USTC/InterOperatorDistance
From 2007.igem.org
< USTC(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:USTC_DNALooping.png|thumb|'''Figure 1''' Loop conformations and the in vivo free energy of DNA looping by the lac repressor. From [[USTC/InterOperatorDistance#Refereces|[5] ]] ]] | + | [[Image:USTC_DNALooping.png|thumb|400px|'''Figure 1''' Loop conformations and the in vivo free energy of DNA looping by the lac repressor. From [[USTC/InterOperatorDistance#Refereces|[5] ]] ]] |
It has been accounted in a previous paper [[USTC/InterOperatorDistance#Refereces|[1-4]]] that different relative distance of the two operators can cause a periodic fluctuation in co-repression intensity. The reason is that when the two operators are a certain number of nucleotides apart, the Lac Repressor dimer tend to tetramerize and further lead to a partial supercoiling of the DNA, as is shown in the figure. | It has been accounted in a previous paper [[USTC/InterOperatorDistance#Refereces|[1-4]]] that different relative distance of the two operators can cause a periodic fluctuation in co-repression intensity. The reason is that when the two operators are a certain number of nucleotides apart, the Lac Repressor dimer tend to tetramerize and further lead to a partial supercoiling of the DNA, as is shown in the figure. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:21, 24 October 2007
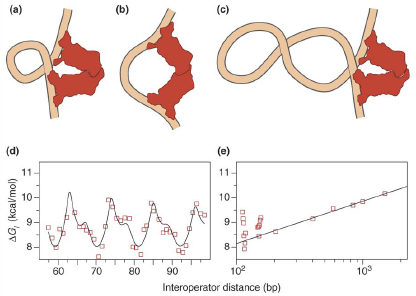
Figure 1 Loop conformations and the in vivo free energy of DNA looping by the lac repressor. From [5]
It has been accounted in a previous paper [1-4] that different relative distance of the two operators can cause a periodic fluctuation in co-repression intensity. The reason is that when the two operators are a certain number of nucleotides apart, the Lac Repressor dimer tend to tetramerize and further lead to a partial supercoiling of the DNA, as is shown in the figure.
Such a partial supercoiling will hinder the binding of the RNA Polymerase to DNA, thus practicing a much stronger repression than a single repressor does. Since the partial supercoiling forms in periodicity according to the different relative distance of the two operators, the co-repression intensity there-caused presents periodicity as well.
References
- Y Flashner and J D Gralla, Dual Mechanism of Repression at a Distance in the lac Operon. PNAS. 1988 Dec;85(23):8968–8972.
- Saiz, L., Rubi, J.M. & Vilar, J.M.G. Inferring the in vivo looping properties of DNA. PNAS. 102, 17642-5 (2005).
- Swigon, D., Coleman, B.D. & Olson, W.K. Modeling the Lac repressor-operator assembly: The influence of DNA looping on Lac repressor conformation. PNAS 103, 9879-9884 (2006).
- Müller, J., Oehler, S. & Müller-Hill, B. Repression of lac promoter as a function of distance, phase and quality of an auxiliary lac operator. J. Mol. Bio. 257, 21-9 (1996).
- Saiz, L. & Vilar, J. M. G. (2006), DNA looping: the consequences and its control., Curr Opin Struct Biol 16(3), 344--350.