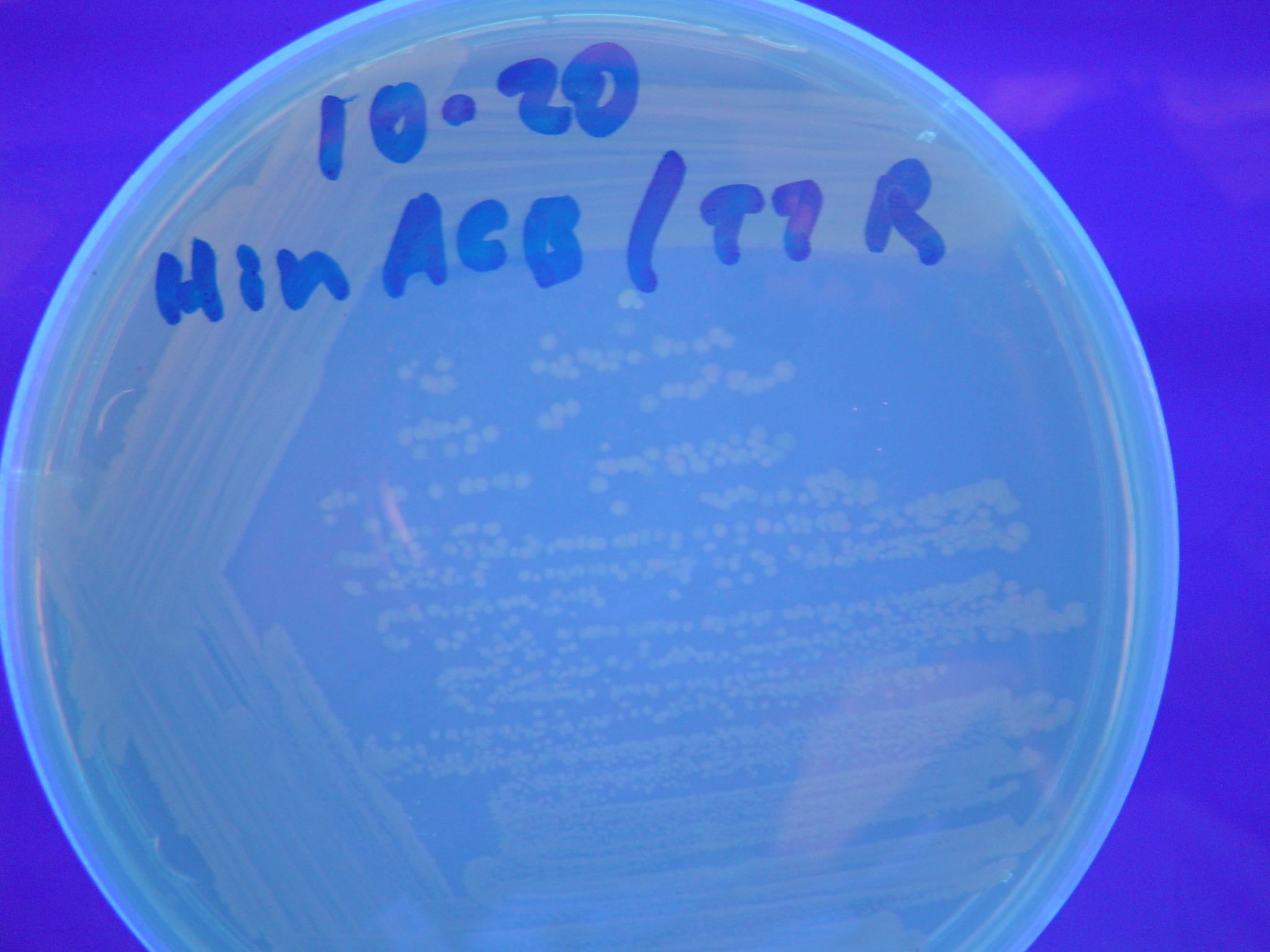Davidson Missouri W/Results2
From 2007.igem.org
Contents |
Gene Splitting
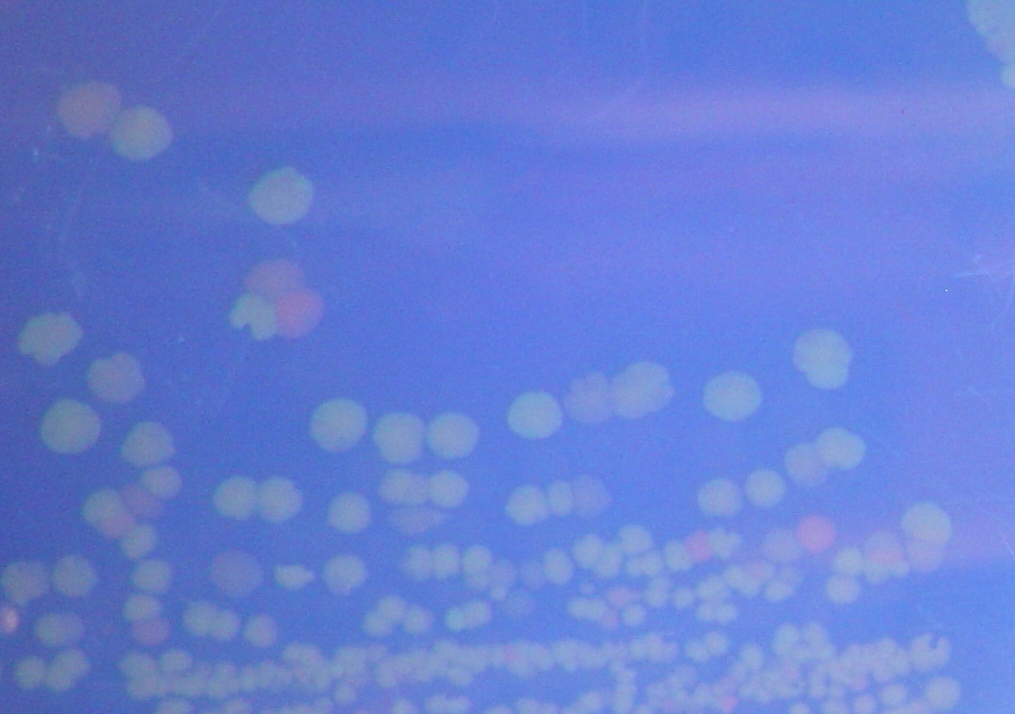
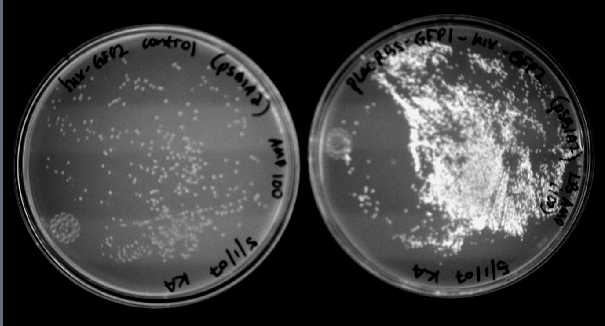
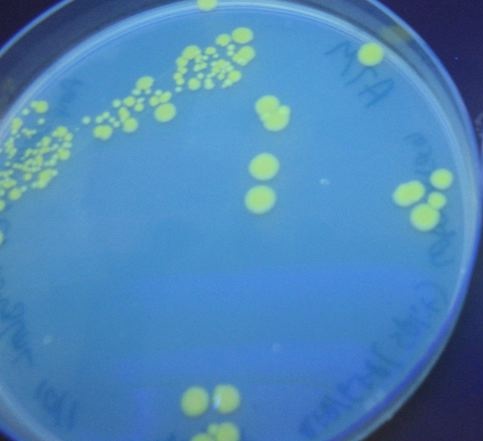
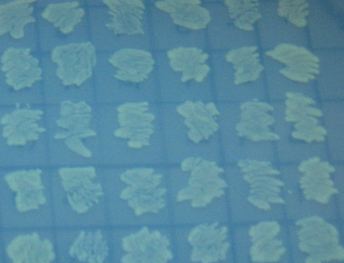
We were able to split two genes: GFP and RFP. Split GFP has strong green fluorescence. Split RFP's red color is much reduced compared to wild-type RFP. It takes overnight incubation at room temperature for the red color to be visible in white light. Both colors are fluorescent under UV light, although the green color predominates. In Figure 1 below, a negative-control (on the left) does not fluoresce, but split GFP (on the right) does. Figure 2 shows a plate of cells containing split RFP.
