Imperial/Infector Detector/F2620 Comparison
From 2007.igem.org
m |
m (→Summary of Comparison) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
=Summary of Comparison= | =Summary of Comparison= | ||
| - | + | We compared our ''in vitro'' characterisation to the characterisation of [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_F2620 F2620] ''in vivo'' to highlight some of the differences between the chassis and investigate how the constructs characteristics may change between chassis. The [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_F2620 F2620] is an ideal construct to compare for comparison because of its detailed characterisation ''in vivo''. The construct is the same as the construct 1 that was used for infecter detector, '''pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFPmut3b'''. The key results the comparison were; | |
| - | *The | + | *The creation of a new unit to allow comparison between ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo'' chassis. |
*The constructs response appears to be largely independent of the chassis used. | *The constructs response appears to be largely independent of the chassis used. | ||
Both of these are important findings and highlight the potential that new chassis offer to synthetic biology. | Both of these are important findings and highlight the potential that new chassis offer to synthetic biology. | ||
Revision as of 00:51, 26 October 2007

Summary of Comparison
We compared our in vitro characterisation to the characterisation of F2620 in vivo to highlight some of the differences between the chassis and investigate how the constructs characteristics may change between chassis. The F2620 is an ideal construct to compare for comparison because of its detailed characterisation in vivo. The construct is the same as the construct 1 that was used for infecter detector, pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFPmut3b. The key results the comparison were;
- The creation of a new unit to allow comparison between in vitro and in vivo chassis.
- The constructs response appears to be largely independent of the chassis used.
Both of these are important findings and highlight the potential that new chassis offer to synthetic biology.
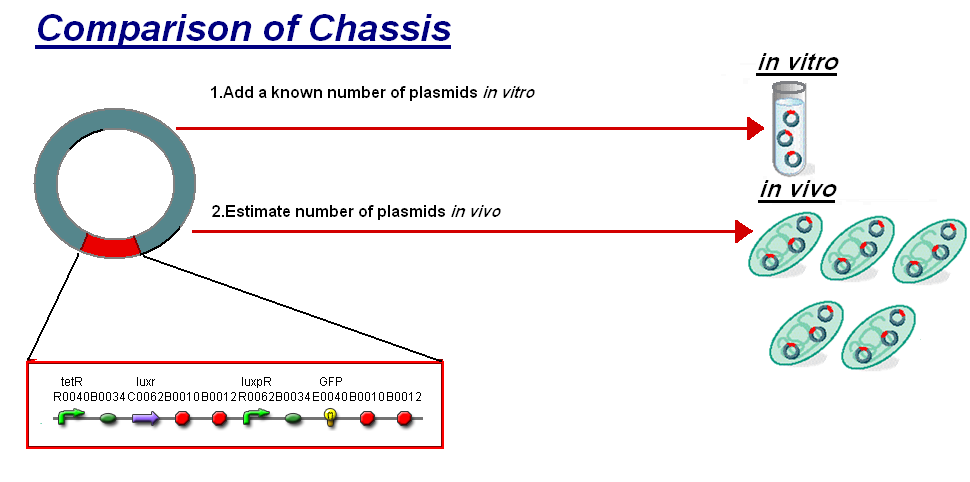
For further analysis the results of our in vitro testing have been compared to the work in vivo on BBa_F2620(pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFPmut3b), the construct being the same as our construct 1 for infecter detector. The motivation of the comparison is to see how this construct will respond in different chassis. To do this we investigated a standard unit s to allow the comparison between in vitro and in vivo.
The basis for comparison is to normalise the in vitro chassis on the number of plasmids to give a platform for comparison:
- In Vitro - 4µg of DNA was added which for pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFPmut3b is 904823007 plasmids
- In Vivo - Each cell the plasmids number was estimated at 30 per cell
To compare we normalised the data of in vitro GFPmut3b molecules synthesised per 30 plasmids to allow some comparison to the in vivo data.
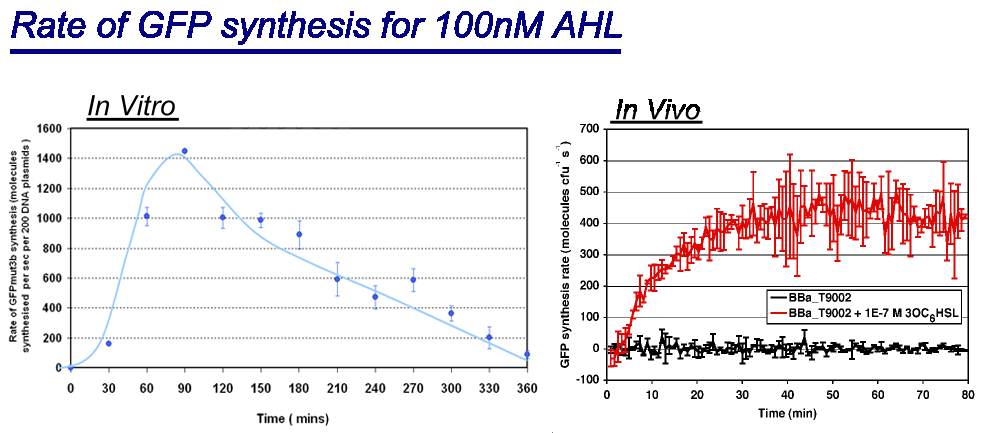
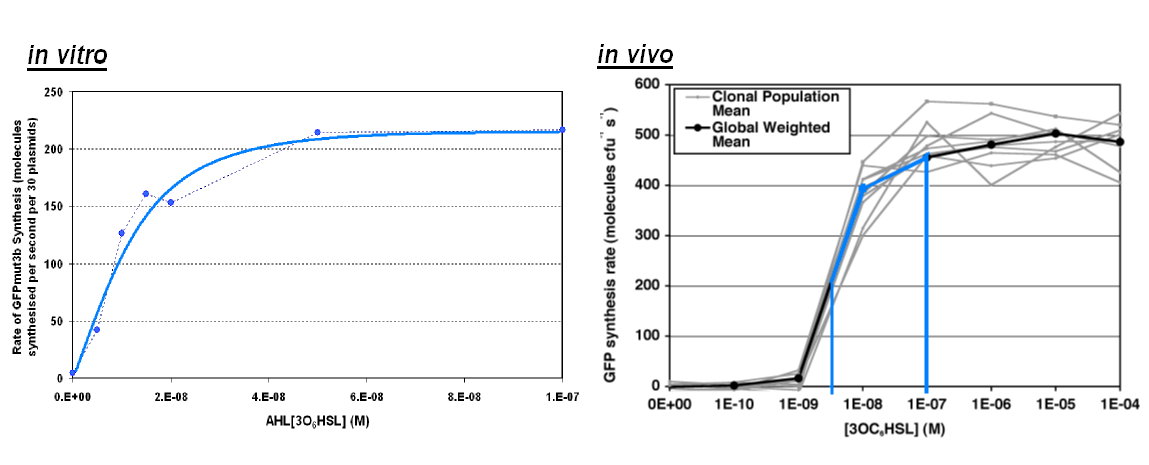
Of particular interest was to compare the:
- Rate of GFP synthesis of 100nM
- Transfer Function.