Imperial/Wet Lab/Results/Chas1.1
From 2007.igem.org
In vitro Testing of pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFP Construct

Aims
Working with DNA construct:
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_T9002 pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFP]
To determine the consistency and efficacy of using different combinations of cell extract:
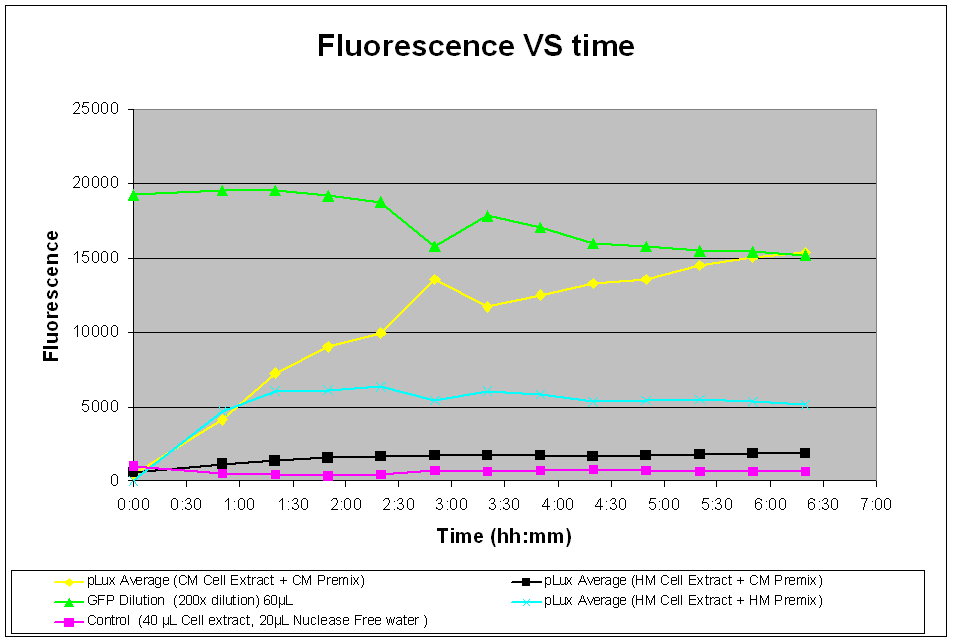
- pLux with Commercial(CM) S30 cell extract and CM Premix
- pLux with Homemade(HM) S30 cell extract and HM Premix
- pLux with HM S30 cell extract and CM Premix
Since it has been ascertained that the commercial extract works with pTet, the pLux construct should work in the first combination. This is to be compared with that of the second combination to test for the efficiency of the HM extract. The third combination investigates the possibility of combining our homemade cell extract with the commercial premix rather than the homemade one.
Materials and Methods
Link to Protocol
Results
[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_T9002 pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFP]
In vitro Testing of pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFP at 25°C
Controls:
- Positive control - diluted GFP solution of equal volume
- Negative control - S30 cell extract of equal volume
Raw Data
Discussion
From Fig.1, it seems that there is a very strong fluorescent signal observed from the pLux construct using the first combination as its fluorescence has intersected with the positive control after 6 hours. On the other hand, the HM cell extracts did not compare well in terms of fluorescence despite both extracts having the same amount of pLux DNA.
This performance discrepency of cell extracts is further accentuated in the thid combination, where the combination of HM cell extract and CM premix resulted in an even lower performance that was comparable to that of the negative control.
Fig.1 indicates that there was a fair amount of expression of GFP with the pTet-LuxR-pLux-GFP construct, leading to an increase in fluoresence over time. To this, it can be concluded that the construct is working well in vitro.
The optimization of cell extracts for commercial use is probably the reason for the discrepency in terms of coupled transcription/translation performance. Indeed while the homemade cell extract was found to be working, it was less than half as efficient as that of the commercial extract, presumably due to the fact that it was a crude attempt at emulating protocols obtained from various journals. Despite the reduction in efficiency, homemade cell extracts have the advantage of being more cost effective, and larges batches of homogenous cell extracts can be obtained as opposed to the reaction mixtures sold by commercial firms.
The use of large batches of homogenous cell extracts is essential for the consistency of subsequent experiments as it was found that the quality control of commercial cell extracts depended on its minimum yield. This means that the variation across cell extracts can be significant, and different batches of cell extracts will yield different coupled transcription/translation performance. As such, it may be a wiser decision to maintain the homogeneity of cell extracts across each experiment.
Conclusion
- Commercial cell extracts performed better than our homemade cell extracts.
- It is integral to maintain the homogeneity of cell extracts across our experiments.