Imperial/Wet Lab/Lab Notebook/2007-09-11
From 2007.igem.org

11 September 2007
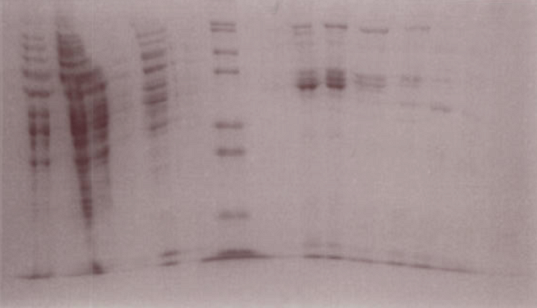
LuxR Purification
The gel suggests that fractions 15-18 contain the LuxR protein.
Plate Evaporation
We have been investigating how to prevent evaporation from our samples being measured in a plate reader. Because of the length of our testing, evaporation is a big problem. We are looking at use of organic oils to prevent evaporation. Today we tested to see if GFP is still fluorescence in oil. From looking in the literature we tested two types of oil at three volumes;
- Parafin Oil - 10ul, 20ul, 90ul
- Mineral Oil - 10ul, 20ul, 90ul
The results are on the following link to the [http://www.openwetware.org/wiki/IGEM:IMPERIAL/2007/Projects/Experimental_Design/Improve_Methodology | Results]
Vesicles
Formation of Vesicles
Three commercial S30 cell extract mixes were prepared, with the ratio of 1:4:3 AA Mixture : Premix : S30 Extract. These were then used to form three reactions:
- 50μl Negative Control: 33,3μl of S30 mix, 16,7μl nuclease free water.
- 50μl Experiment: 33,3μl of S30 mix, 3,8μl Plux GFP DNA, 12,9μl nuclease free water.
- 20μl Positive Control: 13,4μl of S30 mix, 1,5μl Plux GFP DNA, 5,1μl nuclease free water.
Two of the three suspensions prepared the day before were used to prepare emulsions containing commercial S30 cell extract mixes:
- Experiment: 10ml emulsion with 50μl of S30 cell extract with Plux GFP DNA
- Negative Control: 10ml emulsion with 50μl of S30 cell extract without DNA.
The third suspension was used to prepare four interfaces (2ml suspension over 3ml Solution A), to become four samples:
- Sample 1: Experiment, with circulation by syringe
- Sample 2: Experiment, without circulation by syringe
- Sample 3: Negative Control, with circulation by syringe
- Sample 4: Negative Control, without circulation by syringe
The remaining 20μl of S30/DNA reaction was used to form postitive controls:
- Concentrated Positive Control: 15μl of S30/DNA reaction
- Diluted Positive Control: 5μl of S30/DNA reaction diluted into 295μl of Solution A
AHL was then added to each of the four samples and the two positive controls above, to reach a concentration of 5μM/dm3.
Results
Samples 1-4 were looked at, as well as both emulsions before and after centrifugation, and the two positive controls.
- Emulsion - Experiment (No pictures taken)
- Before CF: Vesicles of around 2μm diameter found, plus many artifacts.
- After CF: Very few vesicles found, plus many artifacts.
- Emulsion - Positive Control (No pictures taken)
- Before CF: Vesicles of around 2μm diameter found, plus many artifacts.
- After CF: Very few vesicles found, plus many artifacts.
- Positive Controls
- Concentrated: Faint fluorescence throughout, and some aggregates.
