Imperial/Cell by Date/Testing
From 2007.igem.org
m (→Validation and Conclusion) |
m (→<font color=blue>Investigating properties of system under isothermal scenarios</font>) |
||
| (60 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:IC07navmenu}} | {{Template:IC07navmenu}} | ||
| + | <br clear="all"> | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <link rel="stylesheet" href="/igem07/index.php?title=User:Dirkvs/Stylesheets/IC07persist.css&action=raw&ctype=text/css" type="text/css" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div id="tabs"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Introduction" title=""><span>Introduction</span></a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Specification" title=""><span>Specifications</span></a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Design" title=""><span>Design</span></a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Modelling" title=""><span>Modelling</span></a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Implementation" title=""><span>Implementation</span></a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a class="current" href="https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Testing" title=""><span>Testing</span></a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Conclusion" title=""><span>Conclusion</span></a></li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <hr /> | ||
| + | <br clear="all"> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| + | = Cell by Date: Testing = | ||
| - | == | + | ==Summary== |
| + | Key results of our experiments are : | ||
| - | + | 1.'''Operating Range''' : Our System Operates between '''8-37 Degrees''' <br> | |
| + | 2.'''Activation Energy''' : The activation energy of our system is '''1.5kJ/mol''' <br> | ||
| + | 3.'''Optimum DNA Concentration''' : The optimum DNA concentration for our system is '''2-4ug DNA''' <br> | ||
| - | + | ==Aims== | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Having determined that our system worked at a basic level in our [https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Implementation implementation phase] we set out to ascertain a clearer picture of the performance of our system to ultimately reveal whether our design had realised our specifications. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ==Results== | |
| - | === | + | ===<font color=blue>Investigating properties of system under isothermal scenarios</font>=== |
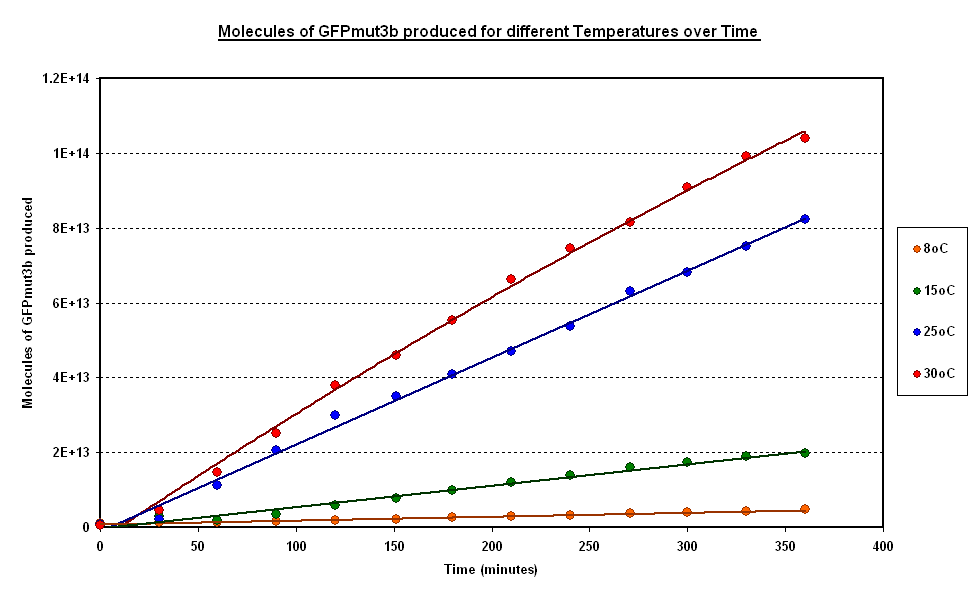
| - | + | To estimate the properties of our system we looked at synthesis of GFPm with time for experiments where temperature is carefully kept constant. (Figure 1).<br> | |
| + | '''General Behaviour:''' <br> | ||
| + | *In all experiment we can observe a linear synthesis of GFP corresponding to a steady rate of GFP synthesis. | ||
