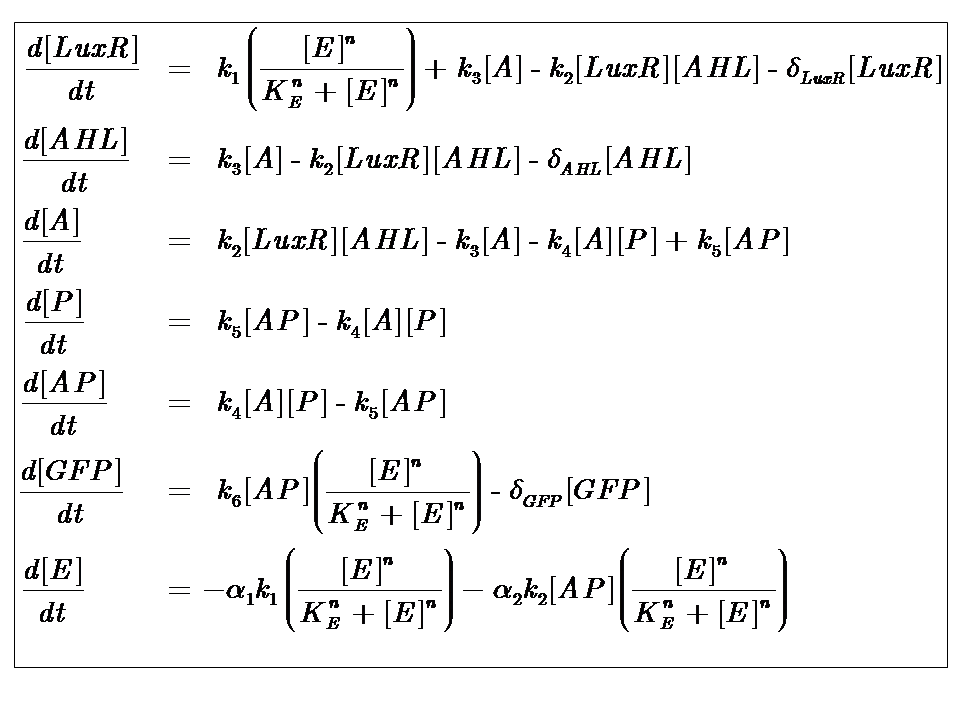Imperial/Infector Detector/Modelling
From 2007.igem.org
(→Discussion) |
(→Discussion) |
||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
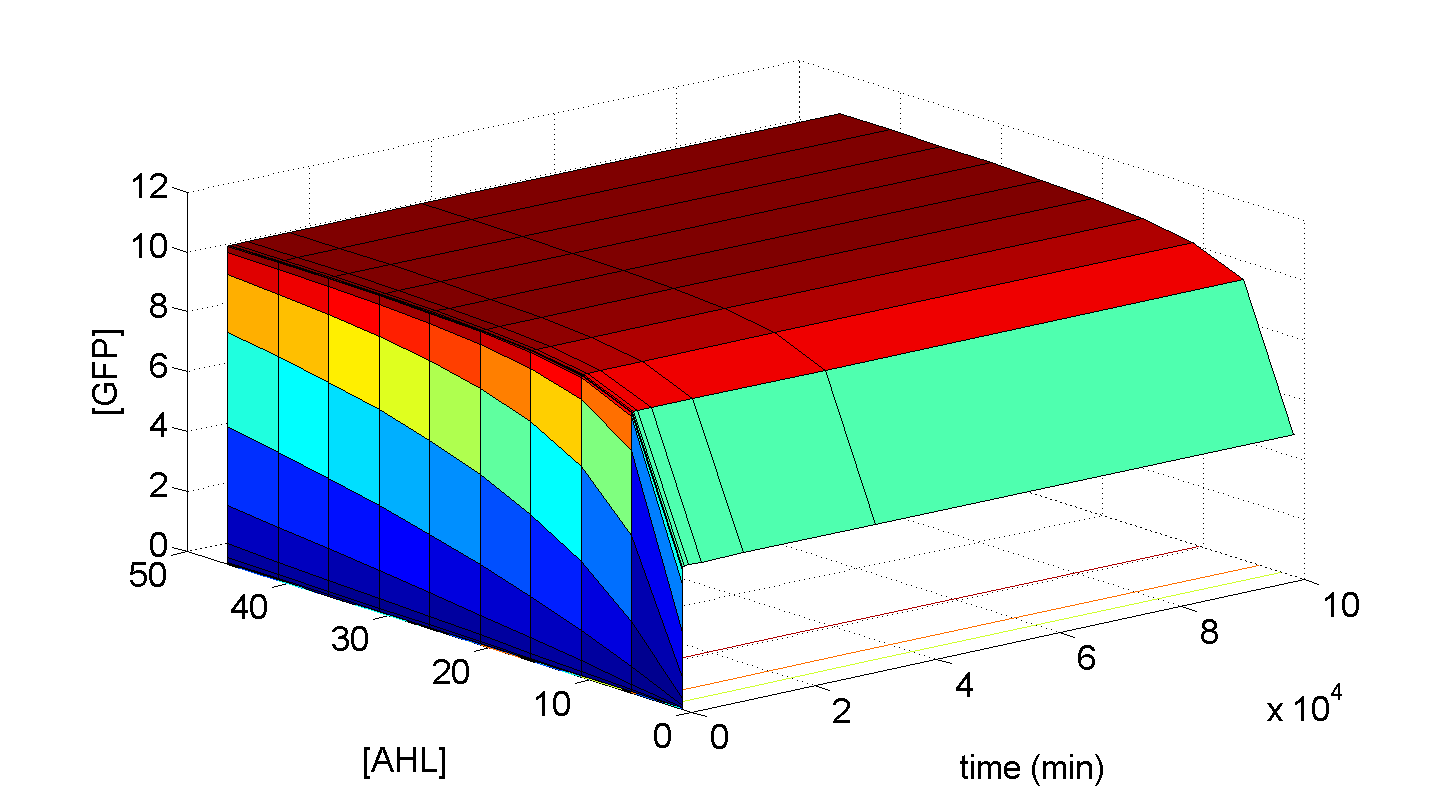
As initial [AHL] is increased, the level of expression increases accordingly to a point were there is negligible difference between the maximal outputs between adjacent tested cases of [AHL]. In fact, from this figure, and for this set of parameters, it is suggestive that saturation occurs at approximately 5 a.u.; in fact, the difference in maximal GFP output between when AHL is increased a several-fold is less than 10%. | As initial [AHL] is increased, the level of expression increases accordingly to a point were there is negligible difference between the maximal outputs