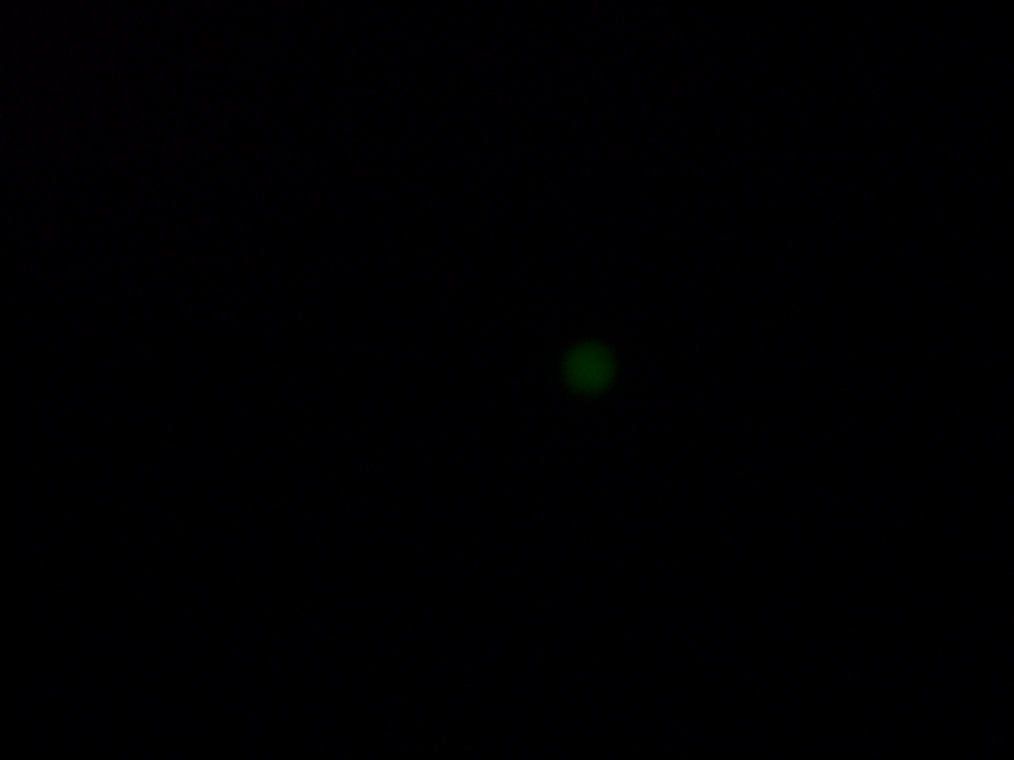
- Diluted: Tiny bright specs of green fluorescence, plus some large aggregates. (See pictures below.)
- Sample 1 (Experiment): Very few vesicles found, with faint fluorescence inside. Many fluorescent aggregates.
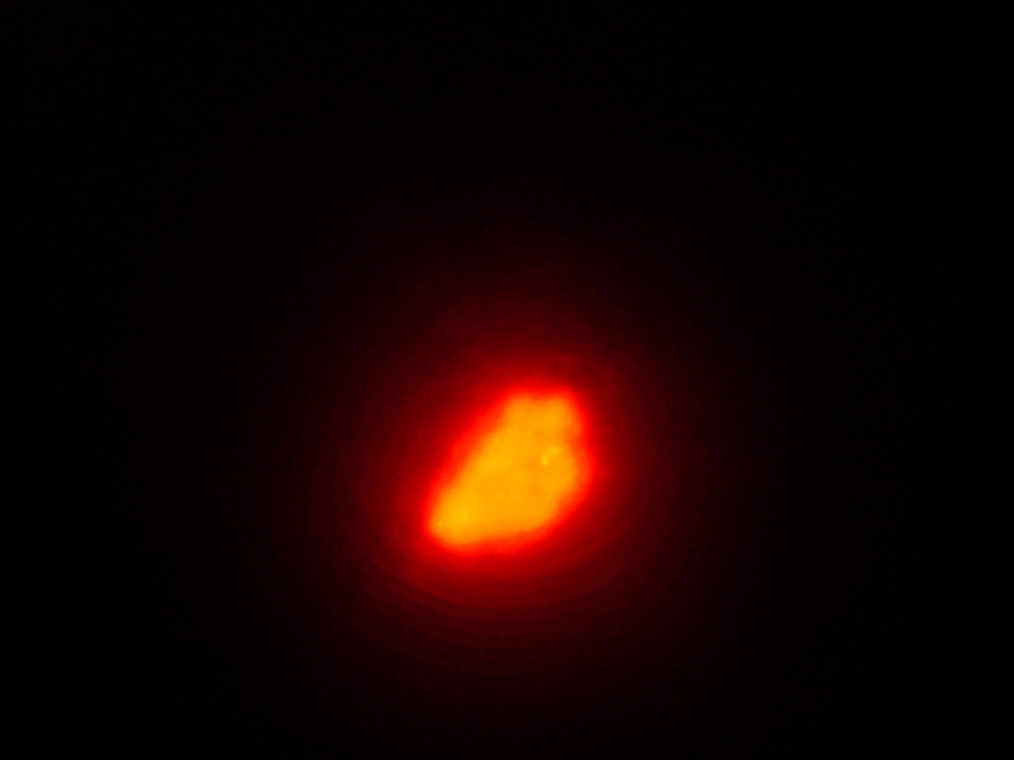
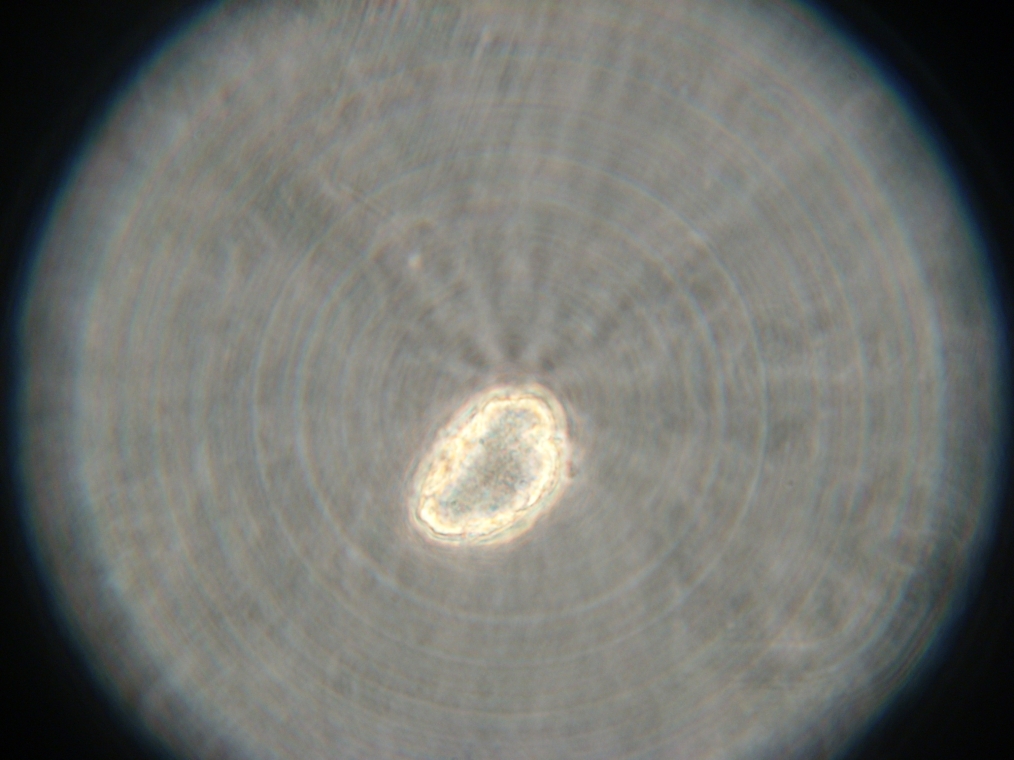
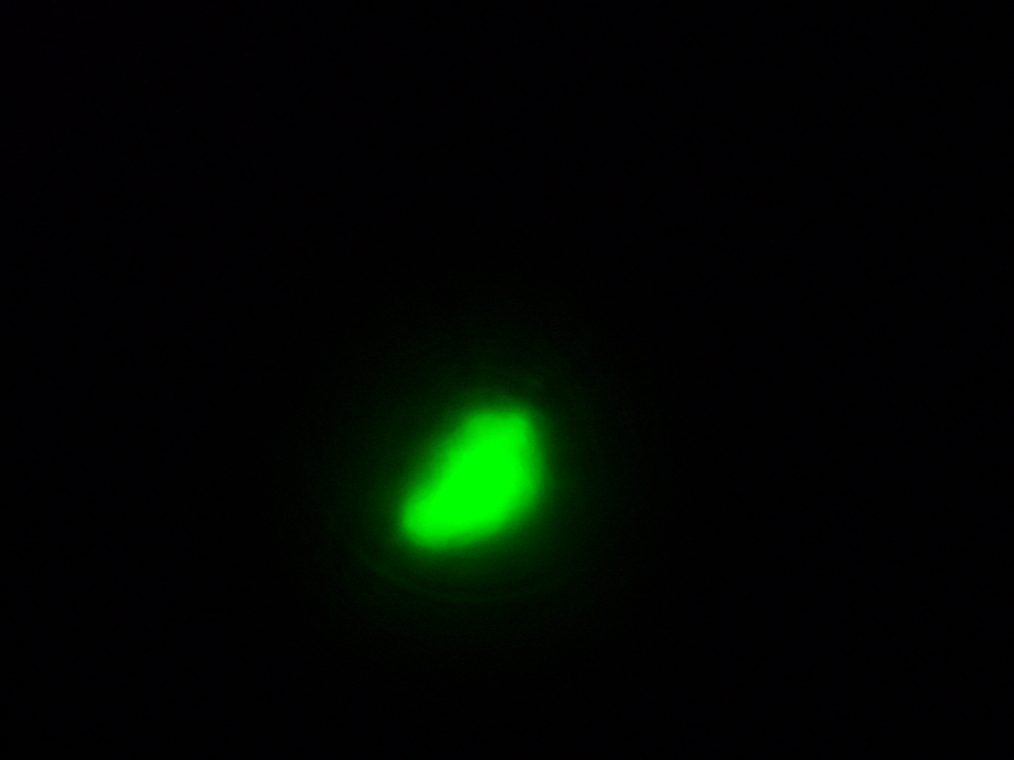
