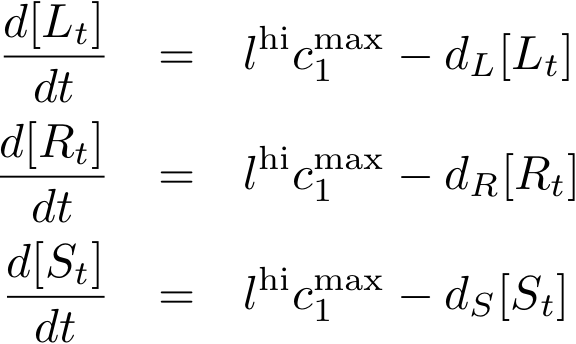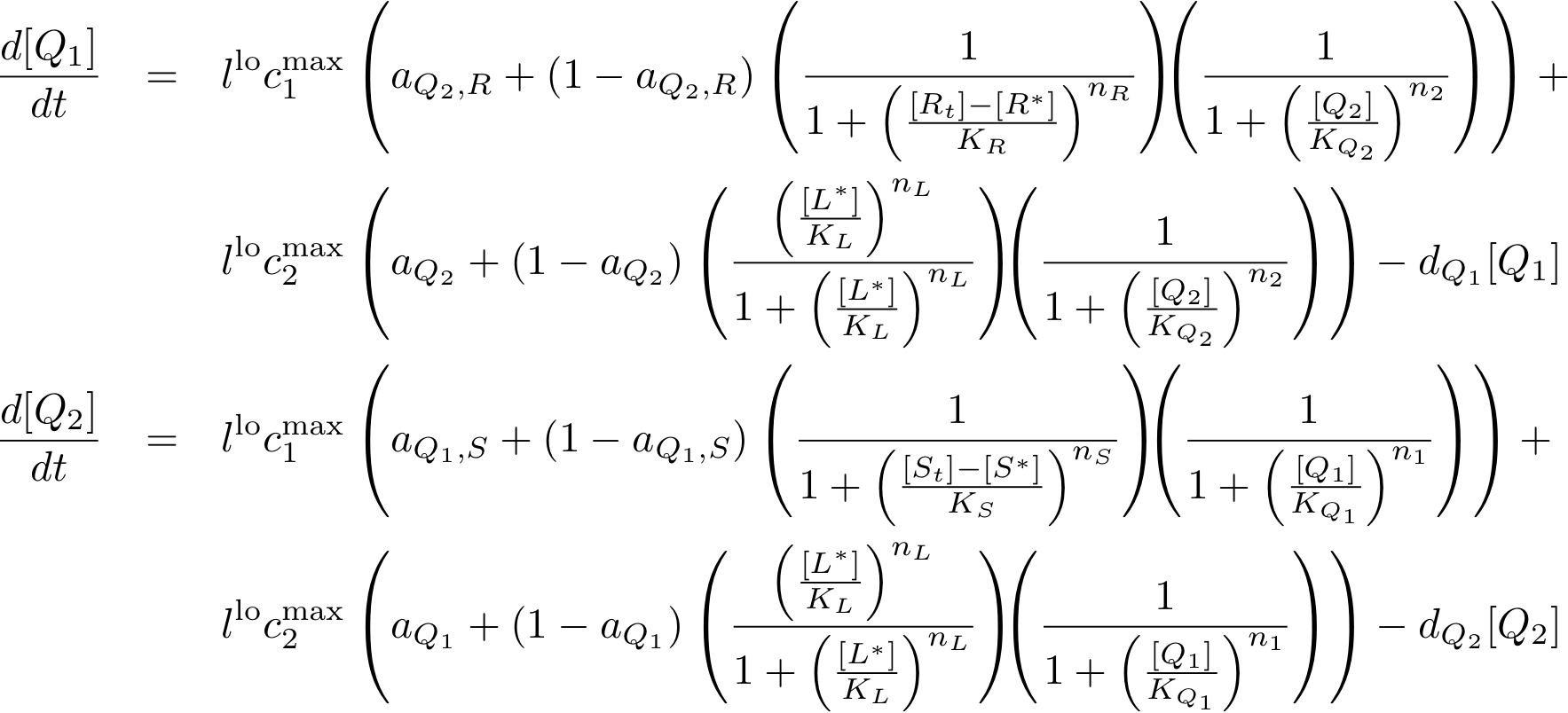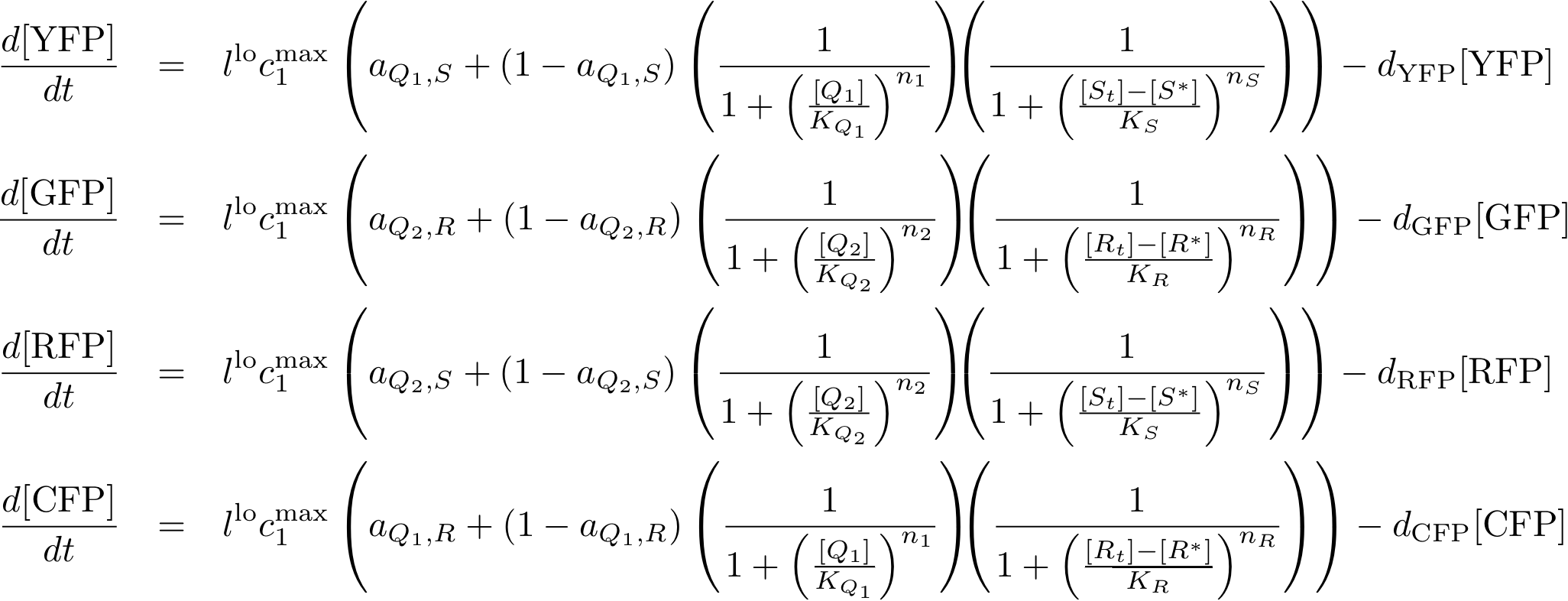ETHZ/Simulations
From 2007.igem.org
Contents |
Basic Model
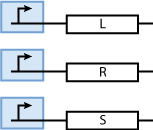
Constitutively produced proteins
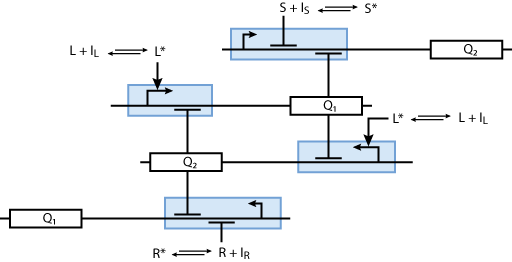
Learning system
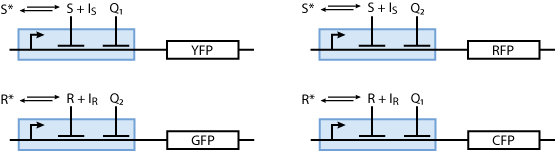
Reporter system
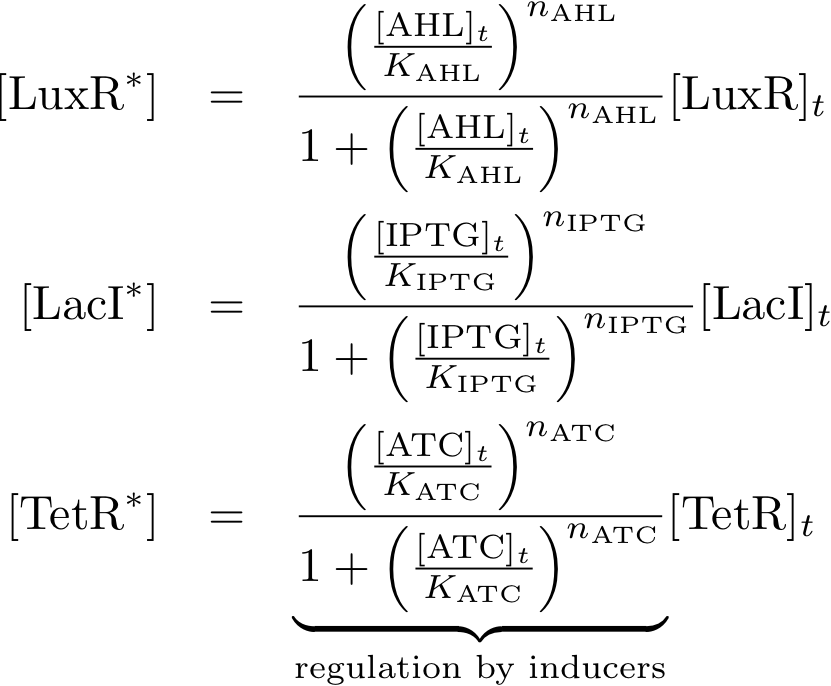
System Equations
Constitutively produced proteins
Learning system
Reporter system
Allosteric regulation
Comments
Note that the three constitutively produced proteins R, S and L exist in two different forms: as free proteins and in complexes they build with IR, IS and IL, respectively. The total amount of protein is denoted with a subscript t (e.g. Rt) in the above formulas. The amount of protein existing as complex is denoted with a superscript * (e.g. R*). The difference is the amount of free protein (e.g. Rt - R*).