Graphs
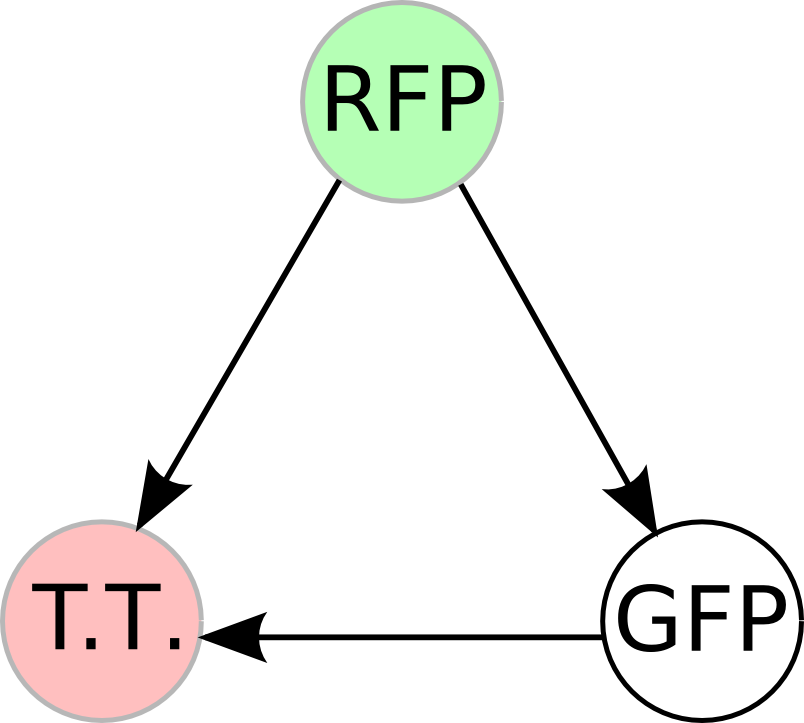
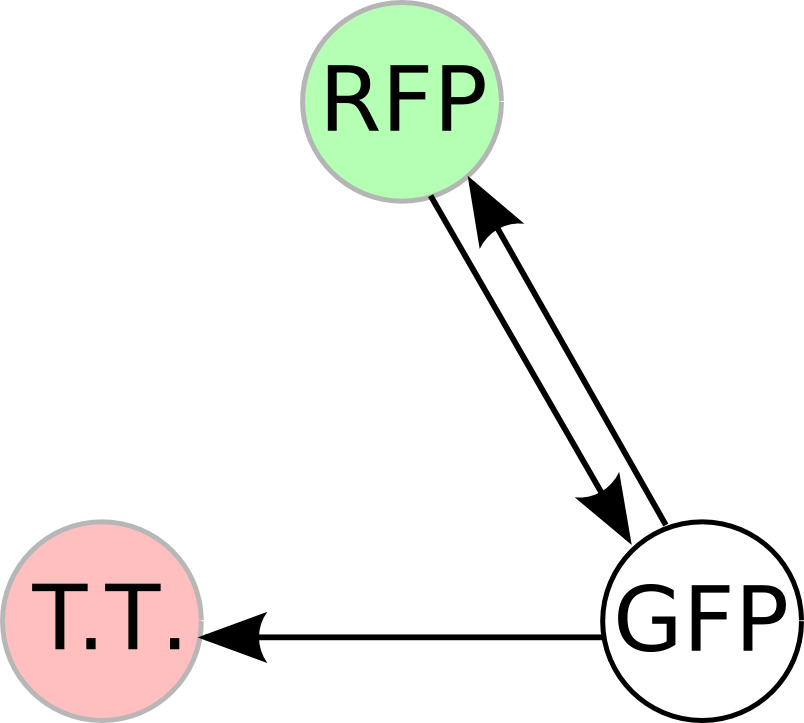
Once we managed to split two genes, we proceeded to implement two different 3-node graphs into plasmids. These graphs were named Graphs A and B and are shown below. For each graph, we wanted to find a Hamiltonian Path from the node represented by RFP (colored in green) to the node represented by the transcriptional terminator (colored in red). The plasmid representation of Graph A is not be capable of flipping into a false positive orientation, while the plasmid representation of Graph B does provide that possibility.
Because solved colonies would be selected for by double fluorescence (both red and green), we first performed control experiments to ensure that we could distinguish solved and unsolved colonies. To test fluorescence phenotypes when both split GFP and split RFP are the same cell, we constructed a positive control plasmid ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I715045 BBa_I715045]) with split RFP and split GFP both downstream of the T7 polymerase promoter. In the presence of T7 polymerase, cells with the split RFP/GFP plasmid should demonstrate both green and red fluorescence.
We first tried cotransforming our split RFP/GFP plasmid with a T7 RNA polymerase plasmid ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I715038 BBa_I715038]). As can be seen in Figure 3 below, this cotransformation resulted in bright green colonies that demonstrated minimal red fluorescence.