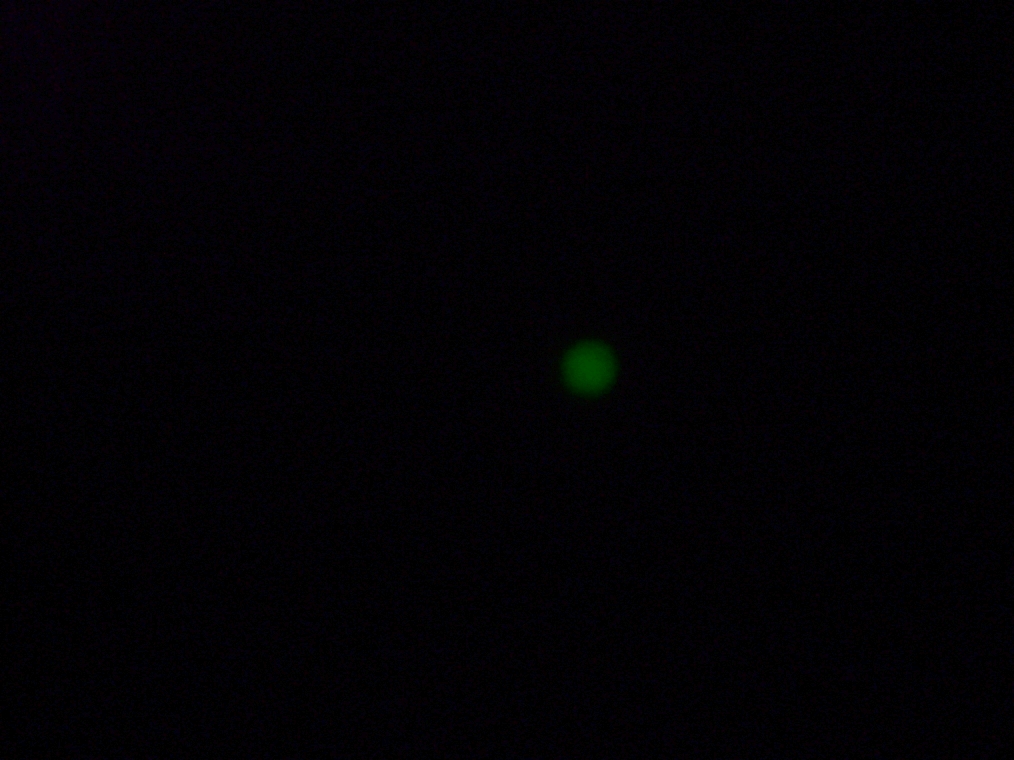
- Sample 2 (Experiment): Vesicles found, and one with very strong green fluorescence. All other vesicles with faint green fluorescence.
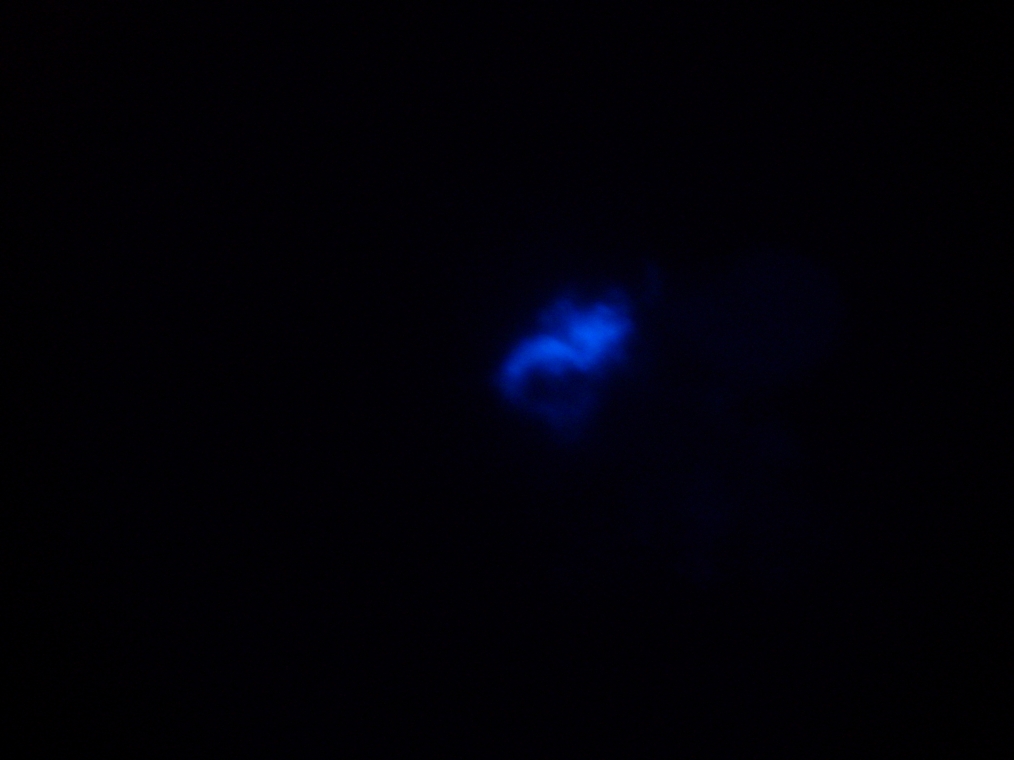
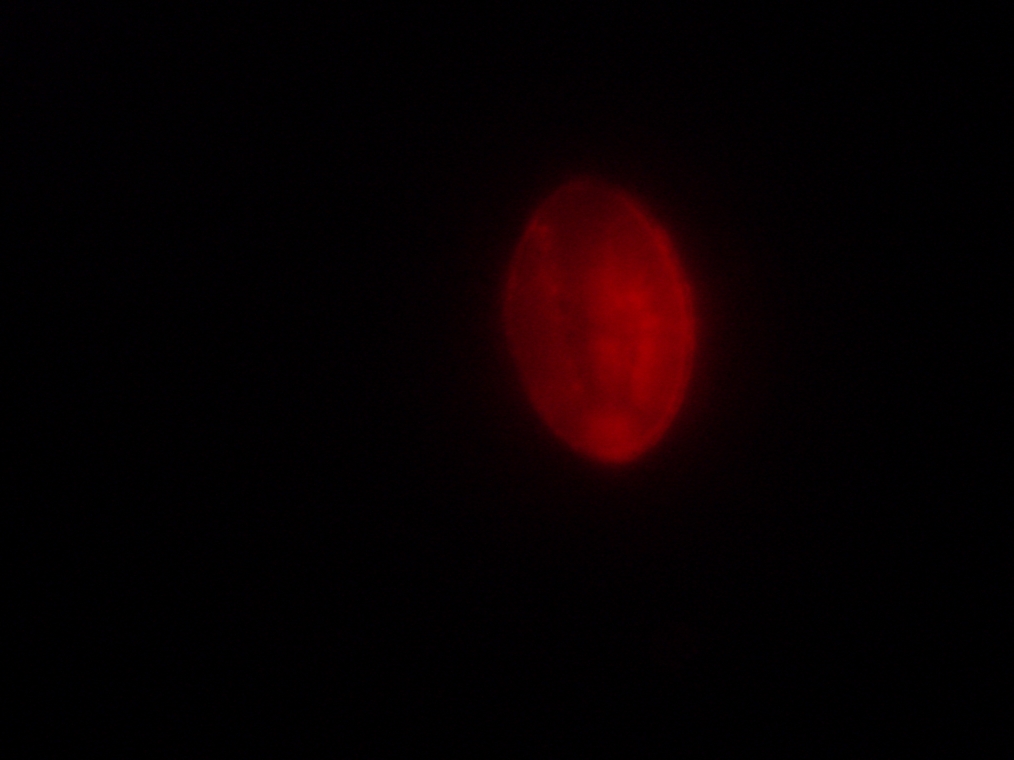
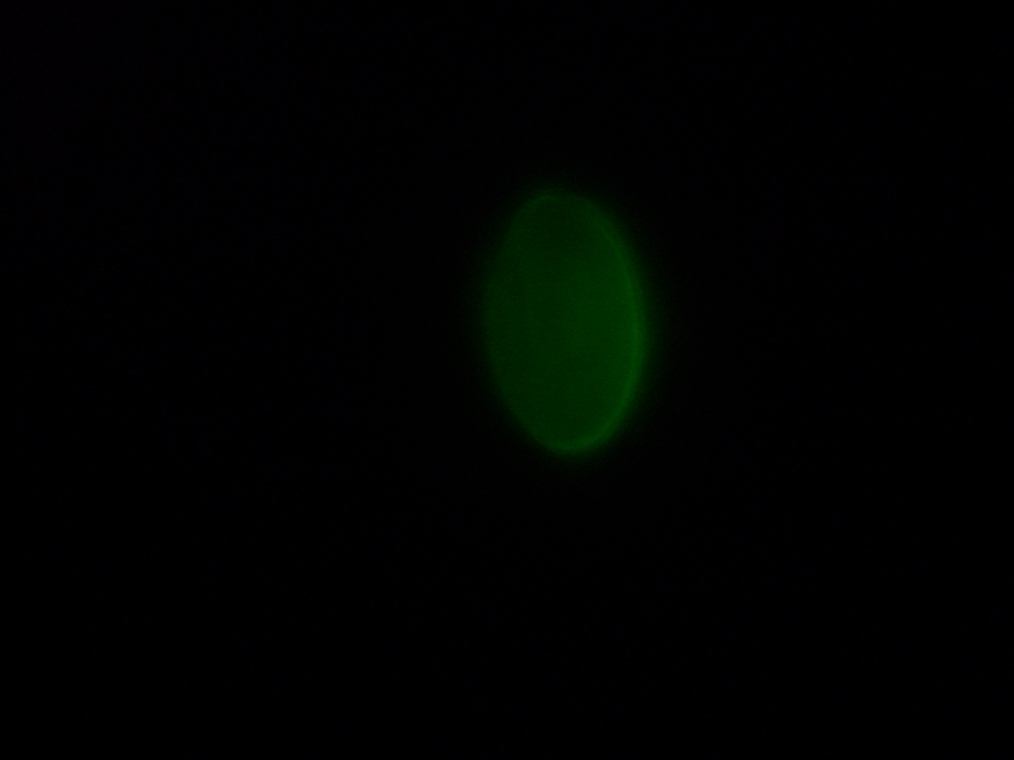
