Chiba/Quorum Sensing
From 2007.igem.org
(→Design) |
(→Result) |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
===Result=== | ===Result=== | ||
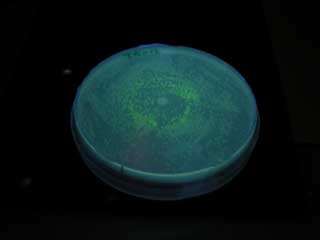
| - | [[Image:AHL test photo 01.jpg|frame|left|'''Fig. | + | [[Image:AHL test photo 01.jpg|frame|left|'''Fig. Cell number of senders required for activating receivers.'''<br> ]] |
| - | + | <br clear="all"> | |
| - | *At least 5x10<sup>4</sup> cell/ml sender required to activate lux promoter. | + | *At least 5x10<sup>4</sup> cell/ml sender required to activate lux promoter in BW25113. |
| - | *Sender performance HIGHLY depends on the strains. | + | *Sender performance HIGHLY depends on the strains: 100x more cells were required to activate the lux promoter in other strain XL10Gold. |
| - | * | + | *Overexpression of metK did not result in the booster effect. It was so even when Methionine (10mM), the direct substrate of metK, was added to the growth media (not shown). Sucks. |
===Discussion=== | ===Discussion=== | ||
Revision as of 03:46, 27 October 2007
|
Introduction | Project Design ( 1.Affinity Tag | 2.Communication Module | 3.Size Control ) | Making Marimos | Our Goal |
Size Control
Our Aim
Since produced AHL diffuses all around the bacteria culture, all receivers can ultimately aggregate to one huge marimo with their sticky hands. This final state is not the case of real marimos. Thus our idea for controlling the size of Bacteria Marimos is based on the high performance quorum sensing or AHL-diffusing inhibition.
- Raise the AHL productivity of Sender
- Increase the AHL sensitivity of Receiver
- Use the AHL degrading enzyme aiiA to localize AHL
1.Improving Sender
Design
AHL is synthesized from methionine by the enzyme MetK and LuxI.
We tested in the hope of combined overexpression of these 2 genes will enhance the sender capacity.
Experiment
Sender
Ptet-LuxI
- Synthesize AHL constantly
metK Sender
- Synthesize AHL and express metK constantly
Receiver
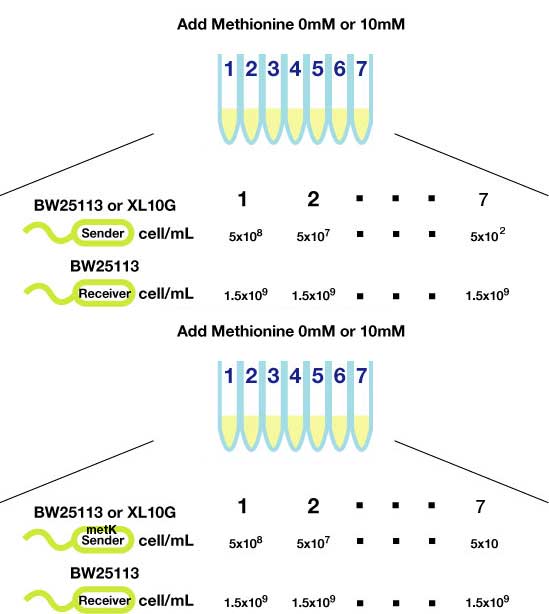
Method(Fig3.)
- Inoculated sender, MetK sender, and receiver in each liquid medias. Incubated at 37℃ 12h.
- Checked OD600. Dispensed receiver in each tube equally. Spin downed senders and resuspended with fresh liquid media.
- Diluted senders to adjust cell population (5x108,5x107,......, 5x102).
- Mix receivers and senders.
- Incubated for 1h to 3h at room tempature
- Spindowned and UV checked.
Result
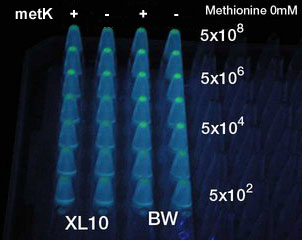
- At least 5x104 cell/ml sender required to activate lux promoter in BW25113.
- Sender performance HIGHLY depends on the strains: 100x more cells were required to activate the lux promoter in other strain XL10Gold.
- Overexpression of metK did not result in the booster effect. It was so even when Methionine (10mM), the direct substrate of metK, was added to the growth media (not shown). Sucks.
Discussion
- No improbement in sending power was observed.
