Tokyo/Works
From 2007.igem.org
(→5.Future works) |
(→3.<span style="color:#0066ff;">Dry </span>: Simulation) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==How to reach our goal== | ==How to reach our goal== | ||
| - | =====We have | + | =====We have alternately implemented <span style="color:#ff33cc;">Wet </span> and <span style="color:#0066ff;">Dry </span> experiments to achieve our goal===== |
<!--<br>我々の目的はGenetic Curcuitを作り、モデルのような挙動(共存安定)をさせることである。 | <!--<br>我々の目的はGenetic Curcuitを作り、モデルのような挙動(共存安定)をさせることである。 | ||
そのために、Dry ApproachとWet Approachを交互に行う方法を行った。 | そのために、Dry ApproachとWet Approachを交互に行う方法を行った。 | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
前段階として、ハイブリッドプロモータの作成、及び機能確認実験を行った。ハイブリッドプロモータは2つの入力を受け取れるプロモータで我々の遺伝子回路を実装するのに必要なパーツである。今回必要な用途を満たしたものが存在しなかったので、配列から設計を行った。--> | 前段階として、ハイブリッドプロモータの作成、及び機能確認実験を行った。ハイブリッドプロモータは2つの入力を受け取れるプロモータで我々の遺伝子回路を実装するのに必要なパーツである。今回必要な用途を満たしたものが存在しなかったので、配列から設計を行った。--> | ||
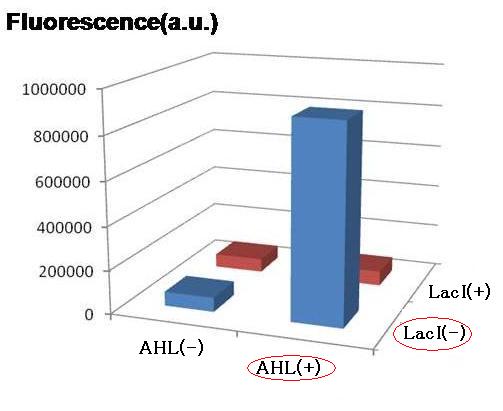
For initial attempts at regulating differentiation of E.coli by a set of two inputs, new hybrid promoter was designed . There is no desirable part among previous publications as well as BioBrick parts. Thus, we designed the parts that can be activated by LuxR and repressed by LacI . (Fig.1).These brand-new parts worked as designed (Fig.2).'''([[Tokyo/Works/Hybrid promoter|See more.]])''' | For initial attempts at regulating differentiation of E.coli by a set of two inputs, new hybrid promoter was designed . There is no desirable part among previous publications as well as BioBrick parts. Thus, we designed the parts that can be activated by LuxR and repressed by LacI . (Fig.1).These brand-new parts worked as designed (Fig.2).'''([[Tokyo/Works/Hybrid promoter|See more.]])''' | ||
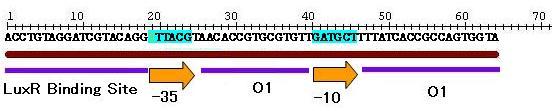
| - | <br>[[Image:Hybridgraph3.JPG|thumb|200px|'''Fig. 1 New Hybrid Promoter''' The newly | + | <br>[[Image:Hybridgraph3.JPG|thumb|200px|'''Fig. 1 New Hybrid Promoter''' The newly devised hybrid promoter is regulated by two inputs, AHL and LacI.|left]][[Image:Hybrid promoter.JPG|thumb|500px|'''Fig. 2 The sequence of the hybrid promoter''' <br> The sequence contains regulatory sites of AHL-LuxR, LacI.|center|left]] |
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
簡単な式からわかることを導きながら、段階を経て今回必要な(←今回の遺伝子回路を実装するような)計算式を導出した。最終的な式では、確率微分方程式を用いている。未知のパラメータを求めることで、双安定、共存安定の解析を行うことができる。--> | 簡単な式からわかることを導きながら、段階を経て今回必要な(←今回の遺伝子回路を実装するような)計算式を導出した。最終的な式では、確率微分方程式を用いている。未知のパラメータを求めることで、双安定、共存安定の解析を行うことができる。--> | ||