- Sample 3 (Negative Control): Few vesicles found, but with no fluorescence inside. Large fluorescent object found, and possibly contaminated.
- Sample 4 (Negative Control): Many vesicles found, but with no fluorescence inside. Bacterial contamination present. Strange textures found that may be oil from the collection process. (No images.)

| 
| 
|
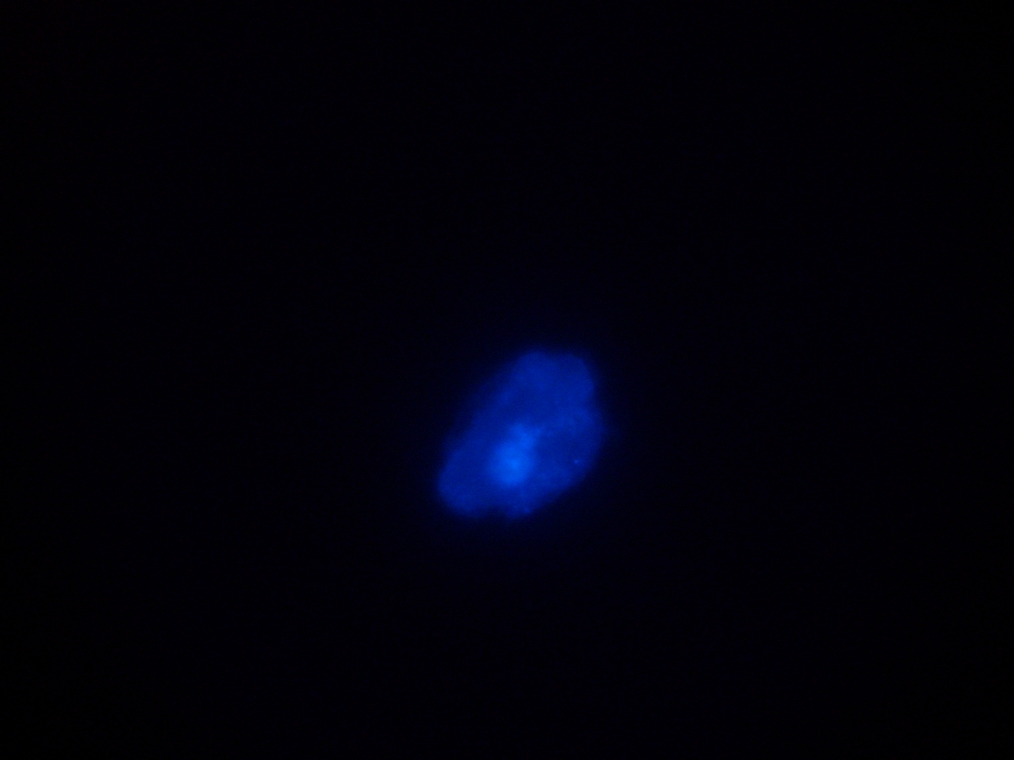
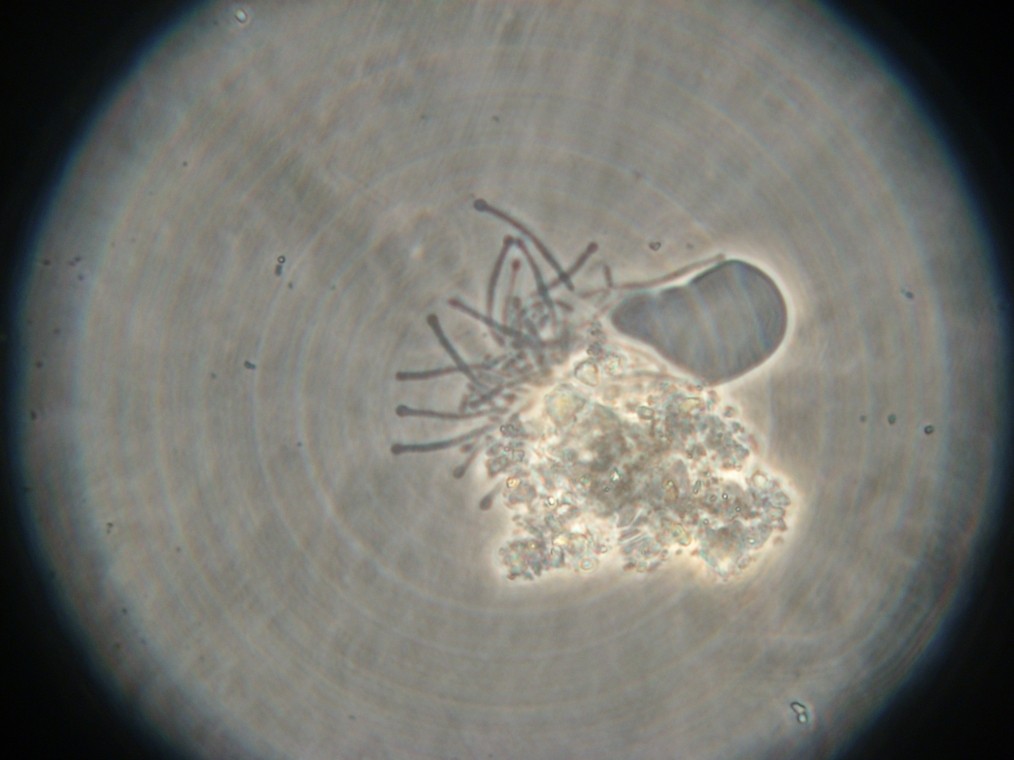