- Assumption (not conclusion): (1) Suply of S-adenosyl methionine (precursor) is probably enough, and luxR is by far the rate-limiting step in AHL synthetic pathway. (2) There exist control mechanism of AHL precursor; overexpression of metK ativates the degradation pathway of its product. Need more reading.
- Note; We haven't confirmed the entire sequencing of the metK gene (PCR cloned) used in this experiment.
2.Sensitizing Receiver
Design
Collins et.al. described the hyper-sensitive variants of luxR to AHL.(Collins, C. H., Arnold, F. H. & Leadbetter, J. R. Directed evolution of Vibrio fischeri LuxR for increased sensitivity to a broad spectrum of acyl-homoserine lactones. Mol. Microbiol. 55, 712–723 (2005))
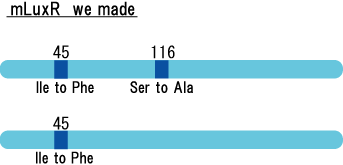
We created two luxR mutants. One is I14F mutant of LuxR, and another is I45F/S116A.
There is no report on I45F/S116A double mutant.By creating/ analyzing this mutant in AHL sensitivity, we can tell the effect of T33A in LuxR.
Experiment
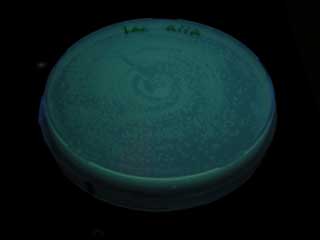
luxR mutants was analyzed in their sensitivity to AHL by following procedure.
- Inoculate Receiver (wild type luxR/BW25113), mutated Receiver (1point mutation/BW25113) in liquid media for 12 h at 37℃.
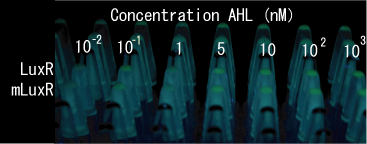
- Adjust the cell density and add AHL (final concentration, 0, 0.1, 1, 5, 10, 100, and 1000 nM)
- Incubate for 1h at room temperature
- Spindown cells and GFP folurescent level checked
Result
- Both wild type and 1point mutation luxR express GFP under 5nM AHL concentration.
- 2point mutation(I45F,S116A) luxR Receiver express GFP without AHL.
Discussion
This table is quoted from paper.
In the paper, DH5α strain was used.
But wild type luxR in our study expressed GFP under 5nM AHL concentration.
Assumption:There is some difference between strains. Required to do same test on other strains
3.Localizing AHL
Design1
![]()
BBa I729006
In addition to the receiver unit, there added AiiA under the control of lac promoter.
AiiA degrades/ inactivates AHL, lowering the AHL concentration in the cell.
This way cells installed with this circuit can respond, but less sensitive, to the sender cells.
Experiment
- Inoculate E.coli carries this aiiA receiver plasmid in Liquid Media.
- At the same time, inoculate AHL sender E.coli in Liquid Media.
- Dilute receiver cells and spread on agar plate, and spot sender 1μL. Incubate at 37℃ 12hour
- Check plate.(GFP expressed?)
Result
GFP expression was not observed on the plate of aiiA receiver.
Discussion
We thought expression of aiiA significantly decrease the cellular level of AHL. It turned out to be true.
However, it went too much. It does not respond to senders anymore, probably due to too fast AHL degradation.
We need more controlled/ moderate expression of aiiA.
Design2
![]()
This gene circuit is expected so that aiiA is synthesized only when the receiver senses AHL signal. If so, the whole Bacteria Marimo becomes AHL quencher. In fact, the bacteria inside of the Marimo degrades AHL and the AHL diffusion outside of Marimo is inhibited.
Experiment
- Inoculate E.coli carries this aiiA receiver plasmid in Liquid Media.
- At the same time, inoculate AHL sender E.coli in Liquid Media.
- Dilute receiver cells and spread on agar plate, and spot sender 1μL. Incubate at 37℃ 12hour
- Put plate 30℃
- Check GFP expression every 1hour.
Result
- When we compared the GFP expression with the test tube of BBa_T9002, the bacteria with the consructed gene circuit did not fluoresce immediately after incubation, however fluoresced in 18~20 hour.
Discussion
- GFP expression means plux is activated. So we could make moderate aiiA receiver.
- But we need more twisted circuit.
Design3
![]()
Above picture describes aiiA is regulated inverted lux promoter with CI inverter.
- High AHL concentration: no aiiA expression, no AHL degrade.
- Low AHL concentration: aiiA expressed, AHL degraded.
Experiment
We could not finish assembling this part. It will be our future work.
Subpart:BBa_S03840