Tokyo/Model
From 2007.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
''' To follow Pareto’s principle like [[Tokyo/Concepts|Ant society]], our model system must follow the three cases in Fig 1 to 3. In our model, all nodes (individual cells) have the same genetic circuits but take two states, A (worker) and B (idler), depending on the surrounding circumstances.''' | ''' To follow Pareto’s principle like [[Tokyo/Concepts|Ant society]], our model system must follow the three cases in Fig 1 to 3. In our model, all nodes (individual cells) have the same genetic circuits but take two states, A (worker) and B (idler), depending on the surrounding circumstances.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
'''Condition 1. Bistable state''' | '''Condition 1. Bistable state''' | ||
Revision as of 13:25, 23 October 2007
Abstruct Concept & Model Requirements Genetic_circuit Works About_our_team
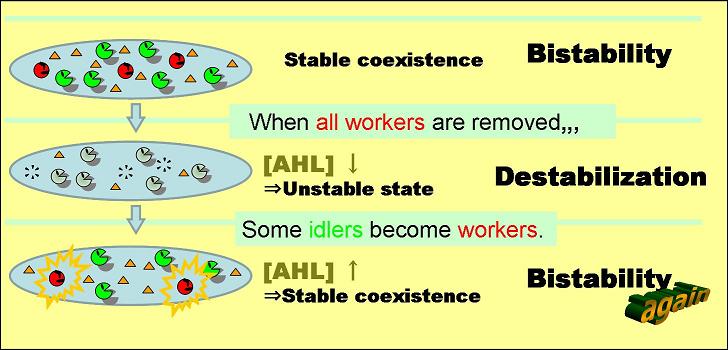
To follow Pareto’s principle like Ant society, our model system must follow the three cases in Fig 1 to 3. In our model, all nodes (individual cells) have the same genetic circuits but take two states, A (worker) and B (idler), depending on the surrounding circumstances.
Condition 1. Bistable state

Fig. 1 The system is stable containing nodes A and B at certain ratio.
Condition 2. Unstable state with node A removed

Fig. 2 By removal of node A, the system containing only node B becomes unstable.
Condition 3. From unstable to stable state
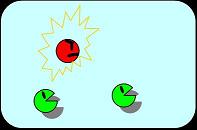
Fig. 3 In the unstable state, some node B become A while the others remain B. The system then becomes stable again.