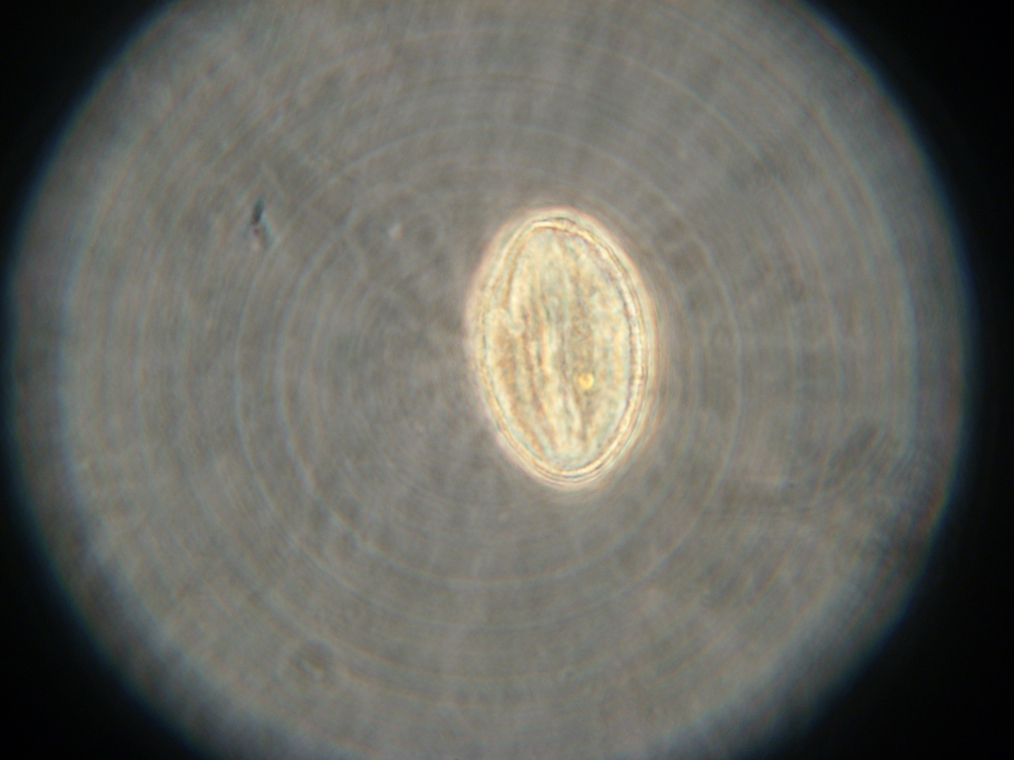
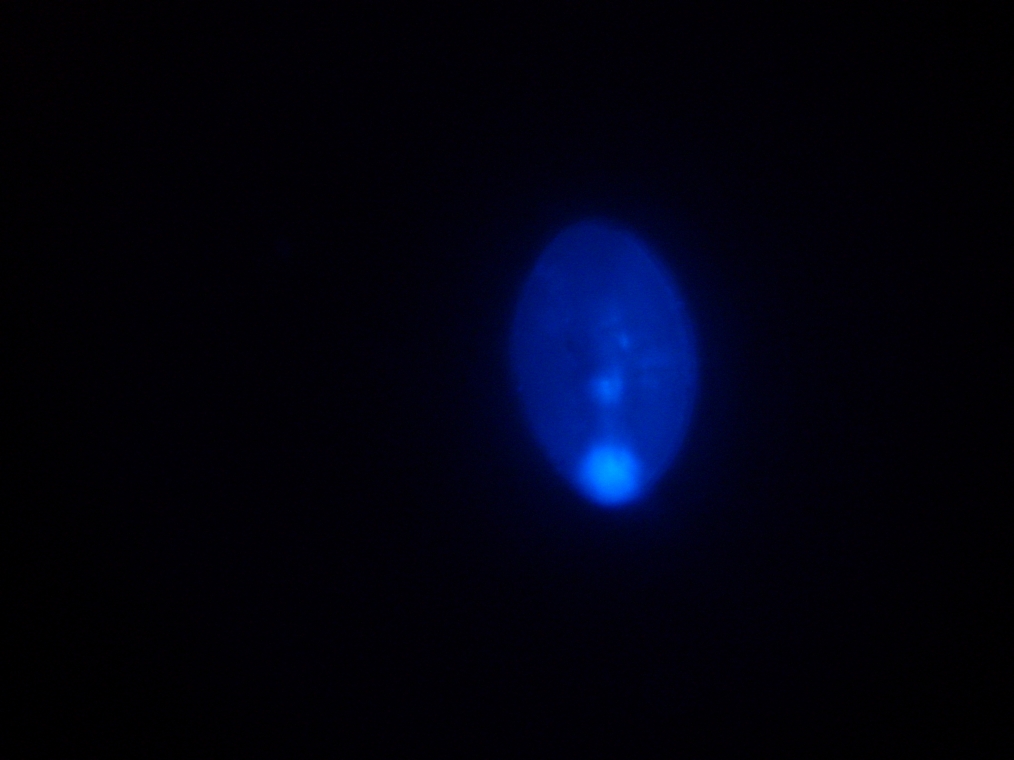
| Sample 2: A fluorescent vesicle was found, pictured above. Such a uniform fluorescence is most likely originating from GFP expressed within the liposome, as it looks exactly like other pictures found in literature. The object showed blue fluorescence as well, but not red. Left: The vesicle seen in white light. Center: The vesicle seen with a green fluorescence filter. Click to enlarge the picture and see the fluorescence clearly. Right: The image in the center, but with full saturation and gamma correction at 1.20. A video was taken as the microscope was focused above and below the vesicle: Focusing Video The video shows how vesicles look at different levels of focus, and also shows the object to the right of the vesicle as being an air bubble on a different plane. | ||
| 
| 
| 
|
| Sample 3: A fluorescent object found in the negative control. It is not a vesicle. The images show it under white light and its fluorescence in red, green, and blue (left to right, respectively). | |||
Cloning of Biobricks
- Placed 5 ml of LB in a 15 ml tube
- Added appropriate antibiotics into the tube
- Picked 6 colony from the fresh overnight plate
- Innoculated the colony in the LB media
- Incubated overnight at 37 °C
- 6x1 Biobricks cloned
Maxiprep of Biobricks (preparation)
- Cells were spun down and pelleted
- Cells stored at -20 °C for Maxiprep tomorrow