We then tried transforming RFP/GFP control plasmids into cells that already contained T7 polymerase in their chromosome (T7 RNAP cells). As can be seen in Figure 4 below, these colonies displayed the yellowish color we expected. Based on our fluorescence data, (shown [below]), we were able to show that GFP and RFP were present at detectable levels in our T7 RNAP control. When we tested the fluorescence of the cotransformed control, RFP was not present at detectable levels. We hypothesize that this difference is due to higher concentrations of T7 RNA polymerase in the T7 RNAP cells than in the cotransformants.
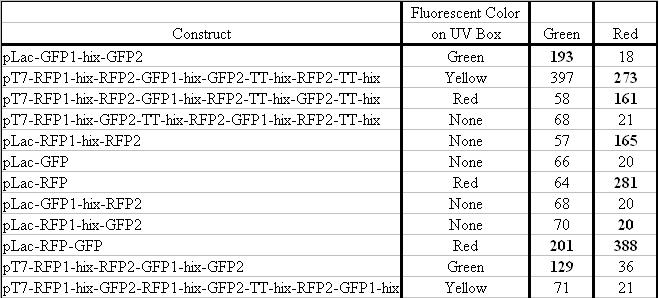
In addition to the regular split GFP and split RFP constructs, we also wanted to test some "hybrid" constructs to ensure that they would not fluoresce. GFP and RFP have similar structures and functions. Previous studies have shown that it is possible to modify GFP to display a wide range of color phenotypes. We created the following parts: Plac-RBS-RFP1-hixC-GFP2 ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I715036 BBa_I715036]) and Plac-RBS-GFP1-hixC-RFP2 ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I715035 BBa_I715035]). A plasmid may, at some point during its flipping process, contain such sequences. We tested to make sure that the similarity of these two proteins did not make them compatible enough to fluoresce. It was found that neither of these parts show any fluorescence or color change.
Constructs
Once we managed to split two genes, we proceeded to implement two different graphs in plasmids.
We built the following constructs:
Part Flipping and Computation
