli, we focused on their flagella that are located outside the cells. We used the following mechanisms:
- Display sticky peptides in flagellar filament.
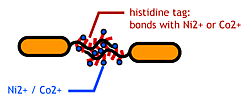
- His-tag. The imidazole group in histidines make a complex with metal ions.
We combined these two and made a His-tagged flagella in the hope to stick them together via metal ions.
About flagella
E.Coli have 5-10 flagella. The flagella is used for swimming and for chemotaxis; the bacteria run when they find attractant, tumble when there is a repellent.
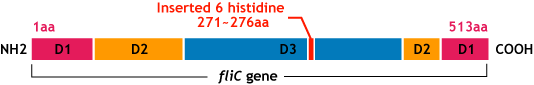
E.coli flagella consist of three parts: a basal body, a hook, and a filament. The filament of E.Coli is a rigid, helical, and cylindrical structure which is 10-15μm long and 23nm thick in diameter. It is built from ~20000 subunits of a ~55kDa single protein, FliC. FliC has three domains, D1,D2,D3; although D1 and D2 are needed for the formation of the functional flagellar filament, D3 domain which sticks outside of the fillament are not essential[1].
"Variable" FliC D3 domain
It is reported that the proteins up to 49.4kDa could be displayed on the cell surface of E.Coli using flagellin fusion protein.[2]
References
- Kuwajima, G. et al.: J. Mol. Bacteriol., 170, 3305-3309 (1988).
- Ezaki, S. et. al.: J. Ferment. Bioeng., 86, 500-503 (1998)
About Histidine Tag
See [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/His-tag wikipedia article].
Experiments
Making FliC-his gene
- We inserted the short peptide with six histidine (“His-Tag”) into the fliC D3 domain.
Checking the "Stickiness": Beads Adsorption
Purpose
Confirm that the his-tags are displaied on the flagella and are capable of binding to Co2+- or Ni2+- surface.
Samples
- JW1908(⊿fliC strain) transformed with
- pUC19-fliC-his
- no plasmid
- GI826(⊿fliC⊿motB strain) transformed with
- pUC19-fliC-his
- no plasmid
Testing Procedure
- pUC19-FliC-His was transformed to JW1908(fliC) and GI826(fliC motB).
- Grown to stationary phase
- Culture suspended with Dynabeads (Metal-IDA), allowing to the affinity adsorption
- Beads washed with a phosphate buffer (x4)
- E" coli" detached from beads by adding imidazole then spreaded on agar plates.
- The number of the colonies on resultant plates.
Results&Discussion
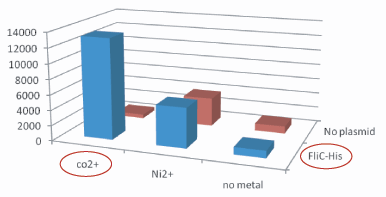
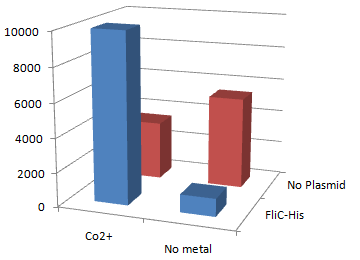
1.Stickiness check
- In the presence of Co2+Histidine tag,beads
Co2+Histidine Tagの存在よって大腸菌がビーズに吸着している.
- Ni2+よりもCo2+のほうがfliC-his存在下でより吸着している.
- Ni2+よりもCo2+のほうがfliC-hisの有無で吸着の差が大きい
- The number of colony dramatically decreased with out Co2+ or FliC-His plasmid.
2.Strainの比較
- この実験結果から言えることは何ですか?それと、上の実験結果との比較は?byとよたろ