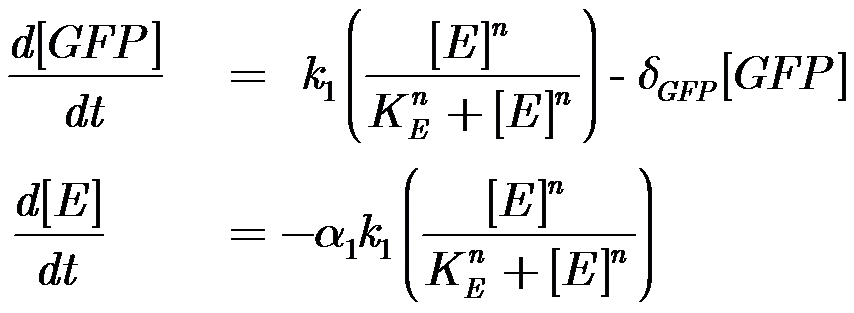Imperial/Cell by Date/Modelling
From 2007.igem.org
(→Navigation) |
m |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:IC07navmenu}} | {{Template:IC07navmenu}} | ||
| + | <br clear="all"> | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/igem07/index.php?title=User:Dirkvs/Stylesheets/IC07persist.css&action=raw&ctype=text/css" type="text/css" /> | <link rel="stylesheet" href="/igem07/index.php?title=User:Dirkvs/Stylesheets/IC07persist.css&action=raw&ctype=text/css" type="text/css" /> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
==Modelling the spoilage of Aerobically Stored Ground Hamburger Meat== | ==Modelling the spoilage of Aerobically Stored Ground Hamburger Meat== | ||
| - | + | [[Image:CBDKoutsoumanisModel.jpg]] | |
| - | Image: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | <br clear = "all" > | ||
| - | + | A substantial body of work already exists on the topic of spoilage of ground beef by living organisms. The above figure shows the results of a model developed by Koutsoumanis (1) to simulate the spoilage under dynamic temperature conditions of meat by Pseudomonas, - an organism responsible for spoiling refrigerated packaged beef.<br><br> | |
| + | An important property was the almost instantaneous response time of the Pseudomonas' growth parameter. To report accurately our system should therefore also share this property.<br><br> | ||
| + | Koutsoumanis' model, along with Giannuzzi ‘s (2) are both based on the larger class of Gompertz model. A remarkable feature of such models is that through manipulation of the Gompertz Parameters and assuming a Arrhenius type relationship between Pseudomonas' growth parameter and temperature we can infer the Activation energy of the spoilage reaction(3)(See figure below).<br><br> | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:CBDModellingGianuzziAndEquations.png]]<br clear = "all"> |
| - | + | Above we can see an arrhenius plot (the log version of the arrhenius equation) of the certain interesting combinations of the parameters in the modifired Gompertz equation such as the Lag Phase Duration (LPD). Doing such a plot allows us to calculate the activation energy of the spoilage reaction. | |
| - | + | ||
| + | As given in our specifications the Activation energy for ground meat seem to be around 30kJ/mol. Again to report accurately our system needs to have a similar activation energy.<br><br><br clear = "all"> | ||
| - | |||
==Modelling our system: Energy-limited constitutive expression by pTET-mut3BGFP== | ==Modelling our system: Energy-limited constitutive expression by pTET-mut3BGFP== | ||
| - | [[Image:CBDFPconcmodel.jpg|thumb|left|420px]][[Image:CBDEnergyDepletionModel.jpg|thumb|right|420px]] | + | [[Image:CBDFPconcmodel.jpg|thumb|left|420px]][[Image:CBDEnergyDepletionModel.jpg|thumb|right|420px]]<br clear="all"> |
| - | <br clear ="all"> | + | |
| + | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
[[Image: CBDModel.png|thumb|left|382px|Energy-dependent model for CBD]] | [[Image: CBDModel.png|thumb|left|382px|Energy-dependent model for CBD]] | ||
| - | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="2" style="text-align:right; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1px #aaa solid; border-collapse: collapse;" | + | {|align right class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="2" style="text-align:right; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1px #aaa solid; border-collapse: collapse;" |