Co-transformation of the unsolved HPP plasmids with the Hin vector begins flipping and computation. Subsequent co-transformation with the T7 RNA polymerase vector then initiates transcription.
We have found that all colonies with the HPP plasmids showed unexpected green color. The green is distinguishable by eye or fluorometer from GFP's color. As a control, we showed that the T7 RNA polymerase vector does not create the green color, so we are confident that the HPP vectors are responsible.
One possibility we had tested was that hybrid parts, such as RFP1-hixC-GFP2 and GFP1-hixC-RFP2 produced functional fluorescent proteins. However, we created these parts and tested them, and found that there was no fluorescence when the pLac promoter was upstream (parts [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I715035 BBa_I715035] and [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I715036 BBa_I715036]).
Another possibility is that these hybrid proteins cannot fluoresce independently, but will emit color when in tetramers. Wild-type GFP and RFP are tetrameric, but the registry versions of the parts, [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_E0040 BBa_E0040] and [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_E1010 BBa_E1010] are monomeric mutants. It would be possible to test this hypothesis by running purified protein on a non-denaturing gel.
Flipping Detection by Phenotype
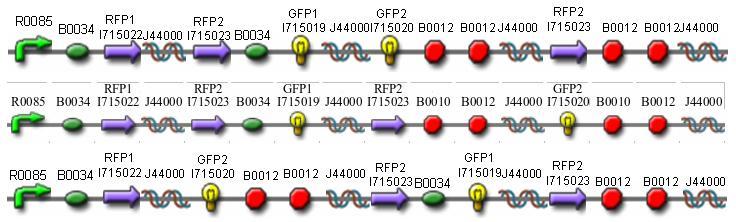
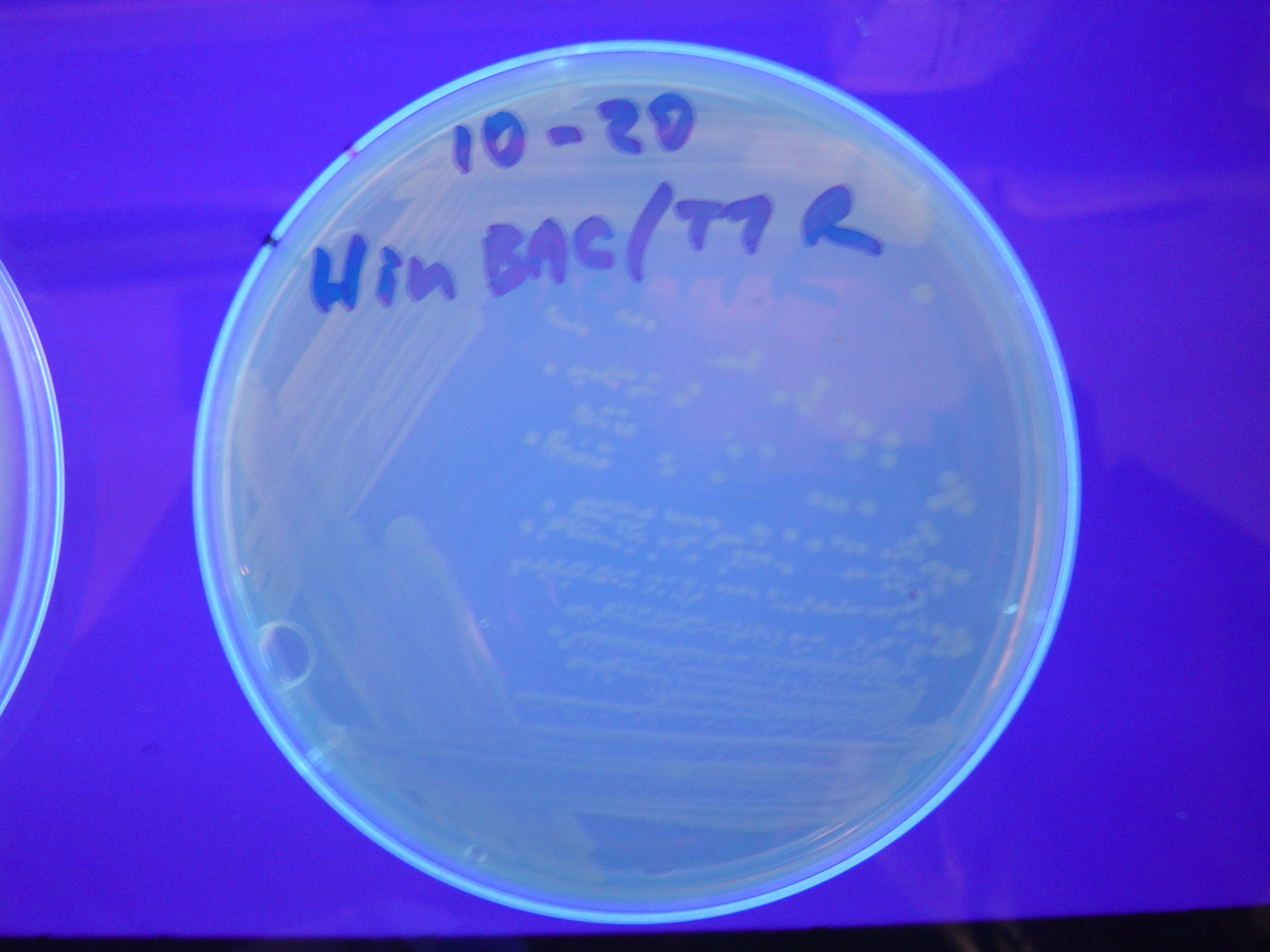
To test for flipping by phenotype, we built 3 constructs, each representing a different starting orientation for Graph A. They were labeled HPP-A0, HPP-A1, HPP-A2, with HPP-A0 already in the solved orientation, HPP-A1 demonstrating only red fluorescence initially, and HPP-A2 demonstrating no initial fluorescence (See Figure 5 below).
