Imperial/Infector Detector/Testing
From 2007.igem.org
m (→DNA Concentrations) |
m (→DNA Concentrations) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
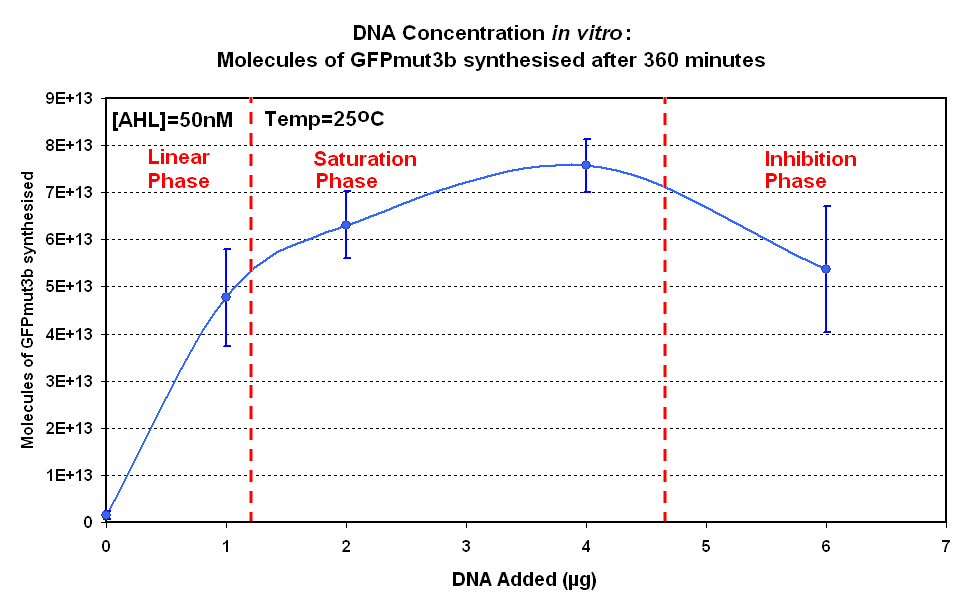
*'''Inhibition phase'''- Increasing the DNA concentration actually inhibits the rate of protein synthesis. | *'''Inhibition phase'''- Increasing the DNA concentration actually inhibits the rate of protein synthesis. | ||
The fact that increasing DNA concentration above 4µg causes a decrease in rate of protein synthesis is very interesting. The reason for this is thought to be that increasing DNA concentration causes problems with premature translational termination. <br> | The fact that increasing DNA concentration above 4µg causes a decrease in rate of protein synthesis is very interesting. The reason for this is thought to be that increasing DNA concentration causes problems with premature translational termination. <br> | ||
| - | + | <br> | |
Although there is only a limited number of data points and there is a lot of error we feel that the results do show that 4µg was taken as the maximum and used for the rest of the testing. This agrees with the instructions provided by Promega which state that above 4µg the rate of protein synthesis is inhibited. | Although there is only a limited number of data points and there is a lot of error we feel that the results do show that 4µg was taken as the maximum and used for the rest of the testing. This agrees with the instructions provided by Promega which state that above 4µg the rate of protein synthesis is inhibited. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 00:55, 27 October 2007

Infector Detector: Testing
Summary
The key results of the testing were:
- The optimum DNA concentration for [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_T9002 pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFPmut3b] in our Commcercial S30 Cell extract is 4µg.
