Tianjin/FLIP-FLOP
From 2007.igem.org
Lovecarrot (Talk | contribs) (→Design) |
Lovecarrot (Talk | contribs) (→Design) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
</font> | </font> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| + | [[Image:TJUzmlrules.jpg]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
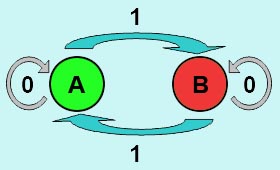
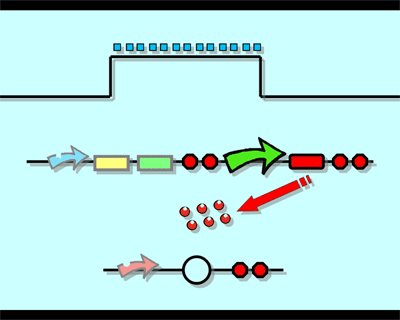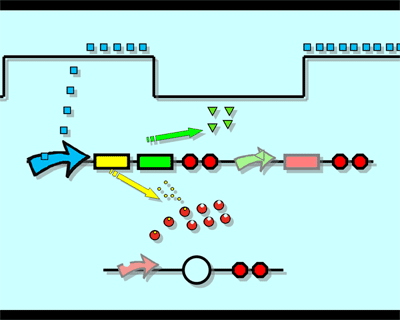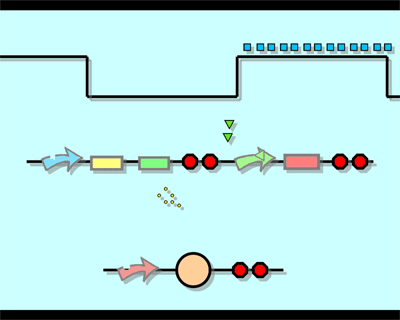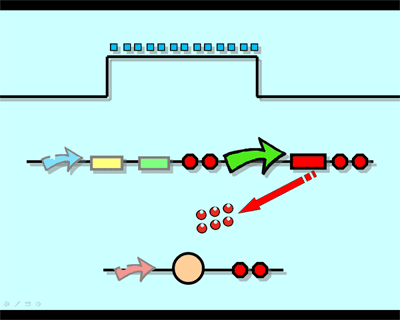
| + | The logic principle of our design is shown above. Unless the input signal transfer from one stable condition to another ( such as 0 to 1 or 1 to 0), the output signal would change into 1, otherwise it would maintain 0. Thus, the immediate response to emergency (input change) enables our design to detect signal variation in a short time, which is beneficial for process control because of its time-saving character. | ||
| + | |||
<font size="3" color="#0000CC">2.</font>[[Tianjin/FLIP-FLOP/Design1|<font size="3" color="#0000CC">Construction of Biological Circuit</font>]] | <font size="3" color="#0000CC">2.</font>[[Tianjin/FLIP-FLOP/Design1|<font size="3" color="#0000CC">Construction of Biological Circuit</font>]] | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 25 October 2007
Design"Flip-flop" is the common name given to two-state devices which offer basic memory for sequential logic operations. Flip-flops are widely used for digital data storage and transfer as well as in banks called "registers" for the storage of binary numerical data. Based on the conception of "Flip-flop" and synthetic biology, we designed the Genetically RS FLIP-FLOP whose output signal is regulated by additional input signal. Besides this, we modulate the performance of Genetically RS FLIP-FLOP to optimize our original design. 1.Introduction to the logic rules of our flip-flop
|
Modeling1.Construction of Mathematical Model 2.Model Result
|
|
==Experiment== |