Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Applications
From 2007.igem.org
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''MENU''' :[[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper| Introduction]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/References|Background]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Applications|Applications]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Design|Design&Implementation]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Modelling|Modelling]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Status|Wet Lab]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/SBApproach|Synthetic Biology Approach]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Conclusions|Conclusions]] | '''MENU''' :[[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper| Introduction]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/References|Background]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Applications|Applications]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Design|Design&Implementation]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Modelling|Modelling]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Status|Wet Lab]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/SBApproach|Synthetic Biology Approach]] | [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Conclusions|Conclusions]] | ||
| - | The Division PoPper is a device designed | + | The Division PoPper is a device designed to be coupled with other devices in order to offer its functionality for more complex systems. The Division PoPper has no signal inputs, so no upstream devices can be connected. Instead it is a generator of output signal, generating a PoPS pulse each time it senses a cell division. In this sense, the use of a standard signal format such as PoPS is an important characteristic for the compositional power and versatility of the device. In the ongoing work of implementing computational ability in cells, we think a device able to "convert" a core physical behaviour (the division) to an information flow (the PoPS pulse) will be of immense interest. Here we detail some potential uses for the Division PoPper when coupled with other devices. |
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==Division Counting== | ==Division Counting== | ||
| - | One possible application is to count the number of | + | One possible application is to count the number of divisions of a cell, by coupling the device to a counter. The simplest configuration is to connect the output of the Division PoPper to the input of the counter. For example, the counter designed by ETH Zurich for the 2005 edition of iGEM is able to receive a PoPS pulse signal and to count how many pulses arrive ([https://2006.igem.org/wiki/index.php/ETH_Zurich_2005#Abstract ETH Zurich counter]). We developed a mathematical model that simulates the behaviour of such a system by integrating our ODE model to the ODE model of the ETH counter (details in the [[Edinburgh/DivisionPopper/Modelling|Modelling]] section). |
| - | Why might it be important to count cell divisions? For example, to trigger cell death after a certain number of divisions, as security control containing the spread of engineered bacteria when released into the environment for certain tasks. Another possibility is to associate a function at each different division number in order to have cell behaviour that changes over time. | + | Why might it be important to count cell divisions? For example, to trigger cell death after a certain number of divisions, as security control containing the spread of engineered bacteria when released into the environment for certain tasks. Another possibility is to associate a function at each different division number in order to have cell behaviour that changes over time. For example, in the use of microorganisms to manufacture therapeutic proteins, cells could be engineered to begin expressing the protein after a certain number of cell divisions. |
Revision as of 08:56, 26 October 2007
MENU : Introduction | Background | Applications | Design&Implementation | Modelling | Wet Lab | Synthetic Biology Approach | Conclusions
The Division PoPper is a device designed to be coupled with other devices in order to offer its functionality for more complex systems. The Division PoPper has no signal inputs, so no upstream devices can be connected. Instead it is a generator of output signal, generating a PoPS pulse each time it senses a cell division. In this sense, the use of a standard signal format such as PoPS is an important characteristic for the compositional power and versatility of the device. In the ongoing work of implementing computational ability in cells, we think a device able to "convert" a core physical behaviour (the division) to an information flow (the PoPS pulse) will be of immense interest. Here we detail some potential uses for the Division PoPper when coupled with other devices.
Contents |
| System view of the Division Counter |
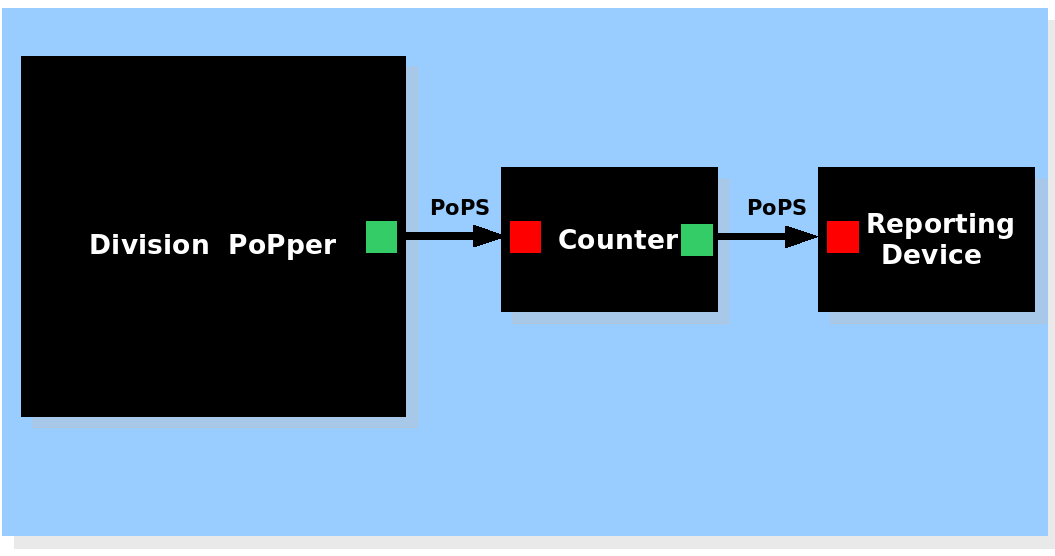 The Division PoPper device generates a pulse signal, the Counter device memorizes the number of pulse and activates the Report device if necessary. The Division PoPper device generates a pulse signal, the Counter device memorizes the number of pulse and activates the Report device if necessary.