between adjacent tested cases of [AHL]. In fact, from this figure, and for this set of parameters, it is suggestive that saturation occurs at approximately 5 a.u.; in fact, the difference in maximal GFP output between when AHL is increased a several-fold is less than 10%. | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | Figure 6, the energy depletion plot, serves to illustrate the effect of increased initial concentrations of AHL. More resources (promoters) need to be employed to accommodate the increasing [AHL]. This obviously increases the rate of energy depletion, until it reaches a saturating value, as saturating behaviour has been attained - promoter saturation. This is the likely explanation for the saturation curve, since the protein degradation terms themselves are almost negligible. | ||
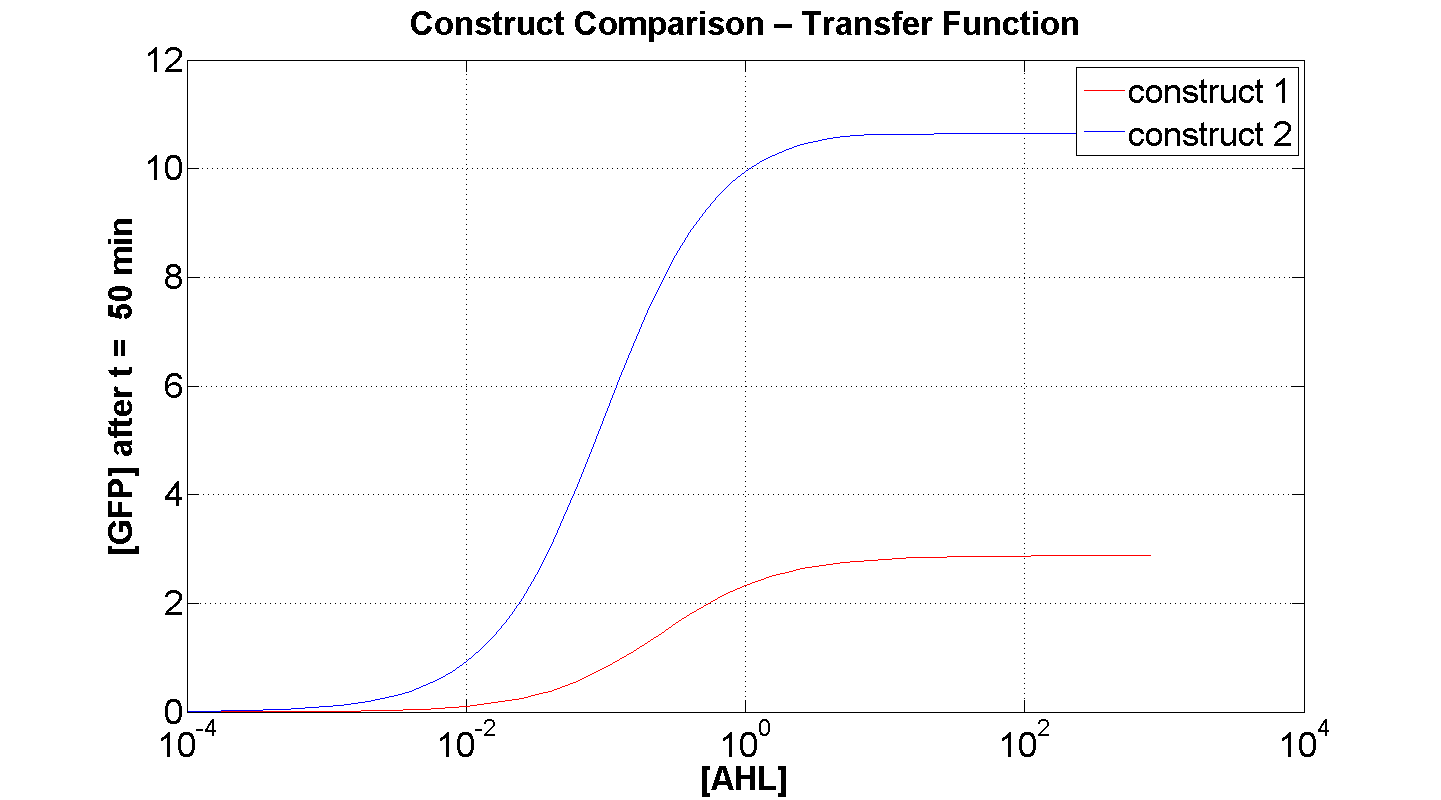
====2. Comparison of constructs: [GFP] vs [AHL] - transfer function curve==== | ====2. Comparison of constructs: [GFP] vs [AHL] - transfer function curve==== | ||
Revision as of 19:16, 26 October 2007

Infector Detector: Modelling
Abstract
Infector Detector (ID) is a simple biological detector, which serves to expose bacterial biofilm. It functions by exploiting the inherent AHL (Acetyl Homoserine Lactone) production employed by certain types of quorum-sensing bacteria, in the formation of such structures.
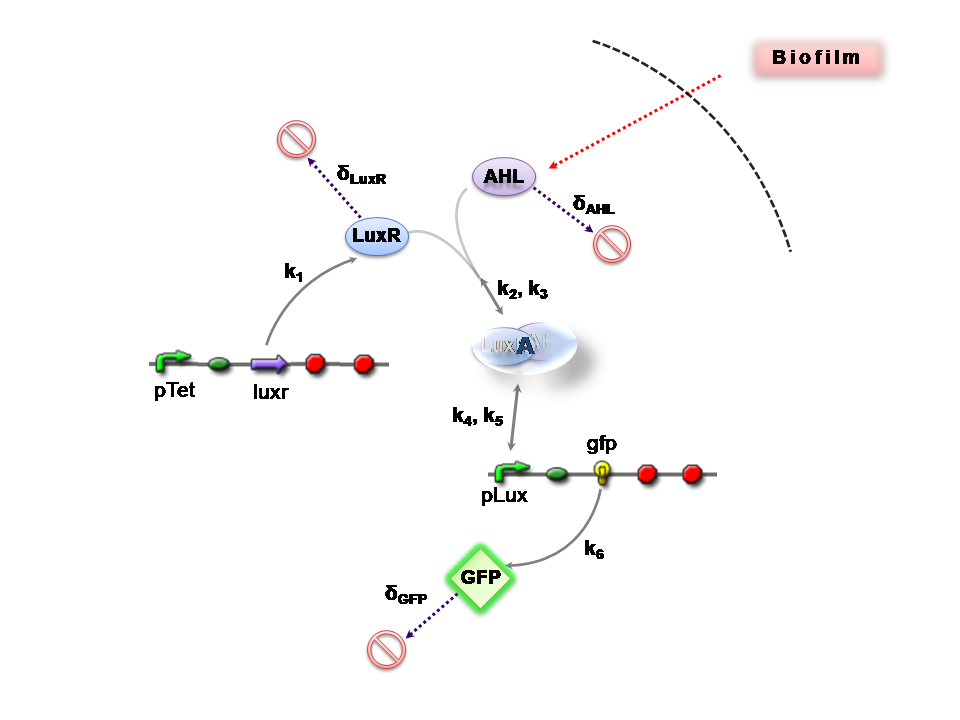
This section presents a preliminary model for an AHL detector, which employs the backbone of the Lux quorum-sensing feedback mechanism. Figures 1 and 2 below illustrate the full system we are investigating.
