Chiba/Engeneering Flagella
From 2007.igem.org
(→About flagella) |
|||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
==Experiments== | ==Experiments== | ||
===[[Chiba/Flagella/Making_FliC-his|Making ''FliC-his'' gene]]=== | ===[[Chiba/Flagella/Making_FliC-his|Making ''FliC-his'' gene]]=== | ||
| - | * | + | *We inserted the gene of six histidine loop peptide (“His-Tag”) into the fliC D3 domain. |
| - | We inserted the gene of six histidine loop peptide (“His-Tag”). | + | |
[[Image:Chiba_flichisgene.png]]<br> | [[Image:Chiba_flichisgene.png]]<br> | ||
Revision as of 21:15, 26 October 2007
|
Introduction | Project Design ( 1.Sticky Hands | 2.Communication | 3.Size Control ) | Making Marimos | Our Goal || Team Members | メンバ連絡簿 |
Stickey Tags
Our Aim
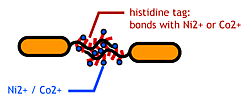
To make stickey hands on E.coli, we focused on their flagella that are located outside the cells. We used the following mechanisms:
- Display sticky peptides in flagellar filament.
- The imidazole group in histidines make a complex with metal ions.
We combined these two and made a His-tagged flagella in the hope to stick them together via metal ions.
About flagella
E.Coli have 5-10 flagella. The flagella is used for swimming and for chemotaxis; the bacteria run when they find attractant, tumble when there is a repellent.
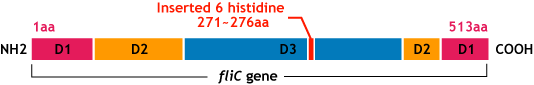
E.coli flagella consist of three parts: a basal body, a hook, and a filament. The filament of E.Coli is a rigid, helical, and cylindrical structure which is 10-15μm long and 23nm thick in diameter. It is built from ~20000 subunits of a ~55kDa single protein, FliC. FliC has three domains, D1,D2,D3; although D1 and D2 are needed for the formation of the functional flagellar filament, D3 domain which sticks outside of the fillament are not essential[1].
"Variable" FliC D3 domain
It is reported that the proteins up to 49.4kDa could be displayed on the cell surface of E.Coli using flagellin fusion protein.[2]
References
- Kuwajima, G. et al.: Nature Biotechnology, 6, 1080-1083 (1988).
- Tanskanen, J. et. al.: Appl. and Env. Microbiol., 4152-4156 (2000)
About Histidine Tag
See [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/His-tag wikipedia article].
Experiments
Making FliC-his gene
- We inserted the gene of six histidine loop peptide (“His-Tag”) into the fliC D3 domain.
![]() Sequence Confirmed
Sequence Confirmed
![]() Swarm Confirmed
Swarm Confirmed
![]() Flagella strained with anti-flagella antibody
Flagella strained with anti-flagella antibody
Checking the "Stickiness": Beads Adsorption
Purpose
Confirm that the his-tag are displaied on the flagella and are capable of binding to Co2+-surface.
Samples
- JW1908(⊿fliC株)
- pUC19-fliC-his
- plasmidなし
- GI826(⊿fliC⊿motB株)
- pUC19-fliC-his
- plasmidなし
Procedure
- pUC19-FliC-His was transformed to JW1908(fliC) and GI826(fliC motB)
- 培養液をビーズと懸濁させ、大腸菌をBeadsに吸着する。
- 吸着した大腸菌をbufferで溶出し、incubate。
Results&Discussion
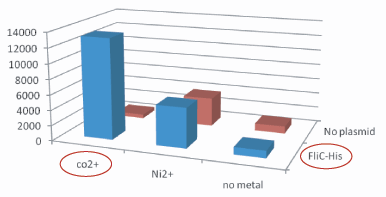
1.Stickiness check
- Plasmidあり、かつCo2+つきビーズ、のコロニー数は、その他のものよりはるかに多い。30倍以上。
- Histidine Tagの存在によって大腸菌がビーズに吸着吸着していることがわかる。
- The number of colony dramatically decreased with out Co2+ or FliC-His plasmid.
- 考察も書いたら? なぜコバルトがニッケルより良いのか?→一般的にニッケルよりコバルトの方が結合力が強いことが知られてて,FilChisに関してもそれは変わらないみたいな・・・by tashiro
2.Strainの比較(データ?)
|
Strain |
Co2+ |
No metal |
|
JW1908 |
吸着していない |
吸着していない |
|
GI826 |
吸着していた |
吸着していない |