Melbourne/Blue Photosensor Background
From 2007.igem.org
<return to top of background> <return to home page>
The background to the design of the blue photosensor is included here. Specifically the design for the chimeric fusion protein that will be the key link in blue light pathway
Contents |
Preliminaries
Restriction Site Analysis - [http://tools.neb.com/NEBcutter2/index.php| NEB cutter]
Sequence Translation - [http://au.expasy.org/tools/dna.html| Translate]
Sequence Aligment - [http://www.jalview.org/download.html| JalView] These were done via known domain databases from GenBank, with a ClustalW Realignment option in the Web Services menu of JalView
- Clustal Color Scheme
- Hydrophobicity Color Scheme
- Helix Propensity Color Scheme
- Turn Propensity Color Scheme
PCR primer design - [http://www.premierbiosoft.com/netprimer/netprlaunch/netprlaunch.html| NetPrimer]
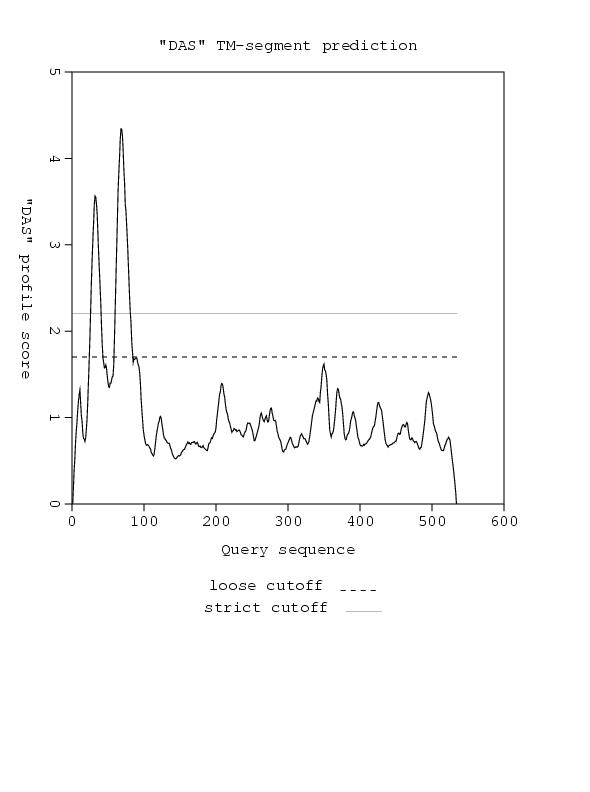
Transmembrane Prediction - [http://www.sbc.su.se/~miklos/DAS/| DAS Transmembrane Prediction]
JalView File of Seq. Alignments - doesn't work ATM
Sequences and Restriction Sites
SopII
sensory rhodopsin II
DNA, AA, [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&cmd=search&term=sopII genbank]
- No IGEM restriction sites
- HaeII (@168) present
HtrII
sensory rhodopsin II transducer
DNA, AA, [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=3702851&ordinalpos=1&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Gene.Gene_ResultsPanel.Gene_RVDocSum genbank]
- No IGEM restriction sites