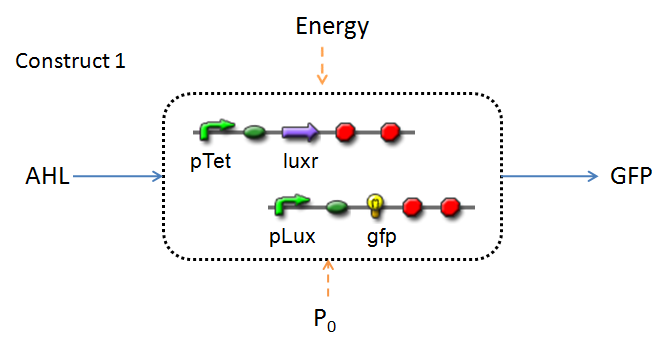
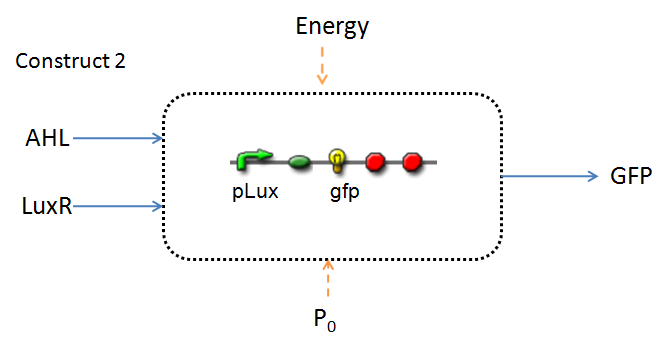
In the design phase, two possible system constructs were proposed, as a solution to the problem of detecting AHL-producing biofilm.
According to our specifications, the most crucial feature of this system is the sensitivity to a minimum [AHL] of 5nm. In other words, we need to identify the minimal AHL concentration for appreciable expression of a chosen reporter protein.
Furthermore, we attempt to define a functional range for possible AHL detection. How does increased AHL concentration impact on the maximal output of reporter protein?
Finally, we investigate how the system performance can be tailored, by exploiting possible inputs to the system (e.g. varying initial LuxR concentration and/or concentration of pLux promoters).
In performing such customizations, the question arises: what is the impact upon the maximal output of fluorescent reporter protein and/or response time?
We attempt to answer such questions by establishing a representative model, and consequently, conducting a simulation of the system in-silico.
Implementation & Reaction Network
In line with the concept of abstraction in Synthetic Biology, the correlation of the output of the proposed system constructs to their inputs, can be visualized by the following black-box illustrations of the two cases.
It is evident that AHL is an input to both constructs; a function of the particular biofilm. Furthermore, energy and promoter concentration are included as auxillary inputs to both system constructs. LuxR, is an additional input, exclusive to construct 2, which lacks constitutive expression of LuxR by pTET.
