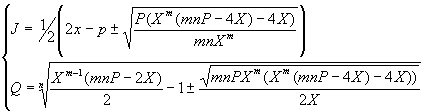Saint Petersburg/AlgebraJQ
From 2007.igem.org
Bistable behaviour of two repressors, mutually repressing each other
Bifurcation set in (J, Q) cross section is given by the following parametric equations:
To obtain the bifurcation curve one should plot the second parameter versus the first, varying X from 0 to P+J. The cusp is located as shown in the figure below. While Q is increasing the cusp tip moves right and upwards.
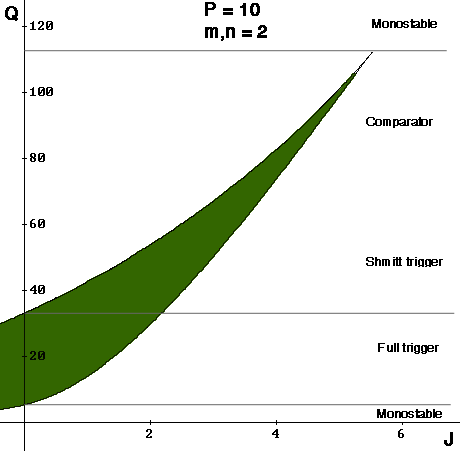
Figure. Cross section of bifurcation set by (J, Q) plane. The case with m=2, n=2, P=10 is shown.
Important findings:
The cusp in this cross-section is located as shown in fig XXX. While Q is increasing the cusp tip moves right and upwards.
Important findings:
At constant value of P and increasing values of Q the behaviour changes in the following way:
- Small Q – monostable behaviour
- Intermediate Q – full trigger
- Large Q – Shmitt trigger/comparator (threshold level increase, while hysteresis width decrease as Q increase)
- Very large Q – monostable behaviour
See also:
(P,Q)-Cross Section - analysis of hysteresis existense
(J,P)-Cross Section - type of responce at various values of P