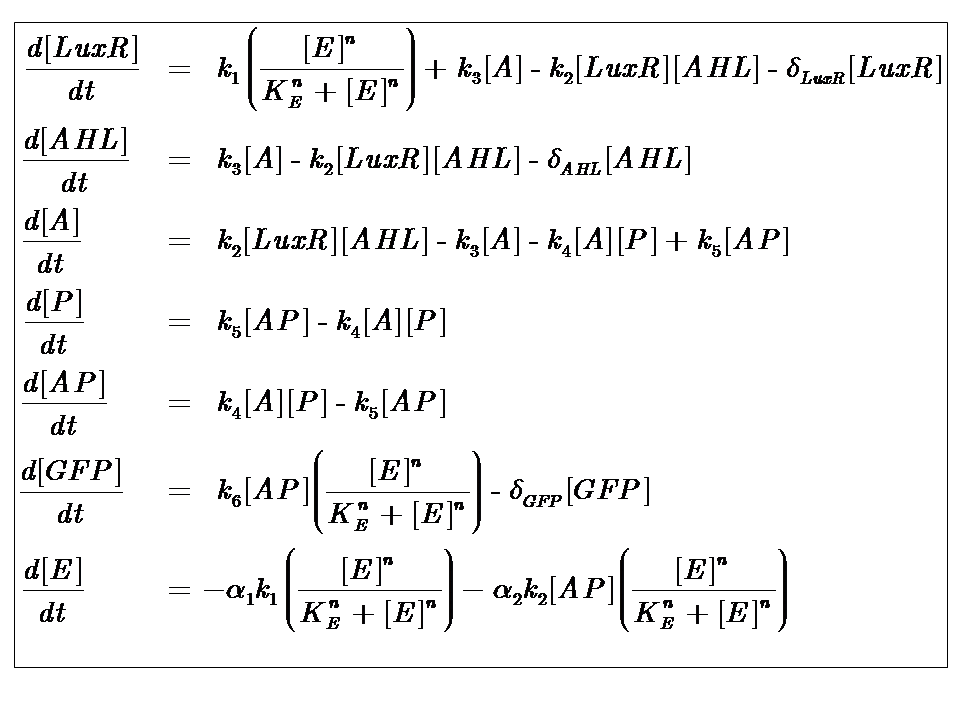Imperial/Infector Detector/Modelling
From 2007.igem.org
(→Simulations) |
|||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
Presented below are the most essential features of the simulation performed. | Presented below are the most essential features of the simulation performed. | ||
| - | + | [[Image: IC07 Construct comp.png|thumb|left|700px]] | |
Revision as of 10:03, 24 October 2007

Infector Detector: Modelling
Abstract
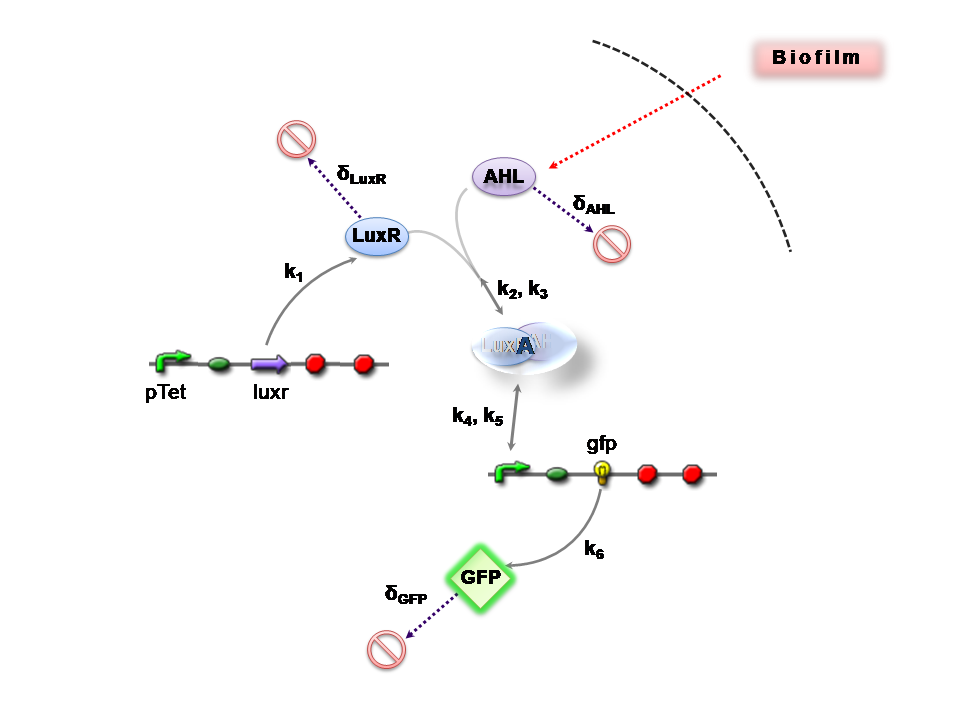
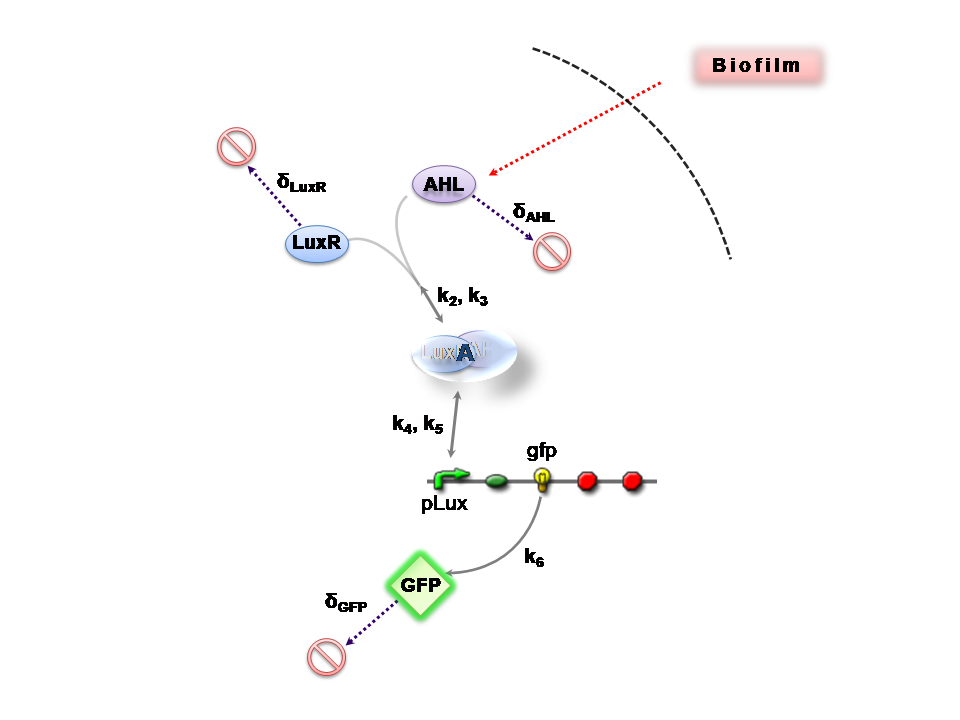
Infector Detector (ID) is a simple biological detector, which serves to expose bacterial biofilm. It functions by exploiting the inherent AHL (Acetyl Homoserine Lactone) production employed by certain types of quorum-sensing bacteria, in the formation of such structures.
This section presents a preliminary model for an AHL detector, which employs the backbone of the Lux quorum-sensing feedback mechanism. Figure 1 illustrates the full system we are investigating.
In the design phase, two possible system constructs were proposed, as a solution to the problem of detecting AHL-producing biofilm. According to our specifications, the most crucial feature of this system is the sensitivity to a minimum [AHL] of 5nm. In other words, this represents the minimal AHL concentration for appreciable expression of a chosen reporter protein. Furthermore, we attempt to establish a functional range for possible AHL detection. How does increased AHL concentration impact on the maximal output of reporter protein? Finally, how can the system performance be tailored, by exploiting possible inputs to the system (e.g. varying initial LuxR concentration and/or concentration of pLux promoters). In performing such customization, what is the impact upon the maximal output of fluorescent reporter protein and/or response time?
We attempt to answer these questions by conducting a simulation of the system in-silico.
Implementation & Reaction Network
Representative Model