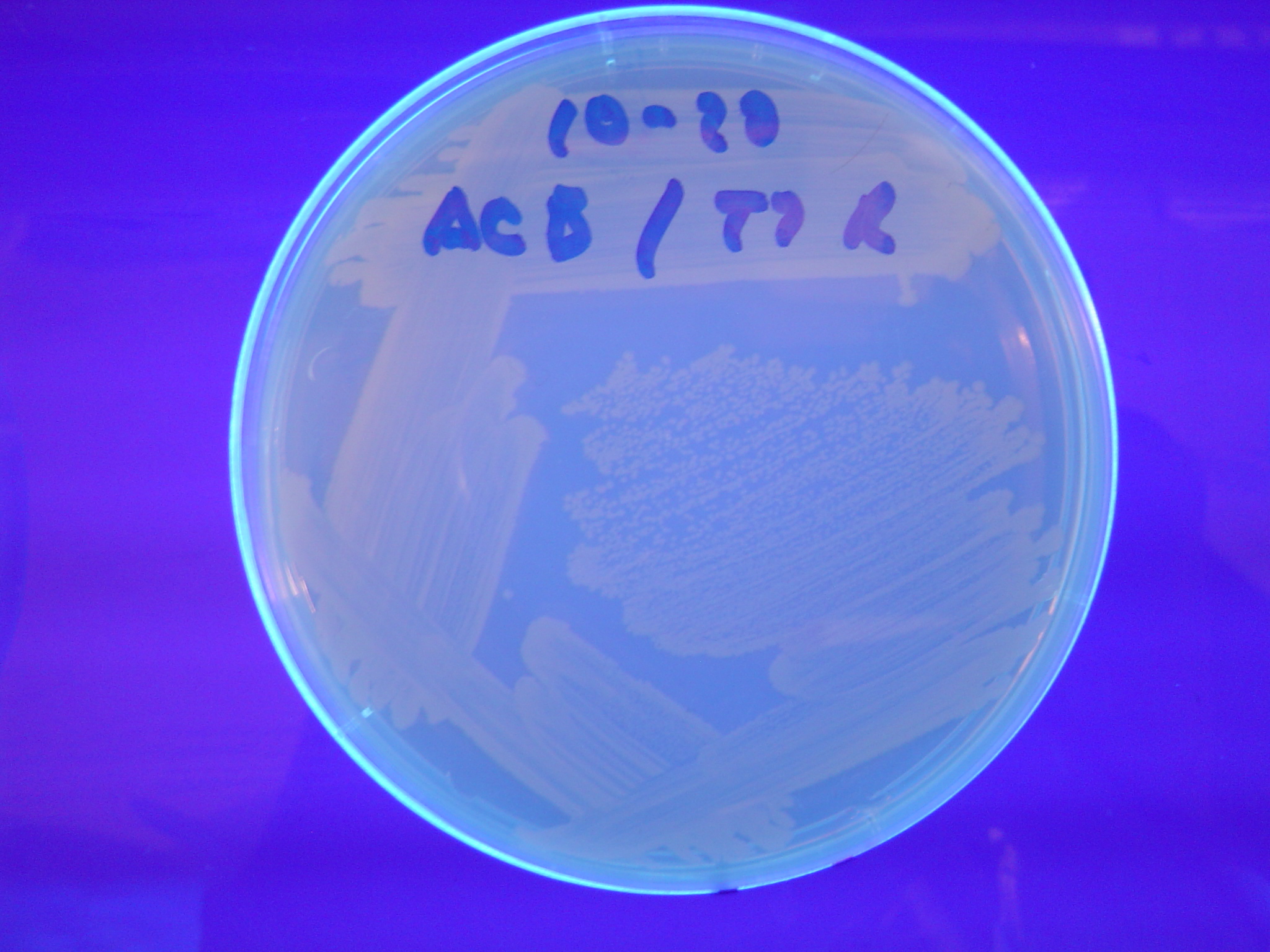
Each of the 3 constructs, HPP-A0, HPP-A1, and HPP-A2, were transformed into E. coli cells expressing T7 RNAP. As expected, the colonies containing HPP-A0 fluoresced yellow (red + green), the HPP-A1 colonies fluoresced red, and the HPP-A2 colonies did not fluoresce. (See Figures 7-9 below).