(this of course occuring within our cell-free chassis)
The Reaction Network
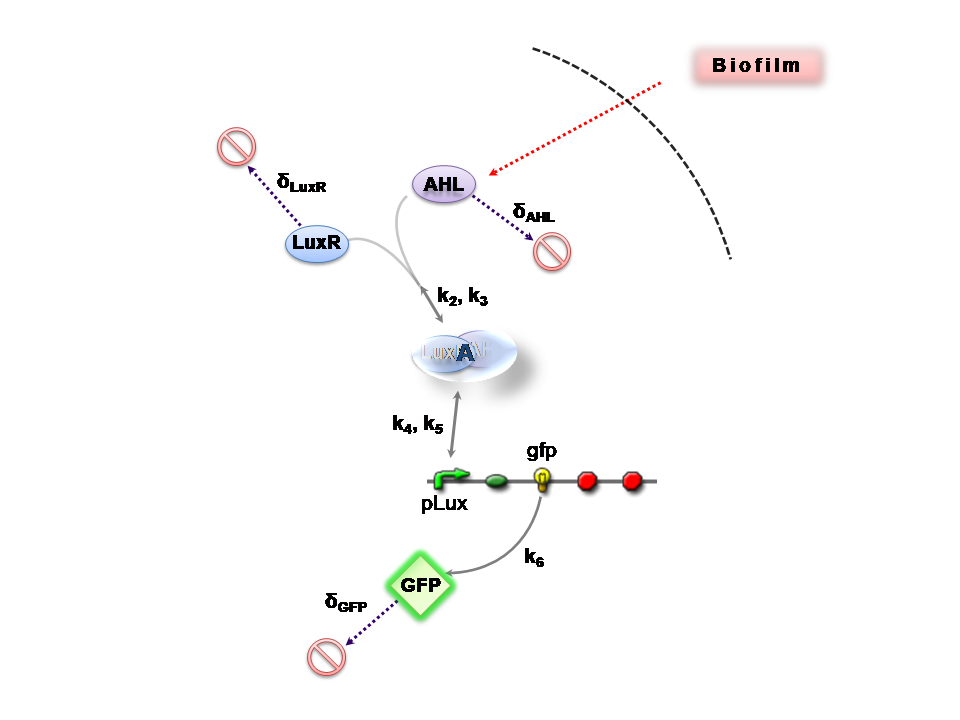
AHL is assumed to diffuse freely "into" the system (we are dealing with cell-free system, which comes into direct contact with the biofilm). The target AHL molecules, produced by the biofilm, equilibrate between the two systems - the detector and the target. Once equilibrium of AHL is reached, AHL binds with the monomeric protein LuxR, which is either constitutively produced by construct 1, or directly introduced in purified form, as part of the solution which is construct 2. The binding of these two proteins yieds the product A, the intermediating LuxR-AHL complex, which is assumed to be immediately transcriptionally competent. The reactions here are considered as reversible (forward and backward reactions of this step governed by the kinetic constants k2 and k3 respectively). The formed transcription factor activates the transcription of the pLux operon, which codes for the relevant reporter protein, presented here as GFP. Activation occurs by way of the reversible binding of this transcription factor, A, to the response sequences in the operon (k4 and k5) . This leads to recruitment of RNA polymerase and increases the frequency of transcription initiation (Fuqua et al., 2001) of the construct gfp gene (strictly forward reaction, governed by k6).
Representative Model
In developing this model, we were interested in the behaviour at steady-state, that is when the system has equilibrated and the concentrations of the state variables remain constant.
At reasonably high molecular concentrations of the state variables, a continuous model can be adopted, which is represented by a system of ordinary differential equations.
It is for this reason that our approach to modelling the system follows a deterministic, continuous approximation.
We can condition the system in various manners, but for the purposes of our project, we will seek a formulation which is valid for both constructs considered, i.e. the governing equations are a represenation of both constructs.
The only difference is with regards to the parameter k1, the maximum transcription rate of the constitutive promoter (pTET). Therefore in construct 1, k1 is non-zero; k1 = 0 for construct 2 (which lacks pTET).
Our analysis took us through a number of models, but presented here is the most pertinent, most representative version. This model is based on energy-dependence (limited nutrient supply), which follows Hill-like dynamics.
The system kinetics are determined by the following coupled-ODEs. For a derivation of the governing equations, please access
Model Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Kinetic Constants | |
| k1 | Maximal constitutive transcription of LuxR by pTET |
| k2 | Binding between LuxR and AHL |
| k3 | Dissociation of protein complex LuxR-AHL (A) |
| k4 | Binding between A and pLux promoter |
| k5 | Dissociaton of A-pLux complex |
| k6 | Transcription of FP |
| Degradation Rates | |
| δLuxR | Degradation rate of LuxR |
| δAHL | Degradation rate of AHL |
| δGFP | Degradation rate of GFP |
| Hill Co-operativity | |
| n | Co-operativity coefficient describing the degree of energy dependence, which follows Hill-like dynamics |
| Energy consumption of transcription | |
| α1 | Energy consumption due to constitutive transcription of LuxR |
| α2 | Energy consumption due to transcription of gfp gene |
We now present the essential features of the system behaviour, simulated for a given set of parameters.
Simulations
Presented below are the most essential results of the simulations performed.