! Parameter | ! Parameter | ||
! Description | ! Description | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
|Positive Cooperativity Coefficient (Hill-coefficient) | |Positive Cooperativity Coefficient (Hill-coefficient) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | |delta;<sub>GFP</sub> | + | |δ<sub>GFP</sub> |
|Decay constant of mut3BGFP | |Decay constant of mut3BGFP | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
'''here''' ''δ<sub>GFP</sub> = 0.0005<br>'' | '''here''' ''δ<sub>GFP</sub> = 0.0005<br>'' | ||
| + | <br clear ="all"> | ||
| + | In order to use the previous results on how Pseuodmonas spoils aerobically stored ground beef we need to understand how our sytem behaves in similar scenarios to the models developed by Koutsoumanis and Giannuzi.<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For isothermal conditions we have been able to develop a simple model of the gene expression in a cell free extract (see chassis characterisation [[Imperial/Cell-Free/Whatis|Cell Free Systems]]) . | ||
| + | An important feature of the model was the introduction of a resource dependent term that curbs the synthesis if the system is depleted. <br><br> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
The m-files used in the following simulations can be accessed on our [[Imperial/Dry_Lab/Software#Download CBD Simulations| Software]] page. | The m-files used in the following simulations can be accessed on our [[Imperial/Dry_Lab/Software#Download CBD Simulations| Software]] page. | ||
| - | |||
| Line 78: | Line 81: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| - | # [http:// | + | # [http://aem.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/72/1/124 Koutsoumanis K, Stamatiou A, Skandamis P, Nychas GJ. Development of a Microbial Model for the Combined Effect of Temperature and pH on Spoilage of Ground Meat, and Validation of the Model under Dynamic Temperature Conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Jan;72(1):124-34.] |
# [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T7K-3S3M25D-B&_user=217827&_coverDate=01%2F06%2F1998&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000011279&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=217827&md5=80630ba21fbc6869b9f5179d334734da Giannuzzi L, Pinotti A, Zaritzky N. Mathematical modelling of microbial growth in packaged refrigerated beef stored at different temperatures. Int J Food Microbiol. 1998 Jan 6;39(1-2):101-10.] | # [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T7K-3S3M25D-B&_user=217827&_coverDate=01%2F06%2F1998&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000011279&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=217827&md5=80630ba21fbc6869b9f5179d334734da Giannuzzi L, Pinotti A, Zaritzky N. Mathematical modelling of microbial growth in packaged refrigerated beef stored at different temperatures. Int J Food Microbiol. 