|
Division Counting
One possible application is to count the number of divisions of a cell, by coupling the device to a counter. The simplest configuration is to connect the output of the Division PoPper to the input of the counter. For example, the counter designed by ETH Zurich for the 2005 edition of iGEM is able to receive a PoPS pulse signal and to count how many pulses arrive (ETH Zurich counter). We developed a mathematical model that simulates the behaviour of such a system by integrating our ODE model to the ODE model of the ETH counter (details in the Modelling section).
Why might it be important to count cell divisions? For example, to trigger cell death after a certain number of divisions, as security control containing the spread of engineered bacteria when released into the environment for certain tasks. Another possibility is to associate a function at each different division number in order to have cell behaviour that changes over time. For example, in the use of microorganisms to manufacture therapeutic proteins, cells could be engineered to begin expressing the protein after a certain number of cell divisions.
| System view of the Division Frequency Analyzer |
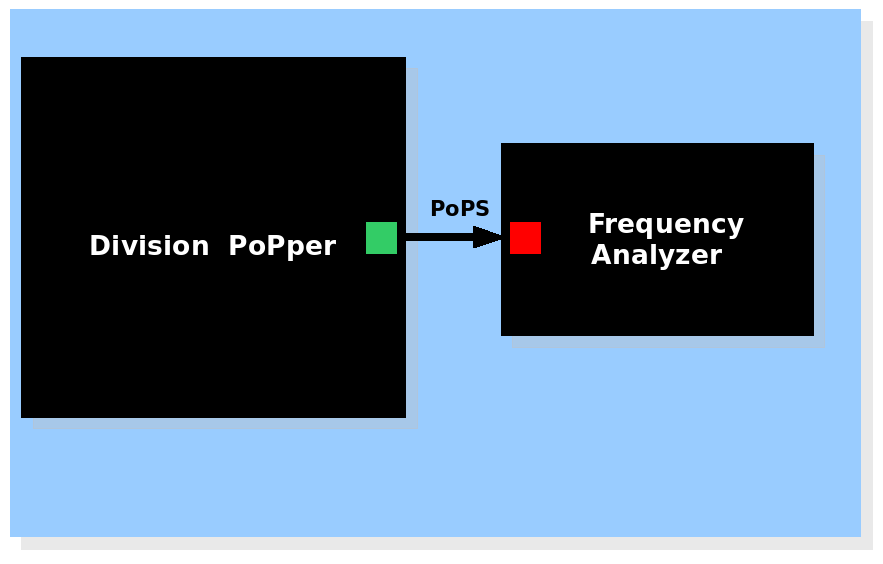 The Division PoPper device generates a pulse signal and the Frequency analyzer device calculates the frequency. The Division PoPper device generates a pulse signal and the Frequency analyzer device calculates the frequency.
|
Division Frequency Analysis
The output of the Division PoPper could be linked to an analyzer of frequency. A very simple method to implement it is to put downstream the production of a slowly degrading protein. Physically this can be easily achieved by putting after the Division PoPper a coding region that codes for the protein. The more frequent the divisions, the more often the PoPS pulse would express the protein and thus increase its concentration. So it it would be possible to associate the quantity of the protein to the frequency of division. Since the frequency of division is sometimes related to diseases in humans, this can be used for example for triggering cell reaction when a cell is dividing too fast.