Aims
From the initial testing we determined that the construct worked in both in vivo and in vitro. Now we were concerned with:
- Optimization - To test and obtain the optimal DNA concentration for construct 1 in vitro to reach the full potential of our infecter detector system.
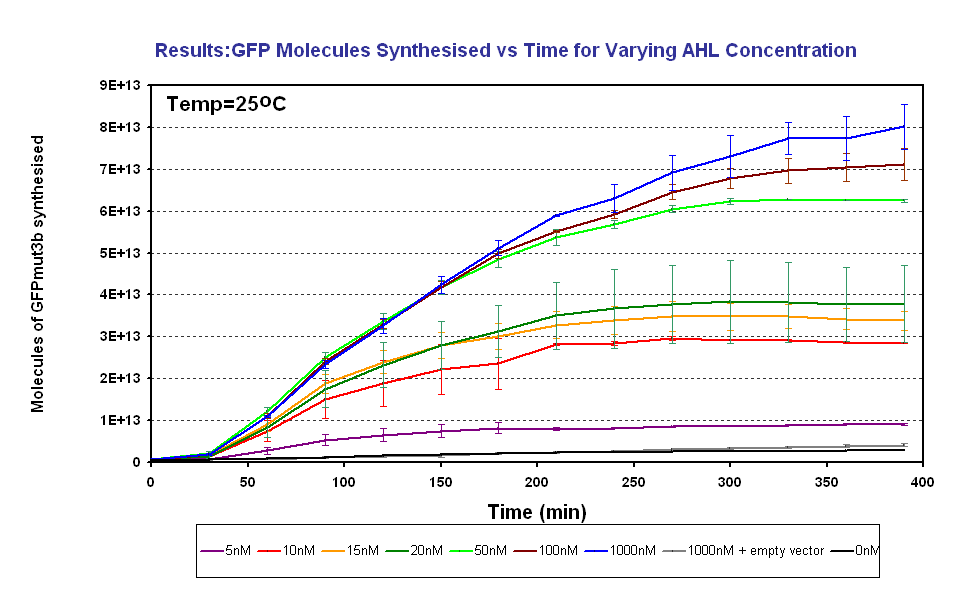
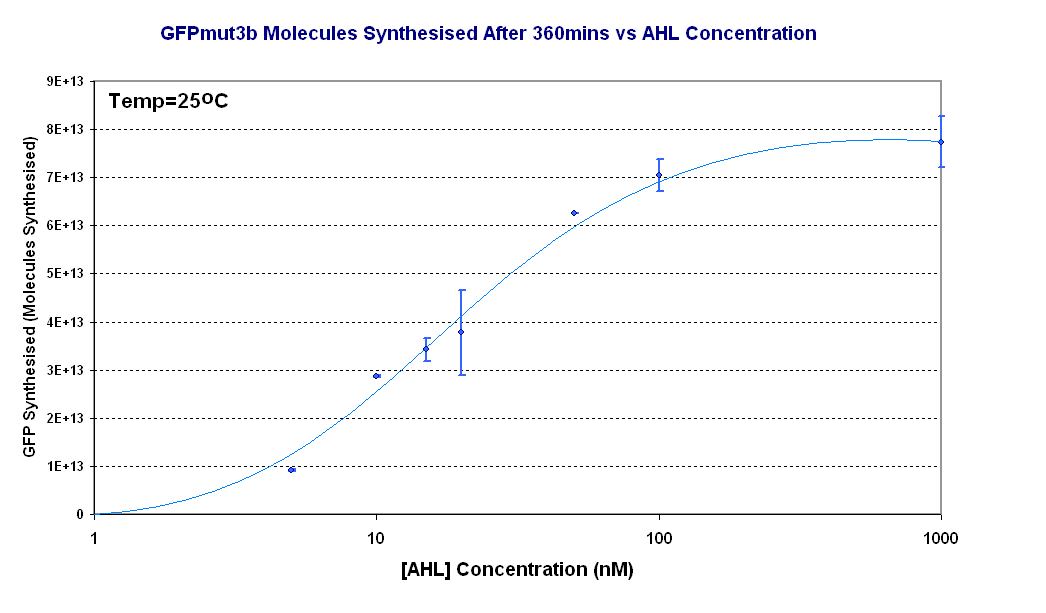
- Test our specifications - To test the range 5-50nM AHL defined in our specifications and characterise the output of GFPmut3b for a range of AHL inputs. We aimed to measure fluorescence and using our calibration curve convert to molecules of GFPmut3b, click here for our calibration curve and for how we used it to convert
Results
DNA Concentrations
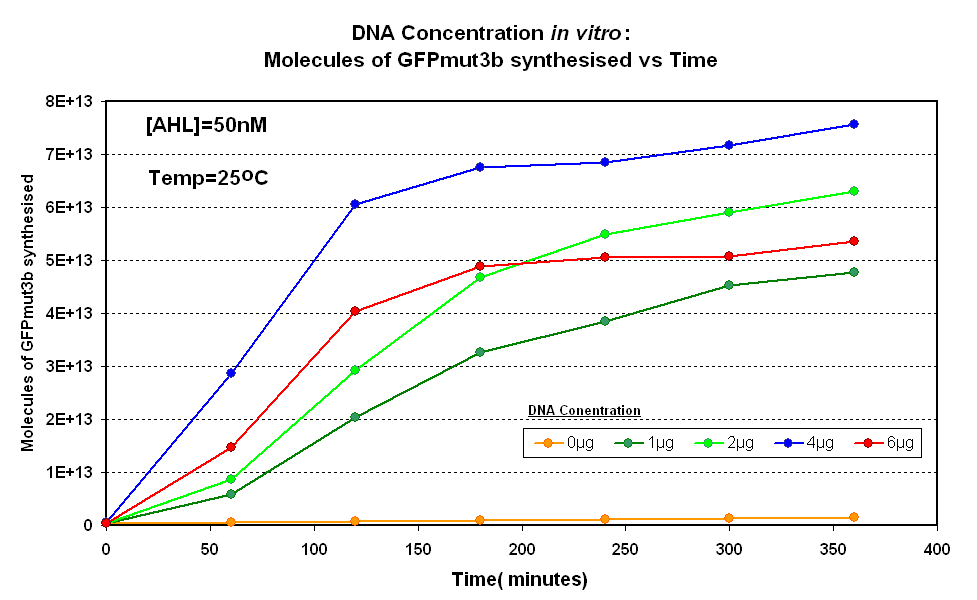 Fig.1.1:Molecules of GFPmut3b synthesised over time, for each DNA Concentration in vitro - The fluorescence was measured over time for each experiment and converted into molecules of GFPmut3b in vitro using our calibration curve Click here for results and protocol. |
The Results above show that the optimum DNA concentration for in vitro is 4µg for 50nM AHL. From figure 1.1. and 1.2 it can be seen that as DNA concentration increases above 4µg the GFPmut3b molecules synthesised decrease. Interestingly for figure 1.2 the graph can be split into several regions of how the DNA concentration changes the output of GFPmut3b synthesis:
The fact that increasing DNA concentration above 4µg causes a decrease in rate of protein synthesis is very interesting. The reason for this is thought to be that increasing DNA concentration causes problems with premature translational termination. |
AHL Testing
Figure 1.3 shows us the following:
Figure 1.4 shows us the following:
For more detailed analysis please see the Results page |