| - | '''Second, we tried to | + | '''Second, we tried to mathematically express our model.''' |
| - | <br>From simple equations, the equations necessary for our model were deviated | + | <br>From simple equations, the equations necessary for our model were deviated systematically. Though a parameter for production rate of AHL changes cell behavior from conventional mutual-inhibition model, Hill coefficients for the promoters are still critical for emergence of bistability.'''([[Tokyo/Works/Formulation |See more.]])''' |
<br>[[Image:Expression3-1.jpg|400px]] | <br>[[Image:Expression3-1.jpg|400px]] | ||
<!--リプレッサーA,B,シグナル分子Sの時間変化を式として表し、安定性解析を行った結果、Hill係数が大切であることがわかった | <!--リプレッサーA,B,シグナル分子Sの時間変化を式として表し、安定性解析を行った結果、Hill係数が大切であることがわかった | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
<!--2.wet実験で求められた値を用いて解析を行った。集団が怠け者の細胞のみとなった場合に、一度不安定化し、続いて働き者と怠け者になることをStocastic Simulationで確認した。このシステムの挙動に必要な他のパラメータ範囲が判明した。--> | <!--2.wet実験で求められた値を用いて解析を行った。集団が怠け者の細胞のみとなった場合に、一度不安定化し、続いて働き者と怠け者になることをStocastic Simulationで確認した。このシステムの挙動に必要な他のパラメータ範囲が判明した。--> | ||
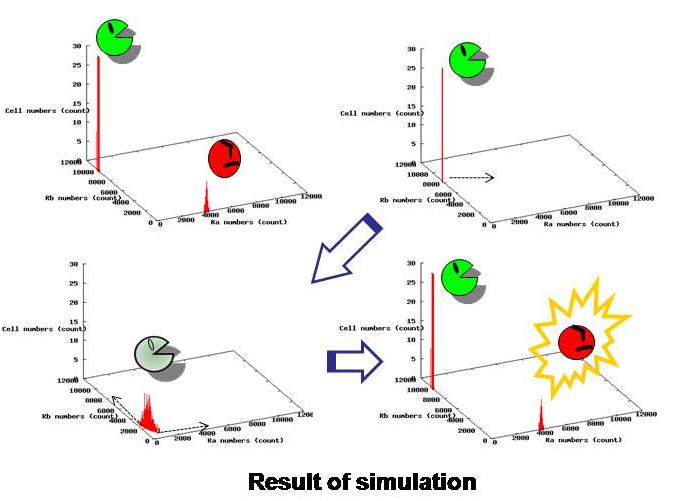
'''Using the data from actual experiments, we simulated behaviors of our model.''' | '''Using the data from actual experiments, we simulated behaviors of our model.''' | ||
| - | <br>Based on stochastic simulation using parameters obtained from our wet experiments, we confirmed that the whole system becomes unstable when there are only idlers left, and then, they become either | + | <br>Based on stochastic simulation using parameters obtained from our wet experiments, we confirmed that the whole system becomes unstable when there are only idlers left, and then, they become either workers or idlers. In addition, we determined other parameters necessary for the desired behavior of this system. '''([[Tokyo/Works/Simulation |See more.]])''' |
<!--最終日に動画と差し替え??--> | <!--最終日に動画と差し替え??--> | ||
Latest revision as of 05:28, 27 October 2007
Abstract Concept & Model Requirements Genetic_circuit Works About_our_team
0. Hybrid promoter 1. Formulation 2. Assay1 3. Simulation 4. Assay2 5. Future works
How to reach our goal
We have alternately implemented Wet and Dry experiments to achieve our goal
To establish our “balanced-differentiation” model, genetic circuit was developed. We drew a navigational chart on our project by Dry approaches, which was confirmed and reinforced by the data from Wet approaches. In short, we alternately conducted successive combinations of Dry and Wet approaches.