Model Parameters
| Parameter | Value | Description | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| aR | basic production of lacI | obsolete | |
| aS | basic production of tetR | ||
| aL | basic production of luxR | ||
| aQ1 | basic production of cI | ||
| aQ2 | basic production of p22cII | ||
| aYFP | basic production of YFP | ||
| aGFP | basic production of GFP | ||
| aRFP | basic production of RFP | ||
| aCFP | basic production of CFP | ||
| dR | 0.06 | degradation of lacI | Ref. [4] --please only add parameter values with proper dimensions, a number like this is useless (Uhrm 04:43, 13 September 2007 (EDT))-- |
| dS | degradation of tetR | ||
| dL | degradation of luxR | ||
| dQ1 | degradation of cI | ||
| dQ2 | degradation of p22cII | ||
| dYFP | degradation of YFP | ||
| dGFP | degradation of GFP | ||
| dRFP | degradation of RFP | ||
| dCFP | degradation of CFP | ||
| cQ1,1 | promoter strength (R/Q2 inhibited) | maybe Ref. [5] can be of help here (for inhibition of R) | |
| cQ1,2 | promoter strength (L activated/Q2 inhibited) | ||
| cQ2,1 | promoter strength (S/Q1 inhibited) | maybe Ref. [5] can be of help here (for inhibition of Q1) | |
| cQ2,2 | promoter strength (L activated/Q1 inhibited) | maybe Ref. [5] can be of help here (for inhibition of Q1) | |
| cYFP | promoter strength (S/Q1 inhibited) | see also cQ2,1 | |
| cGFP | promoter strength (R/Q2 inhibited) | see also cQ1,1 | |
| cRFP | promoter strength (S/Q2 inhibited) | ||
| cCFP | promoter strength (R/Q1 inhibited) | ||
| KR | 1.3e-3 - 2e-3 [mM/h] | lacI repressor dissociation constant | lower value is from Ref. [2], higher value is from Ref. [5] |
| KIR | 1.5e-10 [mM/h] | IPTG-lacI repressor dissociation constant | Ref. [5] |
| KS | tetR repressor dissociation constant | ||
| KIS | aTc-tetR repressor dissociation constant | ||
| KL | luxR activator dissociation constant | ||
| KIL | AHL-luxR activator dissociation constant | ||
| KQ1 | 2e-3 [mM/h] | cI repressor dissociation constant | Ref. [5] |
| KQ2 | p22cII repressor dissociation constant | ||
| nR | 1 | lacI repressor Hill cooperativity | Ref. [5] |
| nIR | 2 | IPTG-lacI repressor Hill cooperativity | Ref. [5] |
| nS | 3 | tetR repressor Hill cooperativity | Ref. [3] |
| nIS | aTc-tetR repressor Hill cooperativity | ||
| nL | 1 | luxR activator Hill cooperativity | Ref. [3] |
| nIL | 1 | AHL-luxR activator Hill cooperativity | Ref. [3] |
| nQ1 | 1.9 | cI repressor Hill cooperativity | Ref. [5] |
| nQ2 | p22cII repressor Hill cooperativity |
References
- A synthetic time-delay circuit in mammalian cells and mice (http://www.pnas.org/cgi/content/abstract/104/8/2643)
- Detailed map of a cis-regulatory input function (http://www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/100/13/7702?ck=nck)
- Parameter Estimation for two synthetic gene networks (http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/iel5/9711/30654/01416417.pdf)
- Supplementary on-line information for "A Synthetic gene-metabolic oscillator" (no link)
- Genetic network driven control of PHBV copolymer composition (http://doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.08.030)
Variable Mapping
| Variable | Compound |
|---|---|
| R | lacI |
| IR | IPTG |
| S | tetR |
| IS | aTc |
| L | luxR |
| IL | AHL |
| Q1 | cI |
| Q2 | p22cII |