1998 Jan 6;39(1-2):101-10.] | ||
# [http://66.102.1.104/scholar?hl=en&lr=&q=cache:thi6BTIW1YMJ:www.vitsab.com/PDF/V507.pdf+TTI+Beef+Activation+Energy Leak, F.W. (2000): Quality changes in Ground beef during distribution and storage, and determination of Time- Temperature-Indicator (TTI) charakteristic of ground beef University of Florida Institute of food and Agricultural Sciences Internet: www.vitsab.com, Stand: April 2003] | # [http://66.102.1.104/scholar?hl=en&lr=&q=cache:thi6BTIW1YMJ:www.vitsab.com/PDF/V507.pdf+TTI+Beef+Activation+Energy Leak, F.W. (2000): Quality changes in Ground beef during distribution and storage, and determination of Time- Temperature-Indicator (TTI) charakteristic of ground beef University of Florida Institute of food and Agricultural Sciences Internet: www.vitsab.com, Stand: April 2003] | ||
#[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T7K-4CP14B0-2&_user=217827&_coverDate=11%2F15%2F2004&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000011279&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=217827&md5=cf92d0ca2566b940589f521601b36eca Lopez, 2004 : Critique of Gompertz Model]<br> | #[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T7K-4CP14B0-2&_user=217827&_coverDate=11%2F15%2F2004&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000011279&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=217827&md5=cf92d0ca2566b940589f521601b36eca Lopez, 2004 : Critique of Gompertz Model]<br> | ||
#[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T7K-485PCG5-3&_user=217827&_coverDate=11%2F01%2F2003&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000011279&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=217827&md5=608c478638b6d194576d0f151be2223f Huang, 2003 Simulation of a Similar Problem using Gompertz Model]<br> | #[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T7K-485PCG5-3&_user=217827&_coverDate=11%2F01%2F2003&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000011279&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=217827&md5=608c478638b6d194576d0f151be2223f Huang, 2003 Simulation of a Similar Problem using Gompertz Model]<br> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:28, 27 October 2007

Cell by Date: Modelling
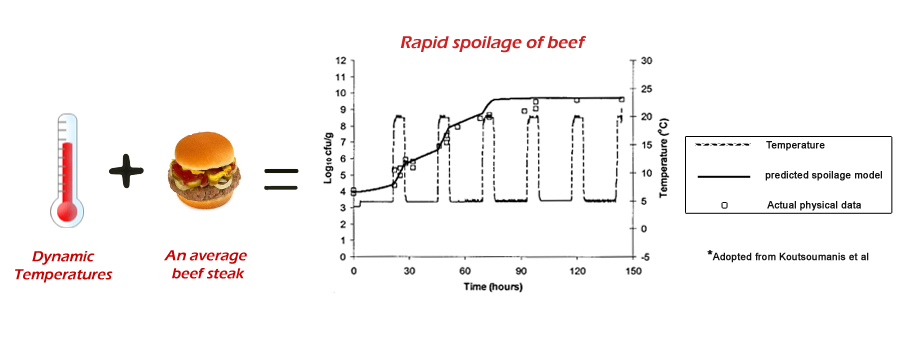
Modelling the spoilage of Aerobically Stored Ground Hamburger Meat
A substantial body of work already exists on the topic of spoilage of ground beef by living organisms. The above figure shows the results of a model developed by Koutsoumanis (1) to simulate the spoilage under dynamic temperature conditions of meat by Pseudomonas, - an organism responsible for spoiling refrigerated packaged beef.
An important property was the almost instantaneous response time of the Pseudomonas' growth parameter. To report accurately our system should therefore also share this property.
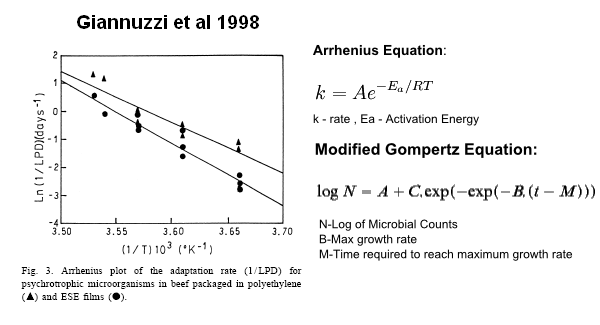
Koutsoumanis' model, along with Giannuzzi ‘s (2) are both based on the larger class of Gompertz model. A remarkable feature of such models is that through manipulation of the Gompertz Parameters and assuming a Arrhenius type relationship between Pseudomonas' growth parameter and temperature we can infer the Activation energy of the spoilage reaction(3)(See figure below).
Above we can see an arrhenius plot (the log version of the arrhenius equation) of the certain interesting combinations of the parameters in the modifired Gompertz equation such as the Lag Phase Duration (LPD). Doing such a plot allows us to calculate the activation energy of the spoilage reaction.
As given in our specifications the Activation energy for ground meat seem to be around 30kJ/mol. Again to report accurately our system needs to have a similar activation energy.