| + | *This steady rate is thought to be because of the degradation of GFP is negligible in our ''in vitro'' chassis, see the [[Imperial/Wet_Lab/Results/Res1.4| Degradation of GFP testing]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Image:CBD isothermal.PNG|thumb|centre|600px|Figr 1:Isothermal Data - Averages GFPmut3b molecules synthesised for pTet-GFPmut3b construct at different temperatures]] <br clear="all"> | ||
| - | + | '''Operating Range:'''<br> | |
| + | *Our system seems to 'turn off' at around 4 degrees C, having negligible rates of GFP synthesis.<br> | ||
| + | *At 8 degrees minimal expression occurs, when the temperature is increased to 37<sup>o</sup>C the GFP expression increases substantial expression.<br> | ||
| - | + | '''Synthesis rate vs Temperature'''<br> | |
| + | *Over the range of temperatures considered here the GFP synthesis and hence the rate was shown to increases with temperature.<br> | ||
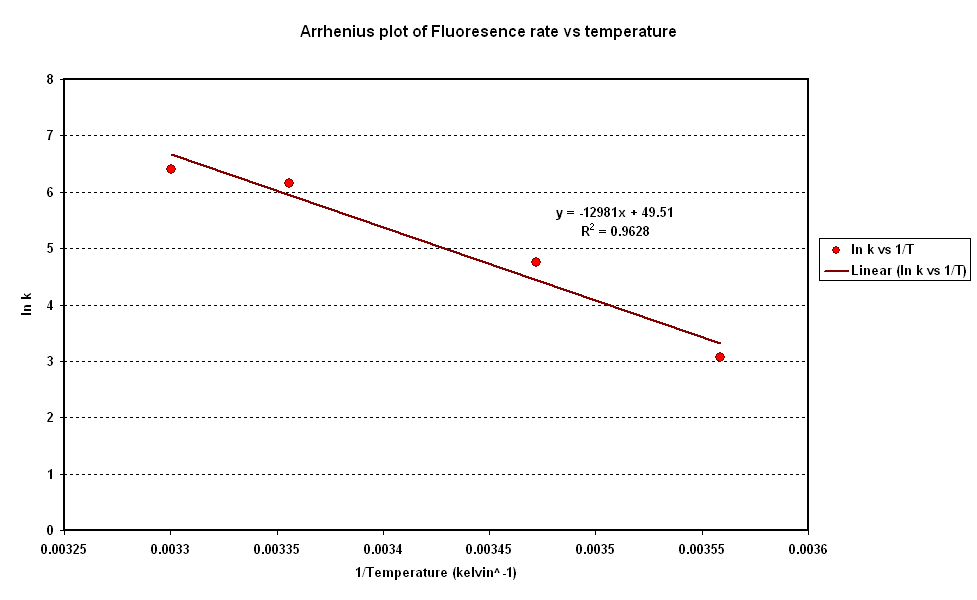
| + | *To investigate the relation between synthesis rate and temperature we extracted the rate of synthesis of GFP for each experiment and plotted it against 1/T (Figure 2).<br> | ||
| + | *A strong linear correlation in the log plot supports an arrhenius type dependence on temperature with an activation energy of 1.5kJ/mol.<br> | ||
| + | [[Image:CBD Arrhenius Plot.PNG|centre|thumb|600px|Fig 2: Arrhenius Plot]] <br clear = "all" > | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more detail on this analysis click [https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Wet_Lab/Results/CBD2.2#Results here] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Other practical considerations:''' <br> | ||
| + | *Unfortunately we have not been able to use a visible reporter and so have no idea whether the construct can in fact produce a visible signal. However we are using a stronger visual reporter such as DsRed express the system could potentially produce a strong visual signal <br> | ||
| + | *In terms of lifespan we have had major problems with evaporation meaning that the lifespan of our system is limited to a few days as discussed in our packaging experiment below. In addition work we worked on vesicles to potentially increase the stability of our system, click here for some more information on [http://partsregistry.org/Chassis/Cell-Free_Systems/Vesicle Vesicles] <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===<font color=blue>Investigating properties of system under dynamic temperature scenarios</font>=== | ||
| + | |||
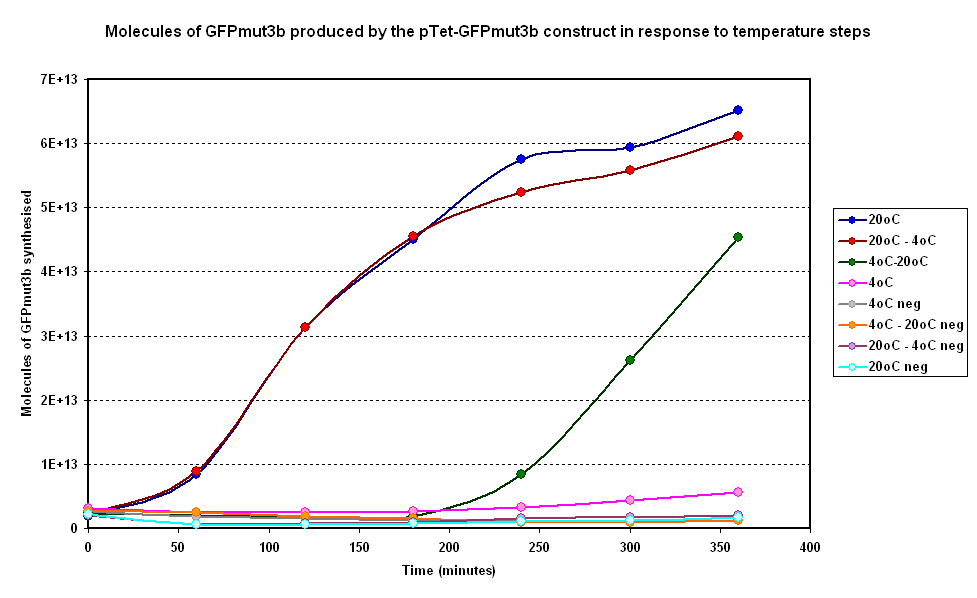
| + | After carrying out the experiments above we saw great potential to expand on our work on rate of synthesis and temperature. As per our [https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Specification specifications] show we are also wanted to expand on the idea of looking at dynamic temperature scenarios which have potential use in monitoring the maintenance of a cold chain. The cold chain is key for transport of many key temperature sensitive products, of particular concern are the transport of vaccines in third world countries. <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Below in figure 3 are the results from one of our experiments in which we subjected our system to a number of steps. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:IC 2007 CBD steps.PNG|600px|center|thumb|Fig 3:Molecules of GFPmut3b produced on average over time for two samples at constant temperatures of 4°C and 20°C and two with a temperature step (4-20°C and 20-4°C)]] <br clear = "all"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''General Behaviour''' :<br><br> | ||
| + | *Step Down from 20 to 4 Degrees : Rate of fluoresence decreases in comparison to the 20 degree isothermal curve. This is a positive result as it correlates with Koutsoumanis' meat model in our modelling section. If temperature increases the rate of synthesis of GFP increases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Step Up from 4 to 20 Degrees : Rate of fluoresence increases rapidly in comparison to the 20 degree isothermal curve. This is a positive result as it correlates with Koutsoumanis' meat model in our modelling section in which the response time of spoilage bacteria in beef is very small. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===<font color=blue>Other Experiments</font>=== | ||
| + | 1. DNA Concentration : We conducted this experiment to tune our system, by varying the concentration of DNA in our cell extract,to realise the optimum performance of our pTet-GFPmut3b construct. We found that the optimum concentration of DNA is between 2-4µg on the basis of material cost and peak expression rate. For more information please click [https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Wet_Lab/Results/Res1.8 here] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Packaging : We conducted this experiment to determine the effect of different packaging methods on the evaporation rate of our system. We found that out none of the packaging methods investigated decreased the rate of evaopration such that our system could survive for a week, as requested by our specifications. For more information please click [https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Wet_Lab/Results/CBD2.1 here] | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <center> [https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Implementation << Implementation ] | Testing/Validation | [https://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Cell_by_Date/Conclusion Conclusions >> ]</center> | |
Latest revision as of 03:44, 27 October 2007

Cell by Date: Testing
Summary
Key results of our experiments are :
1.Operating Range : Our System Operates between 8-37 Degrees
2.Activation Energy : The activation energy of our system is 1.5kJ/mol
3.Optimum DNA Concentration : The optimum DNA concentration for our system is 2-4ug DNA
Aims
Having determined that our system worked at a basic level in our implementation phase we set out to ascertain a clearer picture of the performance of our system to ultimately reveal whether our design had realised our specifications.
