Tokyo/Concepts
From 2007.igem.org
(→Worker Ants) |
(→Worker Ants and Differentiation) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| - | == Worker Ants == | + | == Worker Ants and Differentiation== |
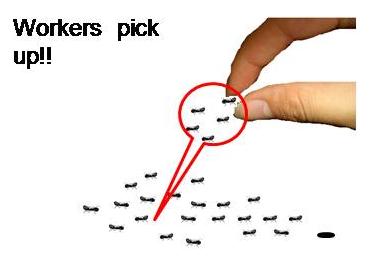
Division of labor is well established in an ant society. There are workers serving for their queen, her children, and the whole group. Though named “worker,” it has been revealed that all of them are not necessarily working. The working population is about 20% while the rest 80% are not and look idlers. | Division of labor is well established in an ant society. There are workers serving for their queen, her children, and the whole group. Though named “worker,” it has been revealed that all of them are not necessarily working. The working population is about 20% while the rest 80% are not and look idlers. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<br>What would happen if all the actual workers were removed? Would some of them start to work? If this is the case, we could expect that the idlers confuse and become unstable, then, some of them, for example 20% again, start to work while the others remain lazy. It seems that only 20% of the workers contribute to the most part of work. | <br>What would happen if all the actual workers were removed? Would some of them start to work? If this is the case, we could expect that the idlers confuse and become unstable, then, some of them, for example 20% again, start to work while the others remain lazy. It seems that only 20% of the workers contribute to the most part of work. | ||
| - | [[Image:Pick up.JPG|250px]]⇒ [[Image:Confusion4.jpg|250px]] ⇒[[Image: | + | [[Image:Pick up.JPG|250px]]⇒ [[Image:Confusion4.jpg|250px]] ⇒[[Image:Worksp.JPG|350px]] |
| - | <br>This 80:20 phenomenon – phenomenon that 80% of the effects comes from 20% of the causes – is empirically found in many cases in nature as well as human societies and called | + | <br>This 80:20 phenomenon – phenomenon that 80% of the effects comes from 20% of the causes – is empirically found in many cases in nature as well as human societies and called Pareto's principle. |
| - | Stimulated by this phenomenon, we set our goal to establish a bacterial society following Pareto’s law – a society consisting of worker and idler Escherichia coli. Here all E. coli having the same genetic components can | + | Stimulated by this phenomenon, we set our goal to establish a bacterial society following Pareto’s law – a society consisting of worker and idler Escherichia coli. Here all E. coli having the same genetic components can differentiate into either workers or idlers. When all workers are removed from the society, some of the idlers start working. As individual ants specialize their work, individual cells differentiate to perform different work. |
| + | |||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_principle| What is Pareto's principle? (Wikipedia)] | ||
== == | == == | ||
||next>>[[Tokyo/Model|Concept & Model]] | ||next>>[[Tokyo/Model|Concept & Model]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:39, 27 October 2007
Abstract Concept & Model Requirements Genetic_circuit Works About_our_team
Worker Ants and Differentiation
Division of labor is well established in an ant society. There are workers serving for their queen, her children, and the whole group. Though named “worker,” it has been revealed that all of them are not necessarily working. The working population is about 20% while the rest 80% are not and look idlers.
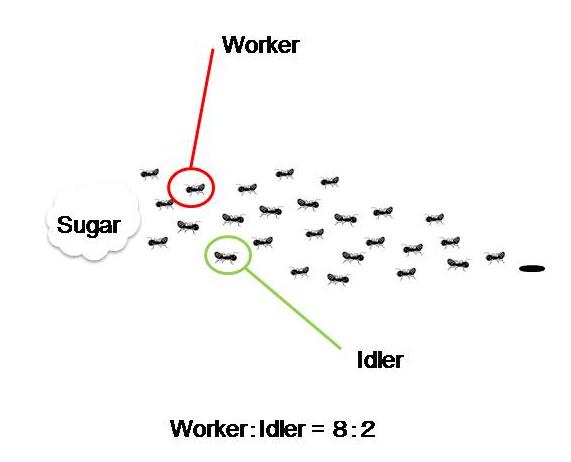
What would happen if all the actual workers were removed? Would some of them start to work? If this is the case, we could expect that the idlers confuse and become unstable, then, some of them, for example 20% again, start to work while the others remain lazy. It seems that only 20% of the workers contribute to the most part of work.
This 80:20 phenomenon – phenomenon that 80% of the effects comes from 20% of the causes – is empirically found in many cases in nature as well as human societies and called Pareto's principle.
Stimulated by this phenomenon, we set our goal to establish a bacterial society following Pareto’s law – a society consisting of worker and idler Escherichia coli. Here all E. coli having the same genetic components can differentiate into either workers or idlers. When all workers are removed from the society, some of the idlers start working. As individual ants specialize their work, individual cells differentiate to perform different work.
- [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_principle| What is Pareto's principle? (Wikipedia)]
||next>>Concept & Model