Tokyo/Activation check by cell-produced AHL
From 2007.igem.org
Works top 0.Hybrid promoter 1.Formulation 2.Assay1 3.Simulation 4.Assay2 5.Future works
assay2
Activation check by cell-produced AHL
Expression level check on promoters + plasmid sets of A and B sides
Activation check by cell-produced AHL
Purpose
To check if worker E. coli (Sender) can produce enough AHL for our model to work by using different copy numbers of plasmids.
Samples
placI luxI on PSB1(high copy) and A4Δp(Sender 1)
placI luxI on PSB4(low copy) and A4Δp(Sender 2)
placI luxI on PBR322(low copy) and A4Δp(Sender 3)
(no promoter)tetR pBR322 and A4 Hybrid promoter(Receiver 1)
(no promoter)luxI pBR322 and A4Δp
Procedure
Start to prepare over night culture (1 tube for each)
Make fresh culture with 3 ul of the overnight culture in 3ml of LB + Amp + Kan (LBAK) (3 tubes for each)
Incubation in a shaker until the observed OD (ODobs) reaches up to 0.2
Equalize ODobs of all the samples by adding LB media.
Centrifugation at 5000 rpm and wash out the LB media.
Add cells with A4Δp and each of the following to 2.4 ml of LBAK
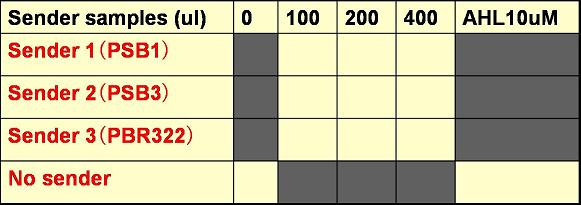
The experiments tested yellow boxes, not gray ones.
The total volume of E. coli culture (A4Δp and senders) was always 400 uM.
Wash
(incubate it until the OD obs. <0.20)
Stop incubation => Wash => FLA analysis(When OD reached 0.8)
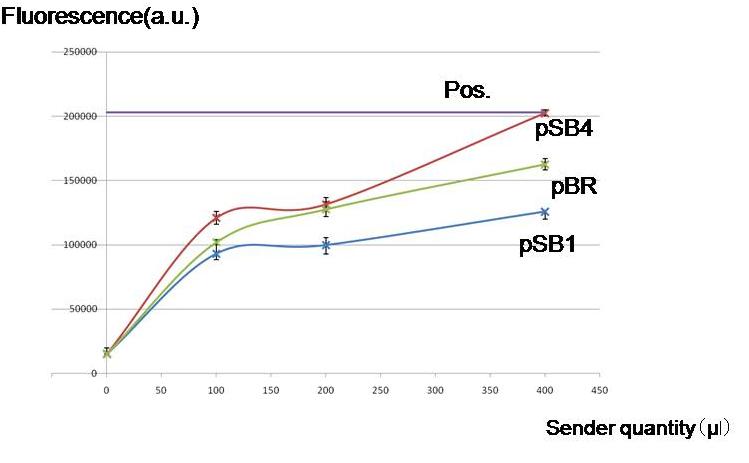
Results Conclusion
Not only high copy number plasmid pSB1, also low copy number plasmid pSB4 and pBR produced enough AHL to activate the LacI hybrid promoter in other cells. Especially, pSB4 remarkably produced AHL in the present experiment.