- No useful restriction site
SopII/HtrII fusion
DNA, AA (frame 2 in Translate - only SopII + HtrII + Linker included in link), linker = TSASA SNGASA,
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&cmd=search&term=sopII genbank]
- No IGEM restriction sites
- Use site from SopII (this is the one that will be used)
ComP
two-component sensor histidine kinase
DNA (includes IGEM forward and reverse primers (VF2 + VR) and IGEM prefix and suffix, AA, [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&cmd=search&term=sopII genbank]
SpeI (@927) deleted HaeII (@1902) inserted
ComA
sensory rhodopsin II transducer
DNA, AA, [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&cmd=search&term=sopII genbank]
SpeI (@12) deleted HaeII (@433) inserted
Chimera Design
Overview
Refer to 4 PCR primer method here, 2001 paper get picture
SopII Analysis
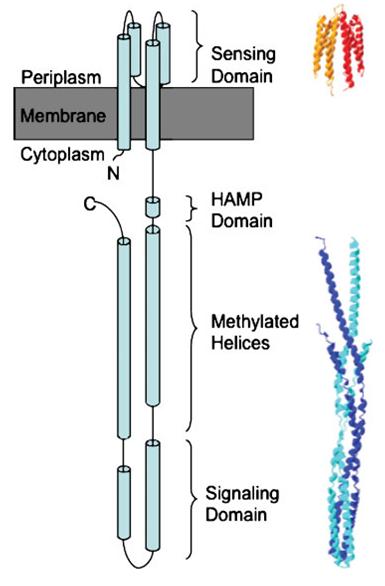
transmembrane photoreceptor, requires all-trans retinal as substrate... linked to HtrII insert TM analysis here. reference the three papers cited in background
This shows consistent TM helicies throughout the whole sequence
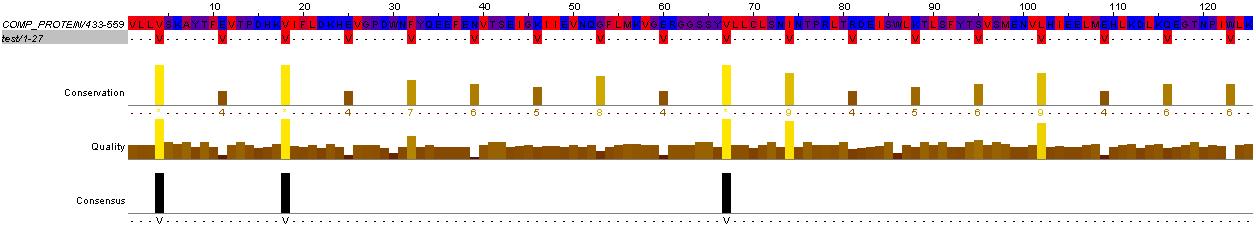
HtrII Analysis
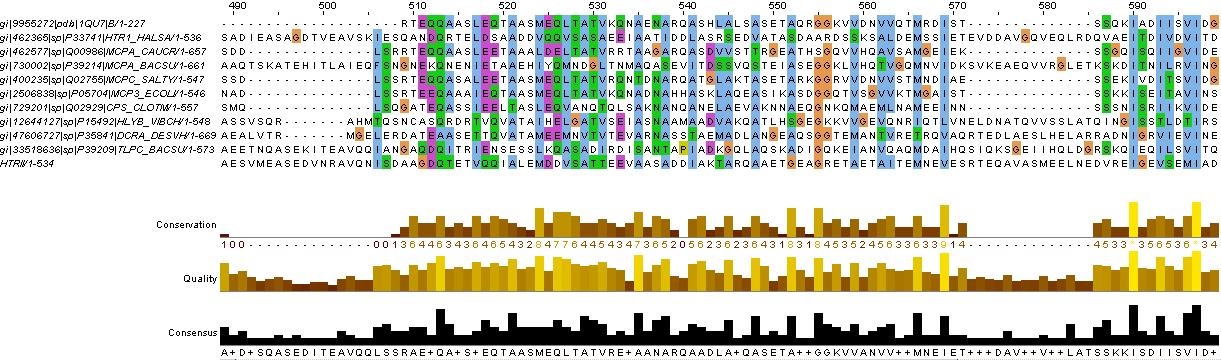
Methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins (MCP) are hypothesized to be modular in structure (ref needed). This modularity and homology between most MCPs is evidence by the clear separation of HAMP domains from methyl-accepting helical domains and the sensor kinases. Below is shown evidence for this in HtrII.
