Imperial/Infector Detector/F2620 Comparison
From 2007.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Transfer Function) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
| - | {|align="center" | + | {|align="center" style="text-align: center; border-top:2px solid #000077; border-right:2px solid #000077; border-bottom:2px solid #000077; border-left:2px solid #000077;" |
| - | + | |<center>[[image:IC2007 BF stage1 construct.PNG |700px]]</center> | |
| - | | | + | {|style="width:800px; text-align: left;" border="0" |
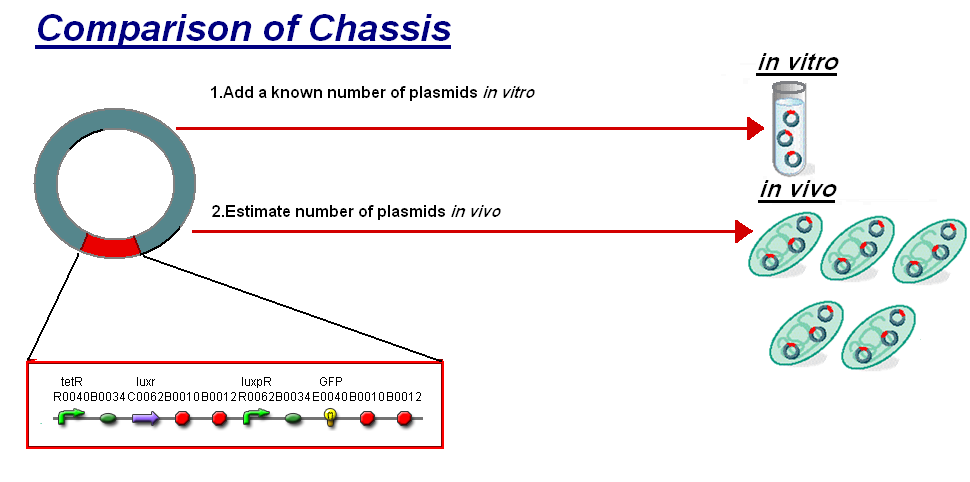
| - | + | |<br>The basis for comparison is to normalise the ''in vitro'' chassis on the number of plasmids to give a platform for comparison: | |
| - | The basis for comparison is to normalise the ''in vitro'' chassis on the number of plasmids to give a platform for comparison: | + | |
*''In Vitro'' - 4µg of DNA was added which for [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_T9002 '''pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFPmut3b'''] is 904823007 plasmids | *''In Vitro'' - 4µg of DNA was added which for [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_T9002 '''pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFPmut3b'''] is 904823007 plasmids | ||
*''In Vivo'' - Each cell the plasmids number was estimated at 30 per cell | *''In Vivo'' - Each cell the plasmids number was estimated at 30 per cell | ||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
#'''Rate of GFP synthesis''' of 100nM | #'''Rate of GFP synthesis''' of 100nM | ||
#'''Transfer Function'''. | #'''Transfer Function'''. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 19:39, 26 October 2007

Summary of Comparison
We compared our in vitro characterisation to the characterisation of [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_F2620 F2620] in vivo with the aim to highlight some of the differences between the chassis and investigate how the constructs characteristics may change between them. The [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_F2620 F2620] is an ideal construct to compare for comparison because of its detailed characterisation in vivo. The construct is the same as the construct 1 that was used for infecter detector, pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFPmut3b. The key results the comparison were;
- The creation of a new unit to allow comparison between in vitro and in vivo chassis.
- The constructs response appears to be largely independent of the chassis used.
Both of these are important findings and highlight the potential that new chassis offer to synthetic biology.