Results
Investigating properties of system under isothermal scenarios
To estimate the properties of our system we looked at synthesis of GFPm with time for experiments where temperature is carefully kept constant. (Figure 1).
General Behaviour:
- In all experiment we can observe a linear synthesis of GFP corresponding to a steady rate of GFP synthesis.
- This steady rate is thought to be because of the degradation of GFP is negligible in our in vitro chassis, see the Degradation of GFP testing
Operating Range:
- Our system seems to 'turn off' at around 4 degrees C, having negligible rates of GFP synthesis.
- At 8 degrees minimal expression occurs, when the temperature is increased to 37oC the GFP expression increases substantial expression.
Synthesis rate vs Temperature
- Over the range of temperatures considered here the GFP synthesis and hence the rate was shown to increases with temperature.
- To investigate the relation between synthesis rate and temperature we extracted the rate of synthesis of GFP for each experiment and plotted it against 1/T (Figure 2).
- A strong linear correlation in the log plot supports an arrhenius type dependence on temperature with an activation energy of 1.5kJ/mol.
For more detail on this analysis click here
Other practical considerations:
- Unfortunately we have not been able to use a visible reporter and so have no idea whether the construct can in fact produce a visible signal. However we are using a stronger visual reporter such as DsRed express the system could potentially produce a strong visual signal
- In terms of lifespan we have had major problems with evaporation meaning that the lifespan of our system is limited to a few days as discussed in our packaging experiment below. In addition work we worked on vesicles to potentially increase the stability of our system, click here for some more information on [http://partsregistry.org/Chassis/Cell-Free_Systems/Vesicle Vesicles]
Investigating properties of system under dynamic temperature scenarios
After carrying out the experiments above we saw great potential to expand on our work on rate of synthesis and temperature. As per our specifications show we are also wanted to expand on the idea of looking at dynamic temperature scenarios which have potential use in monitoring the maintenance of a cold chain. The cold chain is key for transport of many key temperature sensitive products, of particular concern are the transport of vaccines in third world countries.
Below in figure 3 are the results from one of our experiments in which we subjected our system to a number of steps.
General Behaviour :
- Step Down from 20 to 4 Degrees : Rate of fluoresence decreases in comparison to the 20 degree isothermal curve. This is a positive result as it correlates with Koutsoumanis' meat model in our modelling section. If temperature increases the rate of synthesis of GFP increases.
- Step Up from 4 to 20 Degrees : Rate of fluoresence increases rapidly in comparison to the 20 degree isothermal curve. This is a positive result as it correlates with Koutsoumanis' meat model in our modelling section in which the response time of spoilage bacteria in beef is very small.
Other Experiments
1. DNA Concentration : We conducted this experiment to tune our system, by varying the concentration of DNA in our cell extract,to realise the optimum performance of our pTet-GFPmut3b construct. We found that the optimum concentration of DNA is between 2-4µg on the basis of material cost and peak expression rate. For more information please click here
2. Packaging : We conducted this experiment to determine the effect of different packaging methods on the evaporation rate of our system. We found that out none of the packaging methods investigated decreased the rate of evaopration such that our system could survive for a week, as requested by our specifications. For more information please click here