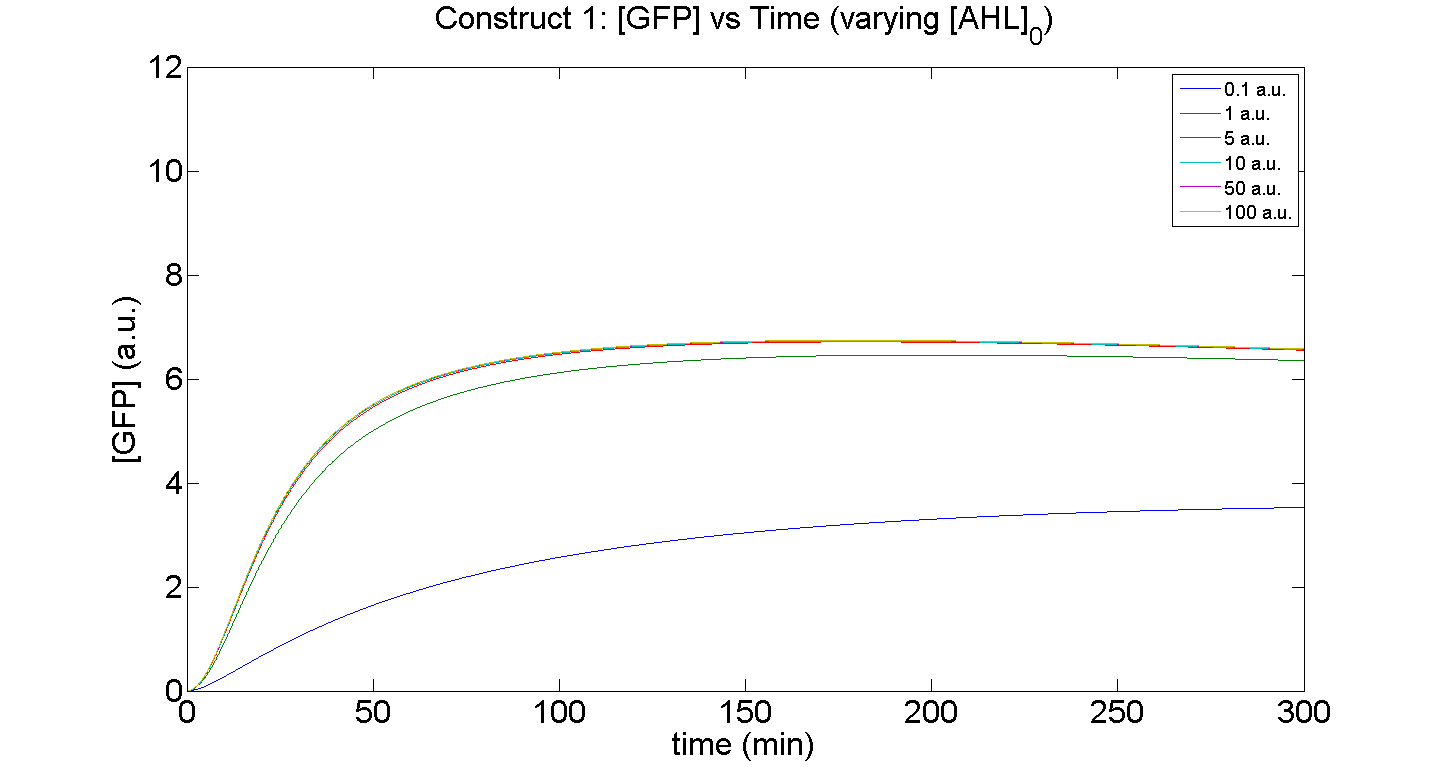
1. Comparison of constructs: [GFP] vs time - varying [AHL]0
Discussion
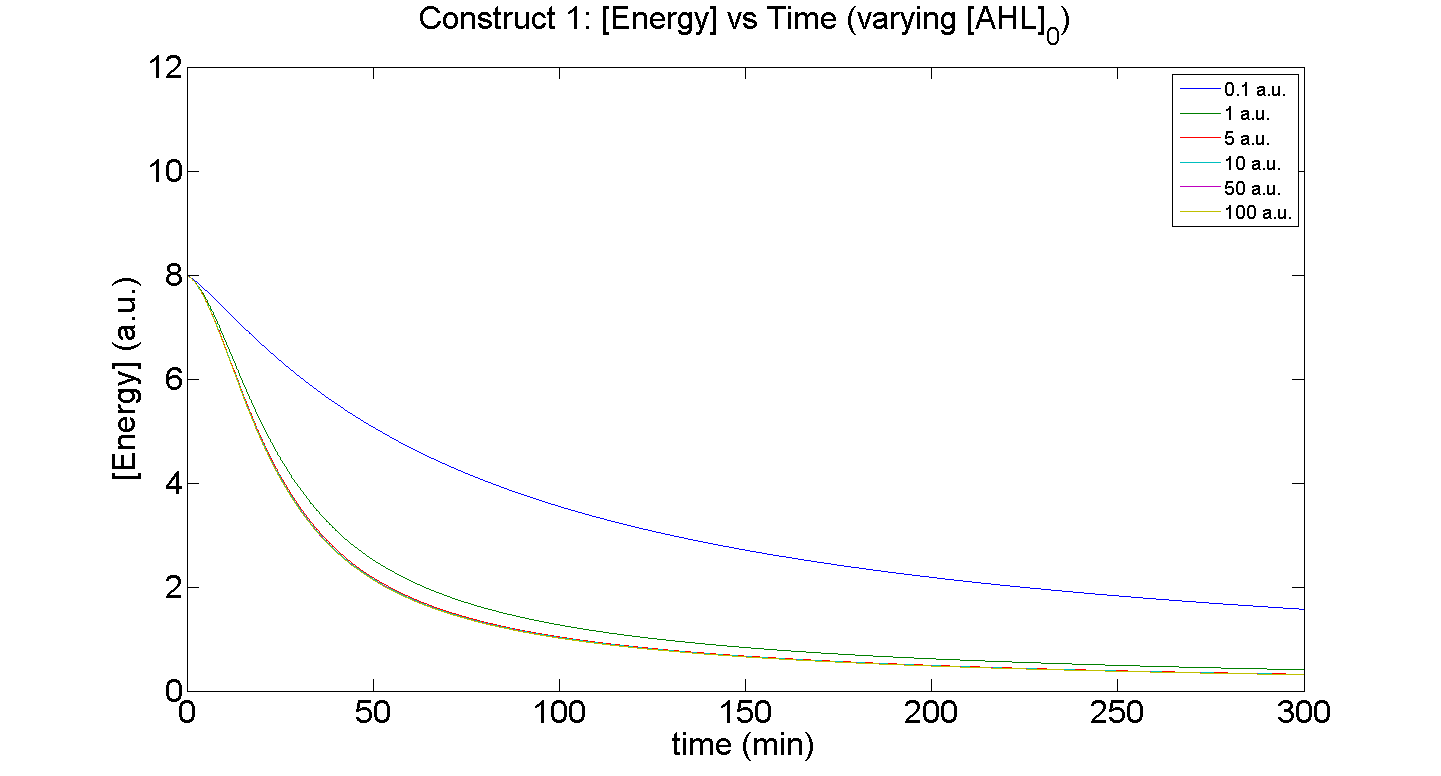
Figures 5 and 6 illustrate GFP expression and Energy depletion of construct 1, at various initial AHL concentrations.
The absolute value of the peak expression is a function of the various rate constants. Here our analysis serves to illustrate the general behaviour offered by construct 1 – a qualitative approach.
As initial [AHL] is increased, the level of expression increases accordingly to a point were there is negligible difference between the maximal outputs between adjacent tested cases of [AHL]. In fact, from this figure, and for this set of parameters, it is suggestive that saturation occurs at approximately 5 a.u.; in fact, the difference in maximal GFP output between when AHL is increased a several-fold is less than 10%.
Figure 6, the energy depletion plot, serves to illustrate the effect of increased initial concentrations of AHL. More resources (promoters) need to be employed to accommodate the increasing [AHL]. This obviously increases the rate of energy depletion, until it reaches a saturating value, as saturating behaviour has been attained - promoter saturation. This is the likely explanation for the saturation curve, since the protein degradation terms themselves are almost negligible.