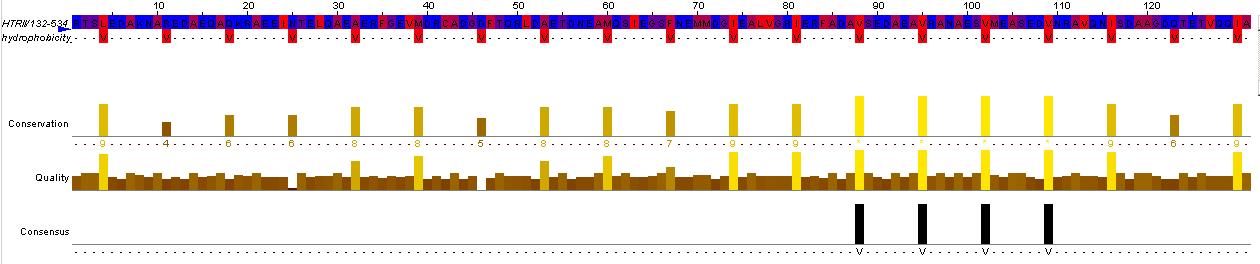
This hisitidine kinase also has a clear TM region, from residues 0-80
Genbank mentions the HAMP domain (Histidine kinases, Adenylyl cyclases, Methyl binding proteins, Phosphatases)
This is the key to the propagation of the excitation signal according to (ref needed)
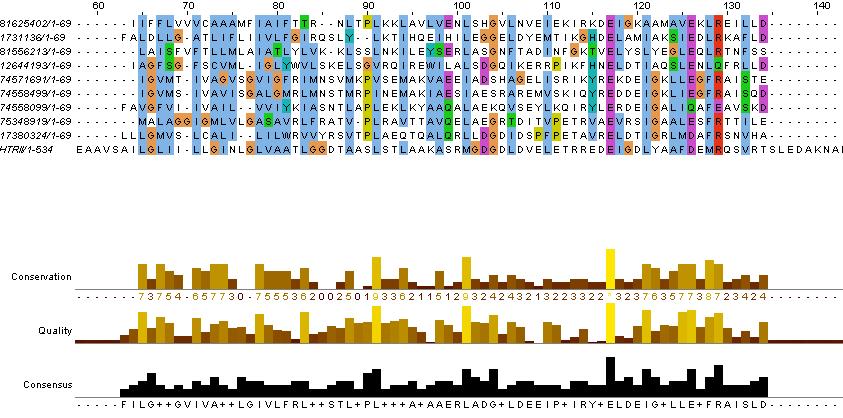
Evidence for the HAMP domain is contained in the following sequence alignment with known HAMP domains from GenBank
evidence for HAMP domain. Alignment suggest homogoly from residue 65 to 134. This conforms with the GenBank analysis shown belown
evidence for methyl-accepting chemo-taxis like domain (these are the likely helices (hydrophobic residue every 7 AA, after the HAMP domain)
The above clearly suggest that HtrII follows the modular structure. The helical domains are evidence by the hydrophobic (blue) residues, that occur every 7-8 residues. This begins at residues 210 in the sequence (EVMDR), which is simliar to the GenBank Analysis
This is further shown by looking at the hydrophicity traces below. Although the consistency of the 7-8 repeat of hydrophobic residue depends on helix turn propensity
- GenBank Analysis
COG5000 Location:99–249 Blast Score:90 NtrY; Signal transduction histidine kinase involved in nitrogen fixation and metabolism regulation [Signal transduction mechanisms]
smart00283 Location:239–446 Blast Score:277 MA; Methyl-accepting chemotaxis-like domains (chemotaxis sensory transducer). Thought to undergo reversible methylation in response to attractants or repellants during bacterial chemotaxis.
pfam00672 Location:99–133 Blast Score:85 HAMP; HAMP domain.