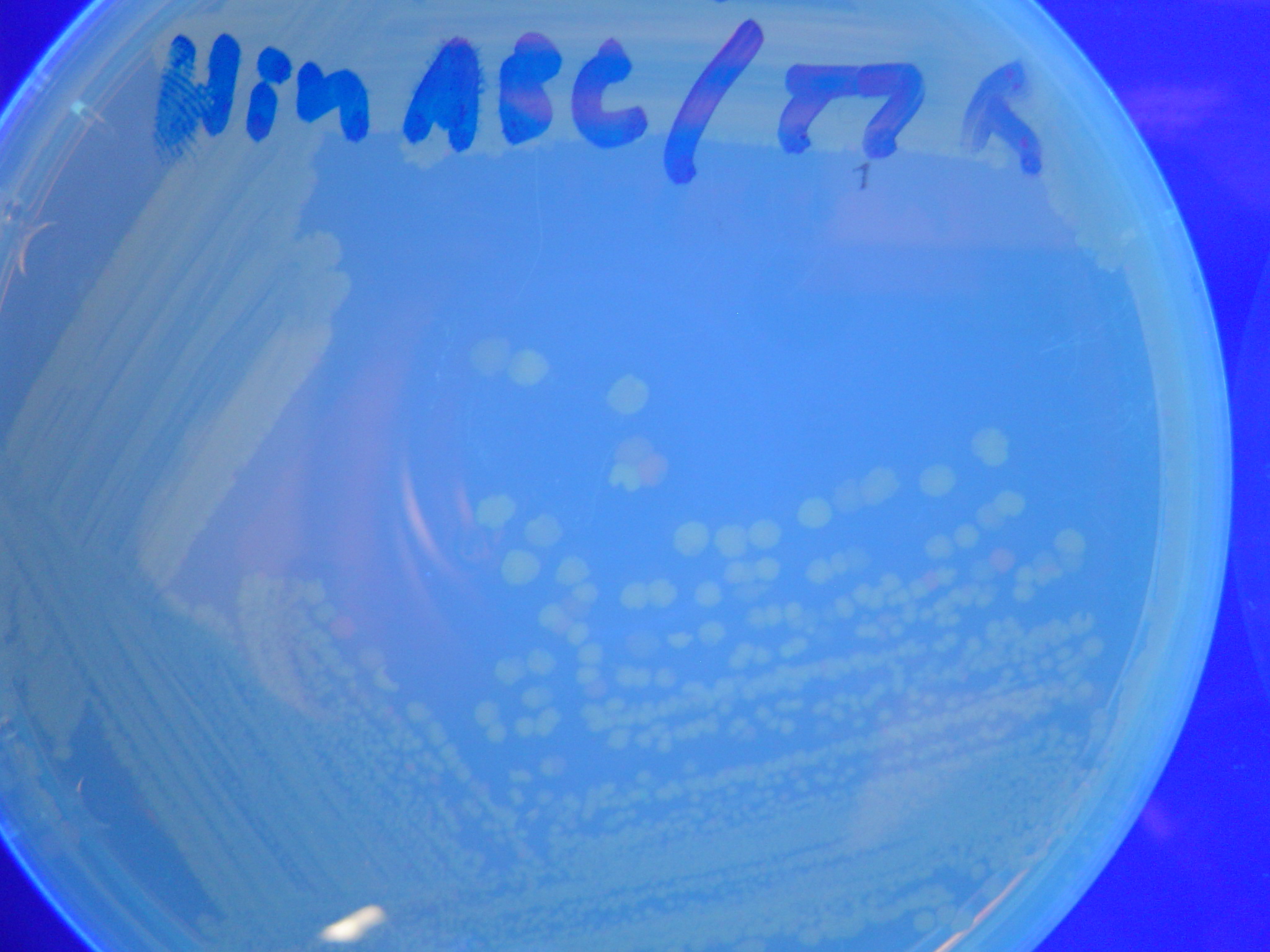
A fragment containing the Hin expression cassette (pLac-RBS-Hin-LVA, [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_S03536 BBa_S03536]) was ligated in front of each of the 3 HPP-A constructs. These HPP-A + Hin plasmids were then transformed into T7 RNAP cells. A colony from each transformation was picked and grown overnight for plasmid mini-prep. Each of the 3 constructs was restriction digested and the insert sizes were verified to be correct. The 3 constructs were then retransformed into T7 RNAP cells, and the resulting transformation mixture was streaked for colony isolation. The HPP-A0 + Hin plate contained mostly yellow colonies but also red and green (See Figures 10 and 13). The Hin HPP-A1 + Hin plate contained red, green and yellow colonies (See Figures 11 and 14). The HPP-A2 + Hin plate contained mostly nonfluorescent colonies with a few green and red colonies (See Figures 12 and 15).
Click twice on the images below for higher resolution.
Flipping Detection by PCR
In order to provide physical evidence of Hin-mediated DNA rearrangement, we designed PCR primers that would allow us to determine the position of one of the GFP2 gene half. The experiment below shows the results of PCR using the universal primer G00101, which binds to vector sequence 3' to the biobrick suffix, and primer GFP2-forward.
