Edinburgh/Yoghurt/Wet Lab
From 2007.igem.org
(→Zeaxanthin Synthesis Pathway) |
|||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
!Reverse Primer | !Reverse Primer | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |CrtE |
| - | |''' | + | |'''crtE f1:''' gca gagctc gcgt tgcc gtaa atgt atc |
| - | |''' | + | |'''crtE r1:''' aa actagt gcga tcgc cgcg aaat g |
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |CrtBI |
| - | |''' | + | |'''crtI f1:''' tga gagctc atcg ttaa agag cgac |
| - | |''' | + | |'''crtB r1:''' gc actagt caaa actt cagg cgac |
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |CrtY |
| - | |''' | + | |'''crtY f1:''' cag gagctc ttaa gtgg gagc ggct atg |
| - | + | |'''crtY r1:''' ac actagt tggt ttca tgta gtcg | |
| - | |''' | + | |
| - | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |CrtZ |
| - | |''' | + | |'''crtZ f1:''' aga gagctc tacc ggag aaat tatg |
| - | + | |'''crtZ r1:''' cc actagt cagg ccct tact tccc | |
| - | |''' | + | |
| - | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | More information on the primers used to amplify the zeaxanthin pathway genes may be found on the [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Cfrench:primerlist#Primers_for_iGEM2007_flavours.2Ffragrances_project french lab] OpenWetWare site | |
| - | More information on the primers used to amplify the | + | |
===Vanillin Biosynthesis Pathway=== | ===Vanillin Biosynthesis Pathway=== | ||
| Line 80: | Line 75: | ||
'''Primers''' | '''Primers''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{| border="1" cellpadding="20" cellspacing="0" | {| border="1" cellpadding="20" cellspacing="0" | ||
!Gene | !Gene | ||
| Line 85: | Line 82: | ||
!Reverse Primer | !Reverse Primer | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |Sam5 |
| - | |''' | + | |'''sam5 f1:''' at gaattc gcggccgc t tctag atg acc atc acg tca cct g |
| - | |''' | + | |'''sam5 r1:''' ct actagt a tta tta ggt gcc ggg gtt gat cag |
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |Sam8 |
| - | |''' | + | |'''sam8 f1:''' at gaattc gcggccgc t tctag atg acg cag gtc gtg gaa cg |
| - | |''' | + | |'''sam8 r1:''' ct actagt a tta tta tcc gaa atc ctt ccc gtc |
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |ech |
| - | |''' | + | |'''ech f1:''' aat gaattc gcggccgc t tctag atg agc aaa tac gaa ggt c |
| - | |''' | + | '''ech f2:''' atc gagctc acacc cagaa caaga gc |
| + | |'''ech r1:''' ct actagt a tta tta gcg ttt ata ggc ttg cag c | ||
| + | '''ech r2:''' tt actagt atcgg gaaca cgttc aagc | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |fcs |
| - | |''' | + | |'''fcs f1:''' aat gaattc gcggccgc t tctag atg cgc tcc ctg gaa ccc |
| - | |''' | + | '''fcs f2:''' gtg gagctc actga agaac agggc gtg |
| + | |'''fcs r1:''' ct actagt a tta tta cgg ttt ggg ccc ggc ac | ||
| + | '''fcs r2:''' aa actagt atgcc gtgac agcaa atagg | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | More information on the primers used to amplify the vanillin pathway genes may be found on the [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Cfrench:primerlist#Primers_for_iGEM2007_flavours.2Ffragrances_project french lab] OpenWetWare site | ||
| + | |||
===Multi Host Plasmid pTG262=== | ===Multi Host Plasmid pTG262=== | ||
Revision as of 14:27, 3 October 2007
 Introduction | Applications | Design | Modelling | Wet Lab | References
Introduction | Applications | Design | Modelling | Wet Lab | References
Contents |
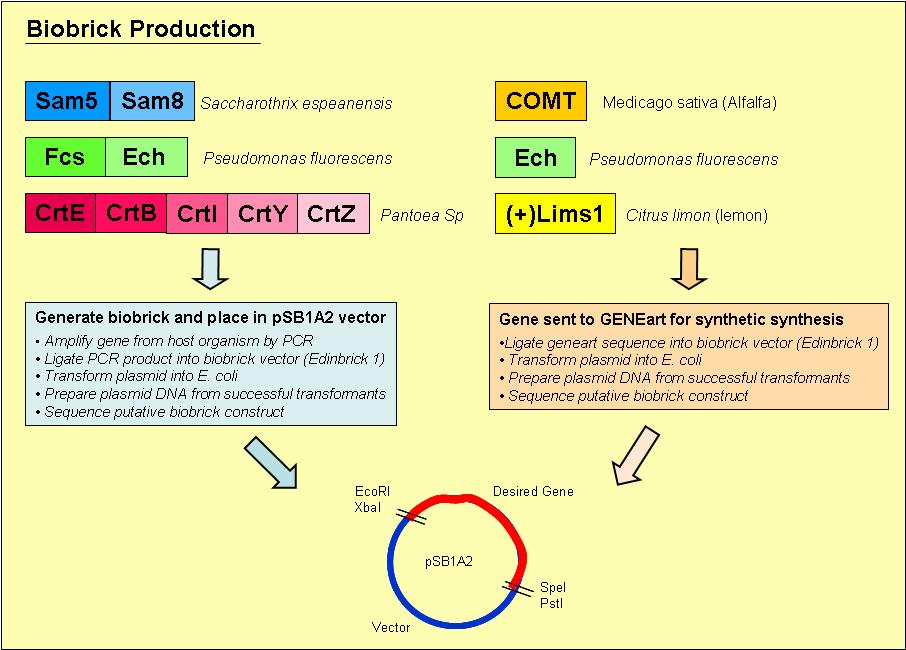
Biobrick Creation
Overview of the process we used to generate our biobricks:
1. Designed primers, which included a ribosome binding site and the biobrick restriction sites, EcoRI, XbaI, PstI and SpeI, to amplify our desired gene out of its host organism
2. Purified the PCR product and loaded onto an agrose gel to check for the presence of PCR product of the right size