imply that the design with tsr worked as this was also a MCP (probably don't need to give evidence for this)
evidence for the kinase
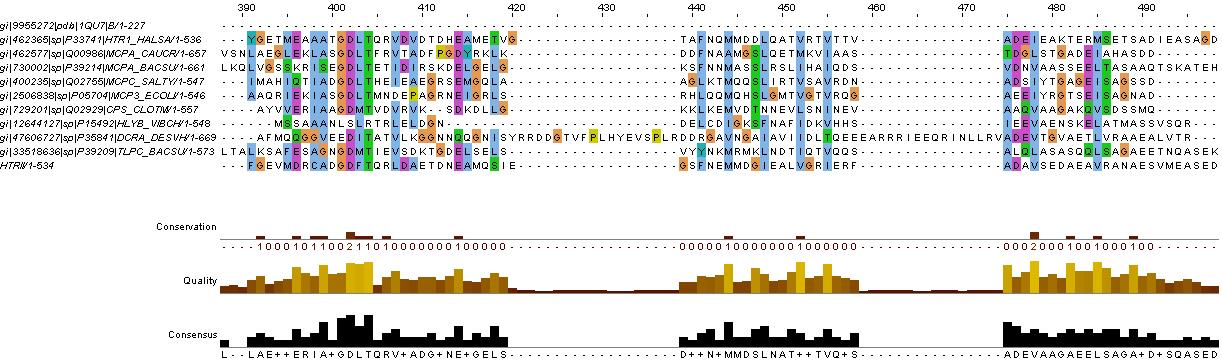
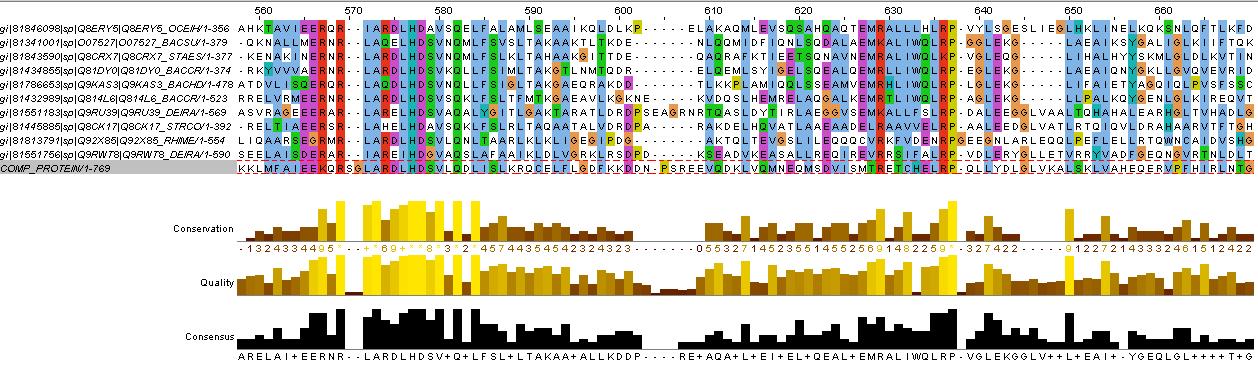
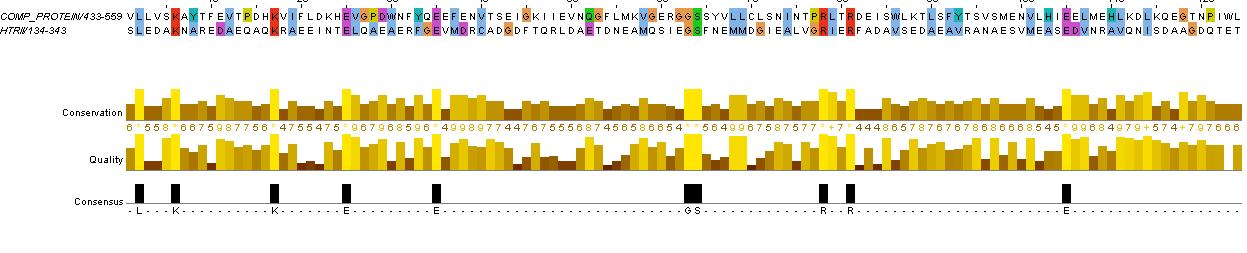
ComP Analysis
evidence for HAMP domain
 same alignment as for HtrII above, it is likely that the gaps are loops. We will account for this in the fusion variants.