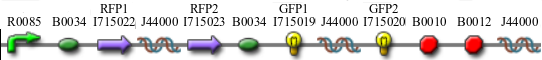
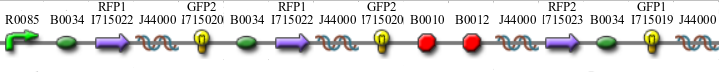
Here is how the primers bind to the 3 HPP-A constructs:
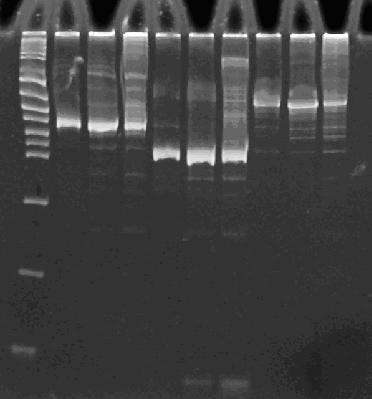
Lane 1 : MW marker (50, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 750, 1000 bp), Lanes 2-4 : HPP-A0 with 14, 16, and 18 cycles, Lanes 5-7 : HPP-A1 with 14, 16, and 18 cycles, Lanes 8-10 : HPP-A2 with 14, 16, and 18 cycles
![]()
Dectection of Fluoresence by Spectroscopy
We used a fluorescent spectrometer to measure the fluorescence of wild type GFP, wild type GFP, the versions of these two split by hix sites, and new combinations of the GFP and RFP gene halves. We were able to detect fluorescence in bacterial cells by simply mixing the cells with 200 ul of water and measuring in a microtiter plate.
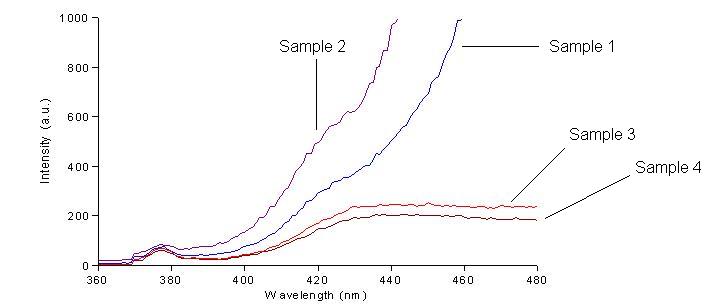
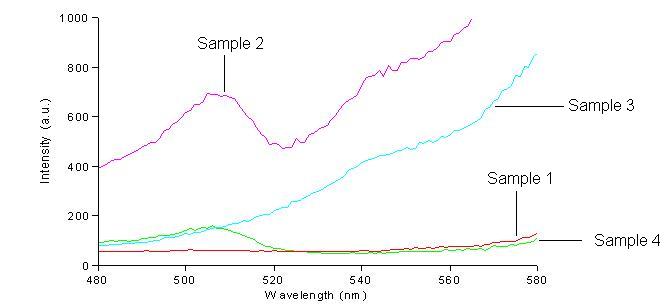
We first had to determine the excitation and emission wavelengths that would allow us to detect the green and red fluorescence. Scans were conducted in order to find these wavelengths. For example, the graphs below shows scans of excitation wavelengths that produce fluorescence at an emission wavelength of 515 nm, the wavelength we found to be best for green, and 608 nm, the best wavelength for red.
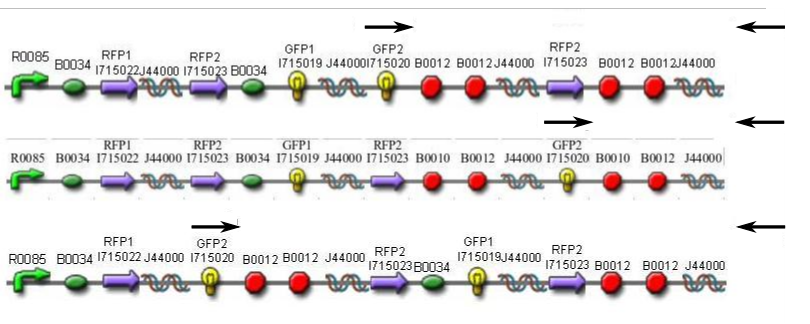
Sample 1 = pLac GFP1-hix-GFP2, glows green on UV box
Sample 2 = pT7-RFP1-hix-RFP2-GFP1-hix-GFP2-TT-hix-RFP2-TT-hix , glows yellow on UV box
Sample 3 = pT7-RFP1-hix-RFP2-GFP1-hix-RFP2-TT-hix-GFP2-TT-hix , glows red on UV box
Sample 4 = pT7-RFP1-hix-GFP2-TT-hix-RFP2-GFP1-hix-RFP2-TT-hix , does not glow on UV box
On the basis of these scans, we used excitation/emission wavelengths of 450 nm / 515 nm for green and 560 nm / 608 nm for red.
Conclusions: We have been able to detect both green and red fluorescence in bacteria. When both of these are present, a yellow color can be observed. A surprise was that the construct that produces RFP1-GFP2 and GFP1-RFP2 is yellow on the UV box, but does not fluoresce green or red by spectroscopy.