3. If a band was present at the right size, we digested the PCR product and vector with the restriction enzymes EcoRI & PstI
4. Digested PCR product and vector were ligated overnight with T4 DNA ligase
5. Ligated vector and gene were then transformed into E. coli and plated onto Blue/ White selection Amplicillin plates
6. Transformants that contained a product ligated into the vector would grow as white colonies and are easy to select
7. Minipreps were prepared of the white colonies
8. Purified vector DNA was digested with restriction enzymes EcoRI and PstI to determine if the vector insert was of the correct size
9. Vectors containing inserts of the correct size were sent for sequencing to confirm if they did indeed contain the correct gene
The complete methods we used to generate our biobricks may be found on the [http://openwetware.org/wiki/French_Lab French Lab] OpenWetWare site
Zeaxanthin Synthesis Pathway
Biobricks created so far
- CrtE
- CrtBI (with PstI restriction sites)
- CrtZ
Primers
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| CrtE | crtE f1: gca gagctc gcgt tgcc gtaa atgt atc | crtE r1: aa actagt gcga tcgc cgcg aaat g |
| CrtBI | crtI f1: tga gagctc atcg ttaa agag cgac | crtB r1: gc actagt caaa actt cagg cgac |
| CrtY | crtY f1: cag gagctc ttaa gtgg gagc ggct atg | crtY r1: ac actagt tggt ttca tgta gtcg |
| CrtZ | crtZ f1: aga gagctc tacc ggag aaat tatg | crtZ r1: cc actagt cagg ccct tact tccc |
More information on the primers used to amplify the zeaxanthin pathway genes may be found on the [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Cfrench:primerlist#Primers_for_iGEM2007_flavours.2Ffragrances_project french lab] OpenWetWare site
Vanillin Biosynthesis Pathway
Biobricks created so far
- Sam8
Genes sent to GENEART for synthesis
- COMT
- ech
Primers
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Sam5 | sam5 f1: at gaattc gcggccgc t tctag atg acc atc acg tca cct g | sam5 r1: ct actagt a tta tta ggt gcc ggg gtt gat cag |
| Sam8 | sam8 f1: at gaattc gcggccgc t tctag atg acg cag gtc gtg gaa cg | sam8 r1: ct actagt a tta tta tcc gaa atc ctt ccc gtc |
| ech | ech f1: aat gaattc gcggccgc t tctag atg agc aaa tac gaa ggt c
ech f2: atc gagctc acacc cagaa caaga gc | ech r1: ct actagt a tta tta gcg ttt ata ggc ttg cag c
ech r2: tt actagt atcgg gaaca cgttc aagc |
| fcs | fcs f1: aat gaattc gcggccgc t tctag atg cgc tcc ctg gaa ccc
fcs f2: gtg gagctc actga agaac agggc gtg | fcs r1: ct actagt a tta tta cgg ttt ggg ccc ggc ac
fcs r2: aa actagt atgcc gtgac agcaa atagg |
More information on the primers used to amplify the vanillin pathway genes may be found on the [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Cfrench:primerlist#Primers_for_iGEM2007_flavours.2Ffragrances_project french lab] OpenWetWare site
Multi Host Plasmid pTG262
The plasmid we recieved had a multicloning site containing EcoRI, XbaI and PstI sites. To convert pTG262 into a biobrick vector we inserted a biobrick between the EcoRI and PstI sites, this simultaneously removed the intravening XbaI site, and introduced all four biobrick restriction enzymes sites (EcoRI, XbaI, SpeI & PstI).
To create the biobrick restriction sites, we inserted a total of three biobricks:
- Plac-RFP (gives red transformants)
- Plac-lacZ (gives blue transformants)
- Ptet-RFP
In order to test the plasmid in a multitude of gram negative bacteria, including Shewanella, Pseudomonas & Agrobacterium, we will transform the pTG262-Plac/RFP construct into our chosen host. This will enable easy detection, as all bacteria capable of retaining and expressing the vector will form easily detected red colonies, when grown on media containing lactose.
Introduction | Applications | Design | Modelling | Wet Lab | References