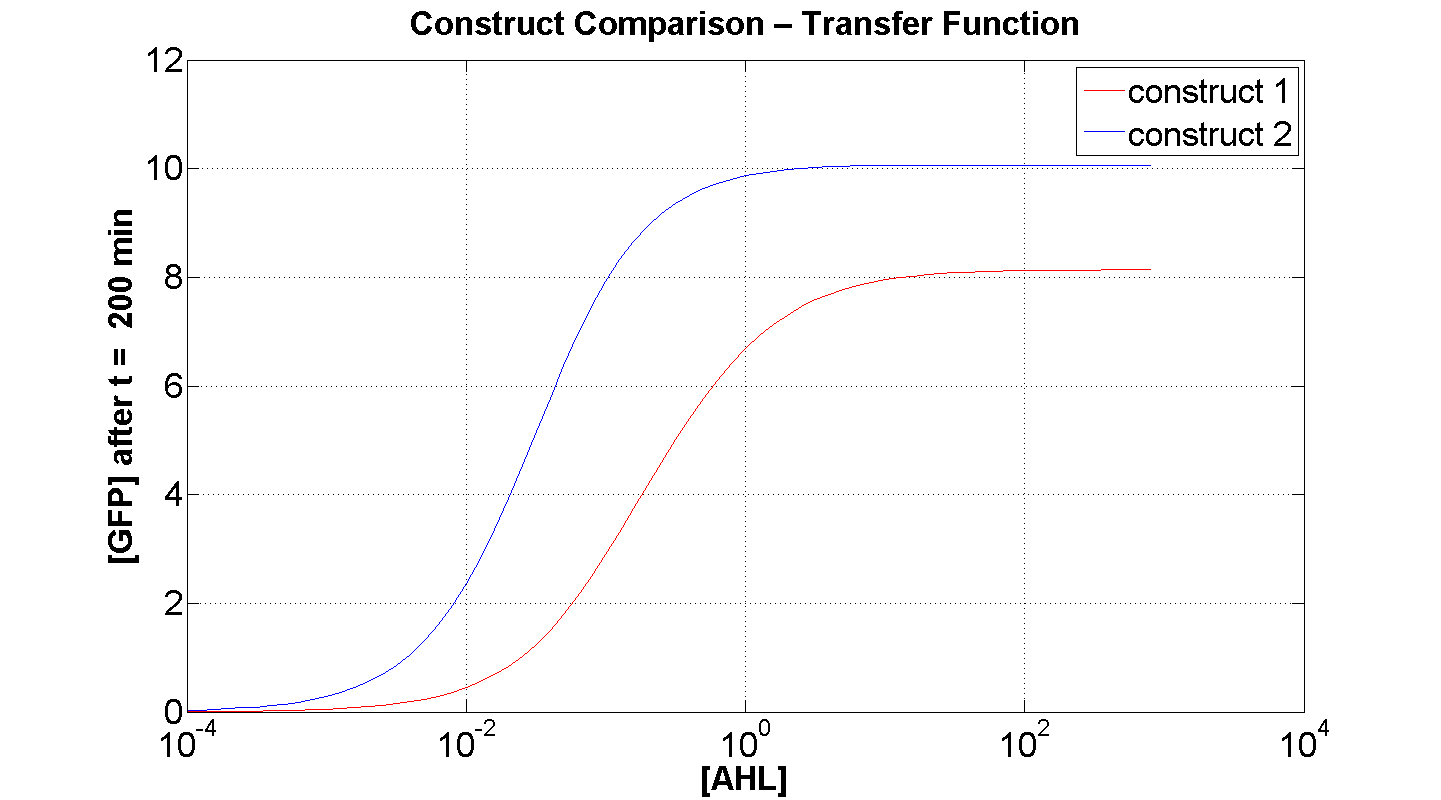
2. Comparison of constructs: [GFP] vs [AHL] - transfer function curve
Discussion
Figures 4 and 5 illustrate the comparison of the transfer function of both constructs, at two time instances: t = 50min and t = 200min. Consider figure 5, which illustrates the greater sensitivity to AHL offered by construct 2. Appreciable expression of GFP occurs at concentration of AHL at least one order of magnitude lower than in the case of construct 1.
It can also be seen, that at saturation, the peak expression, is considerably greater - approximately 25 % greater than that offered by construct 1.
Figure 4, portrays clearly, the far superior response time of construct 2 (as expected).
Conclusions
From the simulations performed, construct 2 outperforms contruct 1 on the basis of sensitivity, response time and maximal output of reporter. Construct 1 is superior in terms of energy-efficiency. Its life-time is far greater than that of its counterpart.
It is evident that both constructs have their major strengths - strengths that require testing and validation in the context of the laboratory - this forms the pathway to their effective characterization.
Data Analysis follows the experimental data gathering stage, with the task of validation of the model, and ultimately extraction of biologically representative parameters.
Just testing image clarity, font size, colours
Software
All deterministic simulations were performed using Matlab 7 (The MathWorks Inc., Natick, MA).
- m-files of all simulations are available on our Software page.