0. Wet : Hybrid promoter
First, the newly devised promoter sensed the Two inputs is necessary for the Genetic_circuit.
For initial attempts at regulating differentiation of E.coli by a set of two inputs, new hybrid promoter was designed . There is no desirable part among previous publications as well as BioBrick parts. Thus, we designed the parts that can be activated by LuxR and repressed by LacI . (Fig.1).These brand-new parts worked as designed (Fig.2).(See more.)
1.Dry : Formulation
Second, we tried to mathematically express our model.
From simple equations, the equations necessary for our model were deviated systematically. Though a parameter for production rate of AHL changes cell behavior from conventional mutual-inhibition model, Hill coefficients for the promoters are still critical for emergence of bistability.(See more.)
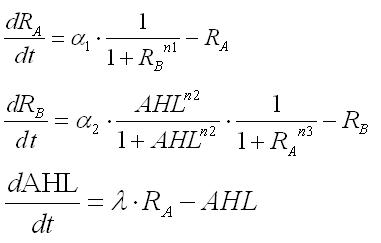
2.Wet : Assay1 using "Externally added" materials
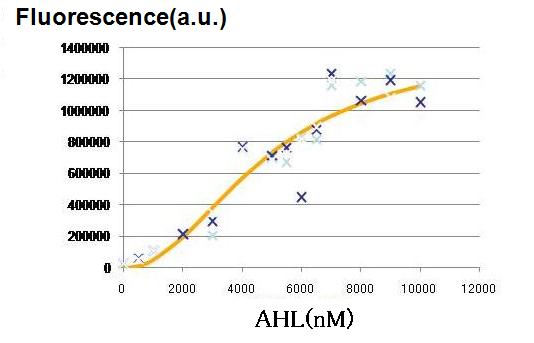
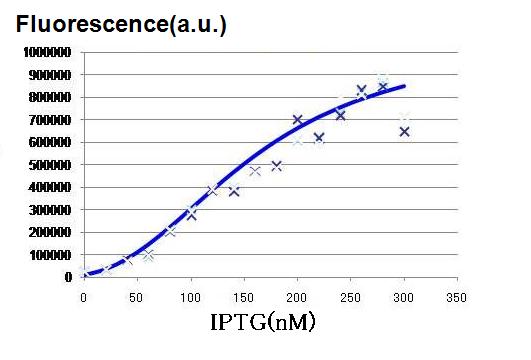
Though Hill coefficients are critical for the differentiation, adjustments of Hill coefficients by DNA sequence modification are much more difficult than those of the other production rate parameters; changes in RBS -35 box, or -10 box allow such easy modification. In order to confirm feasibility of our model, we focused to measure Hill coefficients of our new promoter part.(See more.)
3.Dry : Simulation
Using the data from actual experiments, we simulated behaviors of our model.
Based on stochastic simulation using parameters obtained from our wet experiments, we confirmed that the whole system becomes unstable when there are only idlers left, and then, they become either workers or idlers. In addition, we determined other parameters necessary for the desired behavior of this system. (See more.)
4.Wet : Assay2 on "Cell-produced" AHL and Expression comparison
Here the simulation results were tested by actual wet experiments.
Whether the parameters obtained in 3 is feasible in actual Wet experiments was tested by focusing on the amount of cell-produced AHL as well as the strength of the promoters. Indication from the result is applied for the next work.(See more.)
5.Future works
Through the experiments mentioned above, we have found that our model can be completed by changing some of the parts employed so far. Continuing such simulation oriented construction of genetic circuit, it will be increasingly necessary to exchange parts. Here we would like to offer useful means for part exchanges.
Based on the results from wet experiments, the next dry approach - analysis and simulation - should be performed, which will in turn be testified and confirmed by wet experiments. Continuing these processes, if time permits, would further sophisticate and complete our model. (See more.)