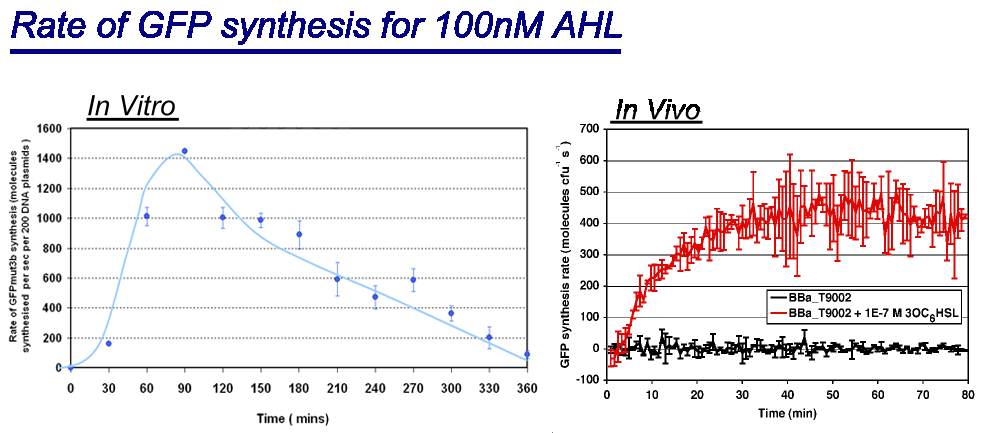 Comparison between in vivo and in vitro for rate of GFPmut3b synthesis for 100nM AHL. The in vivo chassis used was the bacterial strain MG1655 and the in vitro chassis was Promega Commercial S30 Cell Extract. The graph shows the following: *in vivo has a maximal rate of 400-500 molecules of GFP synthesised per second per cell. In addition the rate reaches a steady state after around 30minutes and maintains it for the duration of the testing. *in vitro has the equivalent of 220 molecules of GFP synthesised per second per cell equivalent, the cell equilavent being based upon the normalization of DNA plasmids. Interestingly the in vitro chassis does not reach a steady state, in fact it decreases in rate of synthesis after 90 minutes and keeps decreasing until rate is zero at around 360 minutes. The reason why the in vitro chassis never reaches a steady state is because of the limited energy and metabolites available, this is unlike in vivo which is supported by the media that it is grown upon. Interestingly the values of rate of synthesis are in the same order magnitude of hundreds, this suggesting that the normalisation we are using to compare these chassis is valid. |
Transfer Function
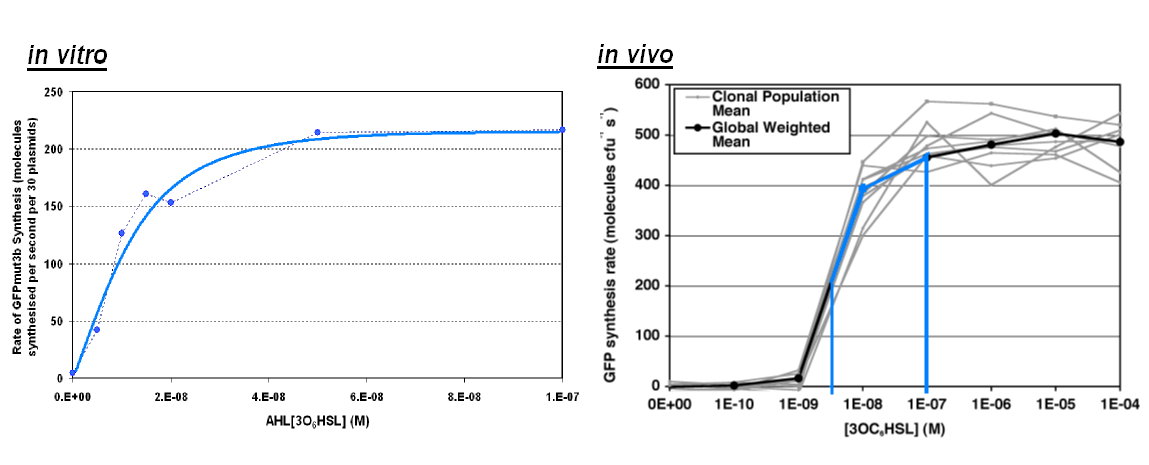 The graph above shows the transfer function of [AHL] input vs rate of GFP synthesis output. The graph shows the max rate of synthesis for each of the chassis; for in vivo this is the steady state reached after about 30 minutes and for in vitro it is the rate between 60 and 90 minutes which is the maximum rate before the energy limitations of the system cause the rate to drop. The blue line on corresponds to the range of AHL and the response of the in vitro chassis. The key difference between the chassis is the rate of GFP synthesis which is lower in the in vitro chassis e.g. for 1000nM of AHL the rate of GFP synthesis in vivo is ~450 GFP molecules per sec per cell, in vitro has an equivalent value of 220 GFP molecules per second. The shape of the transfer function is very similar for both chassis, both begin to saturate at around 1000nM of AHL and the threshold of sensitivity is around 1nM AHL. It is very surprising that a construct works so similar in different chassis, showing the affect of the chassis is minimal to the constructs behavior. |