At reasonably high molecular concentrations of the state variables, a continuous model can be adopted, which is represented by a system of ordinary differential equations.
It is for this reason that our approach to modelling the system follows a deterministic, continuous approximation. In developing this model, we were interested in the behaviour at steady-state, that is when the system has equilibrated and the concentrations of the state variables remain constant.
We can condition the system in various manners, but for the purposes of our project, we will seek a formulation which is valid for both constructs considered, i.e. the governing equations are a represenation of both constructs.
The only difference is with regards to the parameter k1, the maximum transcription rate of the constitutive promoter (pTET) in Construct 1.
Thus k1 = 0 for construct 2 (which lacks pTET).
Our analysis took us through a number of models, but presented here is the most pertinent, most representative version. This model is based on energy-dependence (limited nutrient supply), which follows Hill-like dynamics.
The system kinetics are determined by the following coupled-ODEs. For a derivation of the governing equations, please access
Model Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Kinetic Constants | |
| k1 | Maximal constitutive transcription of LuxR by pTET |
| k2 | Binding between LuxR and AHL |
| k3 | Dissociation of protein complex LuxR-AHL (A) |
| k4 | Binding between A and pLux promoter |
| k5 | Dissociaton of A-pLux complex |
| k6 | Transcription of FP |
| Degradation Rates | |
| δLuxR | Degradation rate of LuxR |
| δAHL | Degradation rate of AHL |
| δGFP | Degradation rate of GFP |
| Hill Co-operativity | |
| n | Co-operativity coefficient describing the degree of energy dependence, which follows Hill-like dynamics |
| Energy consumption of transcription | |
| α1 | Energy consumption due to constitutive transcription of LuxR |
| α2 | Energy consumption due to transcription of gfp gene |
Simulations
Presented below are the most essential features of the simulation performed.