Chiba/Engeneering Flagella
From 2007.igem.org
|
Introduction | Project Design | Bacteria Linker | Communication | Size Controller | Making Marimos | Our Goal || Team Members | メンバ連絡簿 |
Our Aim
To make a stickey hands on E.coli, we focused on their flagella that are located outside of cells. We used 2 following mechanisms:
- Display peptides in flagellar fillament.
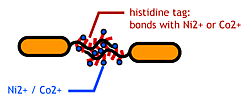
- The imidasol group in histidines make a complex bond with metal ions.
We combined these two and made a His-tagged flagella (hoping for ? in the hope to ?) stick together via metal ions.
大腸菌同士を吸着させるため,我々は(細胞の外側に突出しているもののうち)鞭毛に着目した.
About flagella
E.Coli have 5-10 flagella randomly distributed around the cell. Most of the time their flagella rotate in one direction(counterclockwise) and the cell swims in a rather straight line.Intermittently, the flagella rotate in opposite direction or pause, as a result the cell turns or tumbles(depending to the number of flagella that do so)Bacterial flagella consist of three parts:a basal body, a hook, and a filament.The filament of E.Coli is a highly rigid, helical, and cylindrical structure 10-15 μm long,23 nm diameter.It is built from ~20000 subunits of a ~55kDa single protein, flagellin.In the case of E.Coli, there is only one flagellin, FliC.
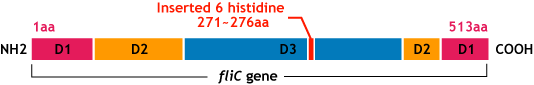
FliC has three or four domains,D0,D1,D2,D3,and although D1 and D2 are needed for the formation of the functional flagellar filament, D3 does not take part in the formation of flagella. (Ref)
大腸菌は5~10本/細胞の鞭毛を持つ.鞭毛を回転/逆回転させることにより環境の良い場所へとtaxisする. 鞭毛は長さ約10~15μm,半径約23nmの空孔のチューブ状である.(図:菌全体) 鞭毛のフィラメント部はFliCという蛋白質が規則正しく配列した多量体である.(図:鞭毛アップ) FliCはD0,D1,D2,D3ドメインを持つ.(種類によってはD1,D2,D3の3つのドメインを持つ) D1とD2はformation of the functional flagellar formation(ffff)の為に必要であるが,D3ドメインは必要でなく可変である(図:蛋白質構造&鞭毛断面図)
"Variable" FliC D3 domain
It is possible to display proteins(up to 49.4kDa)on the cell surface of E.Coli using flagellin fusion protein.
可変なD3ドメインに他の<__aaまでの>アミノ酸を挿入しても鞭毛が合成される[2].詳細も書く.
References
- Kuwajima, G. et al.: Nature Biotechnology, 6, 1080-1083 (1988).
- Tanskanen, J. et. al.: Appl. and Env. Microbiol., 4152-4156 (2000)
Experiments
Making FliC-his gene
- FliC遺伝子のD3領域に、Histidineループをコードする遺伝子を挿入し、ヒスチジンタグとして発現させる。
We inserted the gene of six histidine loop peptide (“His-Tag”).
Display Check: Beads Adsorption
Purpose
FliC-hisが発現され,鞭毛にHistidine-Tagがディスプレイされてるか,を確認する.
To confirm that whether Histidine-Tag protein were displaied on the flagella surface of E.Coli
Method
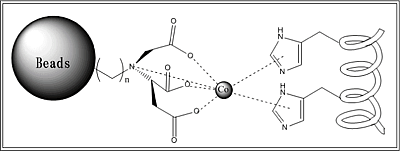
ビーズ吸着の説明. ヒスチジンはCo(またはNi)と錯体結合?をする.表面に金属イオン(本実験ではCo2+およびNi2+)を配置したビーズを使用して,FliC-hisがディスプレイされた大腸菌とそうでないものを調べた.
ビーズには4つのカルボキシル基のついた炭素鎖がついていて、二価の金属イオンの6つの配位部位のうち、4つと配位結合している。さらに残りの二つの配位部位に、Histidineのイミダゾール基が配位する。このため、Histidine Tagが鞭毛にDisplayされている大腸菌と、ビーズ溶液を懸濁させれば、鞭毛上のHistidineと金属イオンとを媒体として、鞭毛がBeadsに吸着する。この懸濁溶液にMagnetを近づけることにより、BeadsはMagnetに引き寄せられ、Beadsを含まない溶液を上澄みとして分離できる。さらにこのBeadsにImidazoleを含むバッファーを加えれば、このImidazoleがHistidineのImidazole基と競合し、金属イオンにHistidineよりも強い力で配位するため、鞭毛がBeadsからはずれる。ここで再びMagnetを近づければ、大腸菌のついていないBeadsと、大腸菌がいる上澄み溶液とに分離される。この上澄み溶液をプレートにinculateし、コロニーをチェックする。コロニーが形成されれば、鞭毛にHistidine TagがDisplayされているということがわかる。
(<不十分&不正確です.直してください)
Samples
- GI826(⊿FliC⊿MotB株)
- pUC19-FliC-His
- plasmidなし
- GI826(⊿FliC⊿MotB株)
- pUC19-FliC-his
- plasmidなし
Procedure
- pUC19-FliC-His,をJW1908(Keio⊿FliC株)にトランスフォーメーション。培養液をビーズと懸濁させ、大腸菌をBeadsに吸着する。
吸着した大腸菌をbufferで溶出し、inculateする。(Negative Control 1:Noplasmid,Negative Control 2:Co2+あるいはNi2+の有り・無し) →吸着していなかった
- pUC19-FliC-His,をGI826(⊿FliC⊿MotB株)にトランスフォーメーション。培養液をビーズと懸濁させ、大腸菌をBeadsに吸着する。
吸着した大腸菌をbufferで溶出し、inculateする。(Negative Control 1:Noplasmid,Negative Control 2:Co2+あるいはNi2+の有り・無し) →吸着していた。
Results
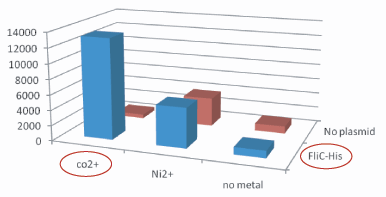
Plasmidあり、かつCo2+つきビーズ、のコロニー数は、その他のものよりはるかに多い。30倍以上。 Histidine Tagの存在によって大腸菌がビーズに吸着吸着していることがわかる。 The number of colony dramatically decreased with out Co2+ or FliC-His plasmid.