USTC/OperatorPosition
From 2007.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
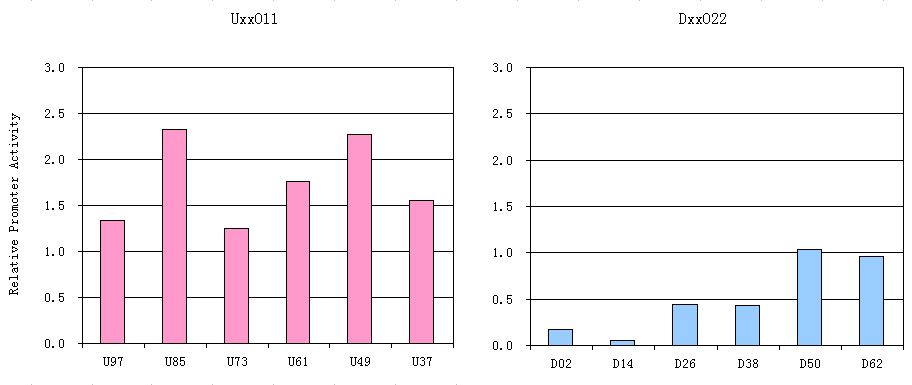
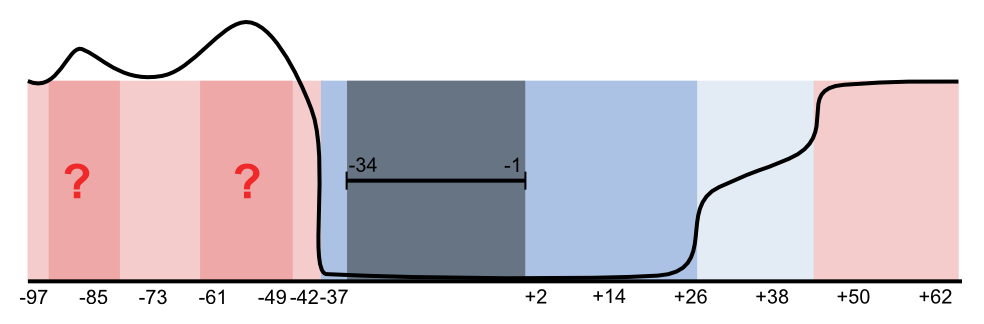
| - | Different locations of an operator plays a role in determining the intensity of repression in vivo[[USTC/OperatorPosition#References|[1]]].Both operators with strong and weak repression are required to the gates. Therefore, we systematically tested the influence of | + | Different locations of an operator plays a role in determining the intensity of repression in vivo[[USTC/OperatorPosition#References|[1]]].Both operators with strong and weak repression are required to the gates. Therefore, we systematically tested the influence of an operator at different locations on the promoter activity. |
[[Image:USTC_RelativePromoterActivity.png|thumb|600px|center|'''Figure 1''' Left: the influence on the promoter’s activity when a single operator is at a different position upstream of the consensus sequence. | [[Image:USTC_RelativePromoterActivity.png|thumb|600px|center|'''Figure 1''' Left: the influence on the promoter’s activity when a single operator is at a different position upstream of the consensus sequence. | ||
Right: the influence on the promoter’s activity when a single operator is at a different position downstream of the consensus sequence. | Right: the influence on the promoter’s activity when a single operator is at a different position downstream of the consensus sequence. | ||
Revision as of 12:30, 26 October 2007
Different locations of an operator plays a role in determining the intensity of repression in vivo[1].Both operators with strong and weak repression are required to the gates. Therefore, we systematically tested the influence of an operator at different locations on the promoter activity.
References
1. Elledge, S. J. & Davis, R. W. (1989), 'Position and density effects on repression by stationary and mobile DNA-binding proteins.', Genes Dev 3(2), 185--197.