Modelling our system: Energy-limited constitutive expression by pTET-mut3BGFP
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| k1 | Maximal constitutive transcription by pTET |
| KE | Half-Saturation Coefficient for Energy Hill function |
| n | Positive Cooperativity Coefficient (Hill-coefficient) |
| δGFP | Decay constant of mut3BGFP |
here δGFP = 0.0005
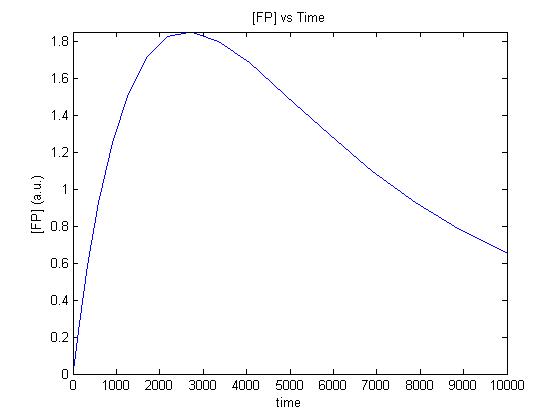
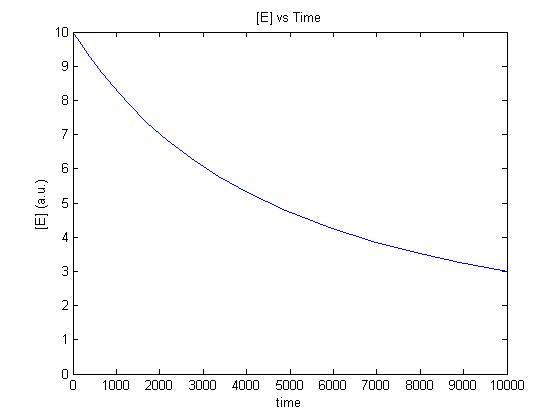
In order to use the previous results on how Pseuodmonas spoils aerobically stored ground beef we need to understand how our sytem behaves in similar scenarios to the models developed by Koutsoumanis and Giannuzi.
For isothermal conditions we have been able to develop a simple model of the gene expression in a cell free extract (see chassis characterisation Cell Free Systems) .
An important feature of the model was the introduction of a resource dependent term that curbs the synthesis if the system is depleted.
The m-files used in the following simulations can be accessed on our Software page.
References
- [http://aem.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/72/1/124 Koutsoumanis K, Stamatiou A, Skandamis P, Nychas GJ. Development of a Microbial Model for the Combined Effect of Temperature and pH on Spoilage of Ground Meat, and Validation of the Model under Dynamic Temperature Conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Jan;72(1):124-34.]
- [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T7K-3S3M25D-B&_user=217827&_coverDate=01%2F06%2F1998&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000011279&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=217827&md5=80630ba21fbc6869b9f5179d334734da Giannuzzi L, Pinotti A, Zaritzky N. Mathematical modelling of microbial growth in packaged refrigerated beef stored at different temperatures. Int J Food Microbiol. 1998 Jan 6;39(1-2):101-10.]
- [http://66.102.1.104/scholar?hl=en&lr=&q=cache:thi6BTIW1YMJ:www.vitsab.com/PDF/V507.pdf+TTI+Beef+Activation+Energy Leak, F.W. (2000): Quality changes in Ground beef during distribution and storage, and determination of Time- Temperature-Indicator (TTI) charakteristic of ground beef University of Florida Institute of food and Agricultural Sciences Internet: www.vitsab.com, Stand: April 2003]
- [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T7K-4CP14B0-2&_user=217827&_coverDate=11%2F15%2F2004&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000011279&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=217827&md5=cf92d0ca2566b940589f521601b36eca Lopez, 2004 : Critique of Gompertz Model]
- [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T7K-485PCG5-3&_user=217827&_coverDate=11%2F01%2F2003&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000011279&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=217827&md5=608c478638b6d194576d0f151be2223f Huang, 2003 Simulation of a Similar Problem using Gompertz Model]