same alignment as for HtrII above, it is likely that the gaps are loops. We will account for this in the fusion variants.
evidence for kinase
confers with GenBank analysis below
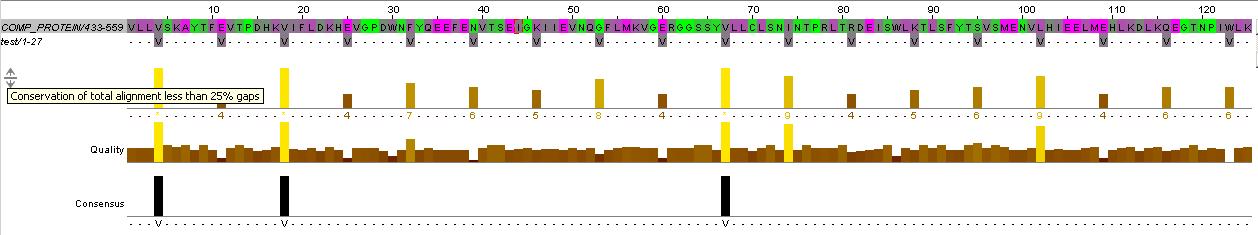
evidence for methylated (or accepting) helices...
analysis based on region between HAMP domain and kinase (between residues KNTILD| and |MFAEIK)
also refer to direct aligment between comP and HtrII helical regions
GenBank Analysis
cd00075
Location:681–767
Blast Score:129
HATPase_c; Histidine kinase-like ATPases; This family includes several ATP-binding proteins for example: histidine kinase, DNA gyrase B, topoisomerases, heat shock protein HSP90, phytochrome-like ATPases and DNA mismatch repair proteins
pfam07730
Location:568–638
Blast Score:138
HisKA_3; Histidine kinase. This is the dimerisation and phosphoacceptor domain of a sub-family of histidine kinases. It shares sequence similarity with pfam00512 and pfam07536.
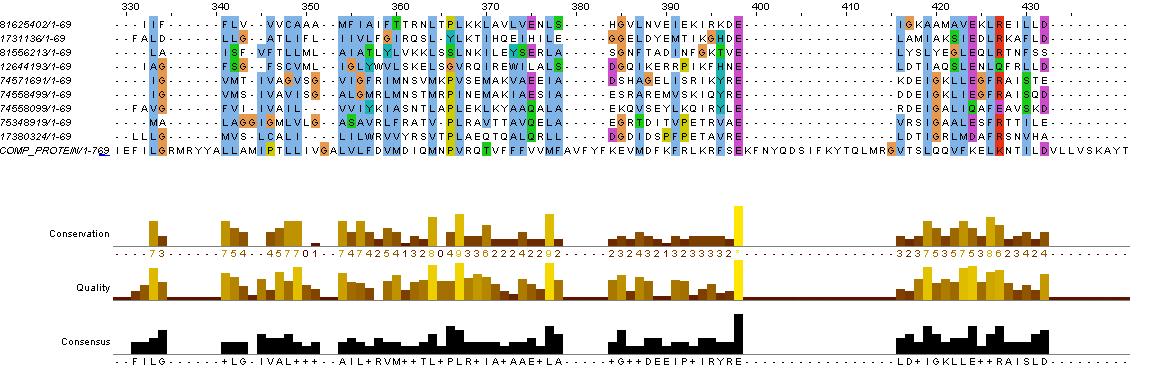
Chosen Fusion Sites
from the paper we chose the were roughly at the start, middle, end of the HAMP domain ...
File:Seq align.jpg Media:Example.ogg