USTC/OperatorComposition
From 2007.igem.org
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[USTC/NamingRules|Naming Rules for Oxx and Oxy below]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[Image:USTC_OperatorCompostions.png|thumb|right|400px]] | [[Image:USTC_OperatorCompostions.png|thumb|right|400px]] | ||
Revision as of 15:41, 26 October 2007
Naming Rules for Oxx and Oxy below
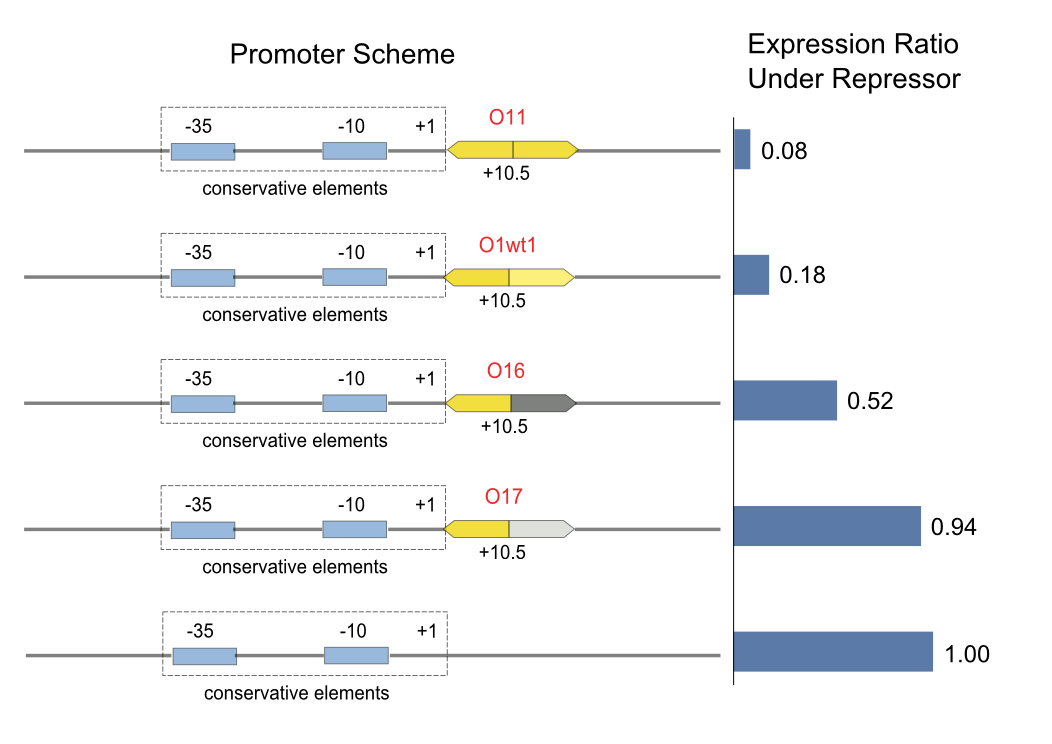
Generally, Lac repressor bind to its operator in the form of dimer [1]. Almost all the according operators in nature are of approximate reverse symmetric structure, that is, each half of the operators consists of about 10 nucleotides and receives the binding of a repressor monomer [2]. It has been reported that it is the perfectly symmetric operator that most tightly binds to native Lac repressor. Based on this fact, an idea was proposed that the binding affinity of a non-symmetric operator might be systematically reduced, exempt from the harm on the binding specificity of the repressor-operator pairs.
Five promoters have been synthesized and tested:
- O11, the perfectly symmetric operator
- O1wt1, the native lac operator at +11 site of Plac promoter
- O16, the right half of O11 replaced by a sequence that weakly binds to Lac repressor, but has the same pattern as O11's.
- O17, the right half of O11 replaced by a random sequence
- NUL, the positive control
After a series of experiments, we came to the conclusion that the method of replacing the right half of the symmetric operator can systematically reduce the binding affinity. Ox6, which means the right half of a symmetric operator is replaced by a weak operator sequence with the same pattern, can be used as a "weak" operator. At the same time, we found that the pattern Ox7 is weaker than that of Ox6, and the affinity of Ox7 is too low for a logic gate.
References
1. Lewis, M. (2005), 'The lac repressor.', C R Biol 328 (6), 521--548.
2. John R. Sadler, Henri Sasmor, and Joan L. Betz, A perfectly symmetric lac operator binds the lac repressor very tightly. PNAS Vol. 80, pp. 6785-6789, November 1983